论文标题:Atypical pituitary hormone–target tissue axis
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Chao Xu, Zhao He, Yongfeng Song, Shanshan Shao, Guang Yang, Jiajun Zhao
发表时间:15 Feb 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0973-7
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
山东第一医科大学附属省立医院赵家军教授等在Frontiers of Medicine发表综述论文《非典型垂体激素 - 靶组织轴》(Atypical pituitary hormone–target tissue axis),本文依据“非典型垂体激素 - 靶组织轴”这一概念综述了垂体多种激素在非经典器官的额外功能,解释了多种疾病病理机制,为相关研究提供了新的见解。
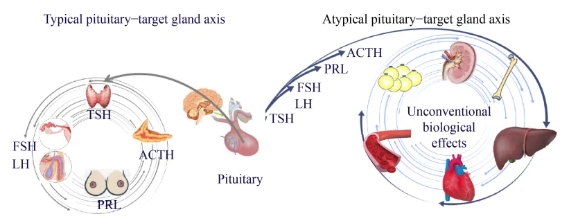
A long-held belief is that pituitary hormones bind to their cognate receptors in classical target glands to actuate their manifold functions. However, a number of studies have shown that multiple types of pituitary hormone receptors are widely expressed in non-classical target organs. Each pituitary gland-derived hormone exhibits a wide range of nonconventional biological effects in these non-classical target organs. Herein, the extra biological functions of pituitary hormones, thyroid-stimulating hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, adrenocorticotrophic hormone, and prolactin when they act on non-classical organs were summarized, defined by the novel concept of an “atypical pituitary hormone–target tissue axis.” This novel proposal explains the pathomechanisms of abnormal glucose and lipid metabolism, obesity, hypertension, fatty liver, and atherosclerosis while offering a more comprehensive and systematic insights into the coordinated regulation of environmental factors, genetic factors, and neuroendocrine hormones on human biological functions. The continued exploration of the physiology of the “atypical pituitary hormone–target tissue axis” could enable the identification of novel therapeutic targets for metabolic diseases.
长久以来的观点认为,垂体激素与经典靶腺中的同源受体结合,从而启动其多种功能。然而,大量研究表明,多种类型的垂体激素受体在非经典靶器官中广泛表达。每种垂体源性激素在这些非经典靶器官中都展现出广泛的非常规生物学效应。本文依据 “非典型垂体激素 - 靶组织轴” 这一新概念定义并综述了垂体激素、促甲状腺激素、促卵泡激素、促黄体生成素、促肾上腺皮质激素和催乳素作用于非经典器官时的额外生物学功能。这一新观点解释了糖脂代谢异常、肥胖、高血压、脂肪肝和动脉粥样硬化的病理机制,同时为环境因素、遗传因素和神经内分泌激素对人类生物学功能的协同调节提供了更全面、系统的见解。对 “非典型垂体激素 - 靶组织轴” 生理学的持续探索,有望确定代谢性疾病的新治疗靶点。
摘要图
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
Atypical pituitary hormone–target tissue axis
作者
Chao Xu¹’², Zhao He¹’², Yongfeng Song¹’², Shanshan Shao¹’², Guang Yang³, Jiajun Zhao¹’²
机构
1. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, China
2. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Shandong Provincial Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan 250021, China
3. Beijing Institute of Tropical Medicine, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
通讯作者
Guang Yang, Jiajun Zhao
引用这篇文章
Chao Xu, Zhao He, Yongfeng Song, Shanshan Shao, Guang Yang, Jiajun Zhao. Atypical pituitary hormone–target tissue axis. Front. Med., 2023, 17(1): 1–17 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0973-7
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-022-0973-7
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-022-0973-7
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。