|
|
|
|
|
FMD 论文速览:驱动基因突变晚期非小细胞肺癌的治疗——现状与展望 |
|
|
论文标题:Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with driver mutations: current applications and future directions
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Jia Zhong, Hua Bai, Zhijie Wang, Jianchun Duan, Wei Zhuang, Di Wang, Rui Wan, Jiachen Xu, Kailun Fei, Zixiao Ma, Xue Zhang, Jie Wang
发表时间:15 Feb 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0976-4
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
中国医学科学院北京协和医学院王洁教授团队在Frontiers of Medicine发表综述论文《驱动基因突变晚期非小细胞肺癌的治疗:现状与展望》(Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with driver mutations: current applications and future directions)。作者检索了PubMed,查找了2013年1月1日至2022年4月1日期间发表的关于带有驱动基因突变的非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的临床试验和医学治疗综述文章,同时,也回顾了主要专业学会的指南,综述了驱动基因突变非小细胞肺癌的治疗现状与未来方向。
With the improved understanding of driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), expanding the targeted therapeutic options improved the survival and safety. However, responses to these agents are commonly temporary and incomplete. Moreover, even patients with the same oncogenic driver gene can respond diversely to the same agent. Furthermore, the therapeutic role of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in oncogene-driven NSCLC remains unclear. Therefore, this review aimed to classify the management of NSCLC with driver mutations based on the gene subtype, concomitant mutation, and dynamic alternation. Then, we provide an overview of the resistant mechanism of target therapy occurring in targeted alternations (“target-dependent resistance”) and in the parallel and downstream pathways (“target-independent resistance”). Thirdly, we discuss the effectiveness of ICIs for NSCLC with driver mutations and the combined therapeutic approaches that might reverse the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment. Finally, we listed the emerging treatment strategies for the new oncogenic alternations, and proposed the perspective of NSCLC with driver mutations. This review will guide clinicians to design tailored treatments for NSCLC with driver mutations.
随着对非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)驱动基因突变认识的不断深入,日益丰富的靶向治疗选择提高了患者的生存率与安全性。然而,患者对这些药物的反应通常是暂时且不完全的。此外,即使携带相同致癌驱动基因的患者,对同一种药物的反应也可能存在差异。再者,免疫检查点抑制剂(ICIs)在致癌基因驱动的NSCLC 中的治疗作用仍不明确。因此,本综述旨在根据基因亚型、伴随突变及动态变化,对驱动基因突变NSCLC的治疗管理进行分类。随后,我们概述了靶向治疗中,因靶向改变(“靶点依赖性耐药”)以及平行和下游通路改变(“靶点非依赖性耐药”)而产生的耐药机制。第三,我们探讨了ICIs对驱动基因突变NSCLC的疗效,以及可能逆转免疫抑制性肿瘤免疫微环境的联合治疗方法。最后,我们列举了针对新的致癌基因改变的新兴治疗策略,并提出了对驱动基因突变NSCLC的展望。本综述可供临床医生为驱动基因突变NSCLC患者制定个性化治疗方案参考。
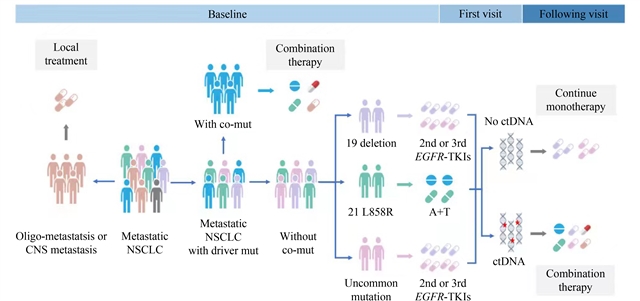
摘要图
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with driver mutations: current applications and future directions
作者
Jia Zhong, Hua Bai, Zhijie Wang, Jianchun Duan, Wei Zhuang, Di Wang, Rui Wan, Jiachen Xu, Kailun Fei, Zixiao Ma, Xue Zhang, Jie Wang
机构
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China
通讯作者
Jie Wang
引用这篇文章
Jia Zhong, Hua Bai, Zhijie Wang, Jianchun Duan, Wei Zhuang, Di Wang, Rui Wan, Jiachen Xu, Kailun Fei, Zixiao Ma, Xue Zhang, Jie Wang. Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with driver mutations: current applications and future directions. Front. Med., 2023, 17(1): 18–42 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0976-4
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-022-0976-4
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-022-0976-4
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。