|
|
|
|
|
FMD 论文速览:ALK变异等位基因频率预测非小细胞肺癌靶向治疗疗效的潜在不可靠性 |
|
|
论文标题:Potential unreliability of ALK variant allele frequency in the efficacy prediction of targeted therapy in NSCLC
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Wei Rao, Yutao Liu, Yan Li, Lei Guo, Tian Qiu, Lin Dong, Jianming Ying, Weihua Li
发表时间: 15 Jun 2023
DOI:10.1007/s11684-022-0946-x
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
中国医学科学院肿瘤医院应建明和李卫华等在Frontiers of Medicine发表研究论文《ALK变异等位基因频率预测非小细胞肺癌靶向治疗疗效的潜在不可靠性》(Potential unreliability of ALK variant allele frequency in the efficacy prediction of targeted therapy in NSCLC)。本研究通过分析非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者的ALK融合基因检测数据,发现基于二代测序(NGS)的变异等位基因频率(VAF)因技术局限性无法可靠评估肿瘤内异质性(ITH)或预测ALK-TKI的疗效。
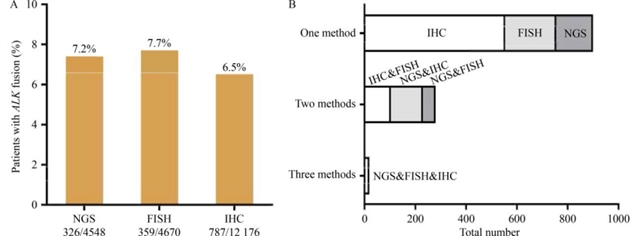
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is the most common fusion gene involved in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and remarkable response has been achieved with the use of ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs). However, the clinical efficacy is highly variable. Pre-existing intratumoral heterogeneity (ITH) has been proven to contribute to the poor treatment response and the resistance to targeted therapies. In this work, we investigated whether the variant allele frequencies (VAFs) of ALK fusions can help assess ITH and predict targeted therapy efficacy. Through the application of next-generation sequencing (NGS), 7.2% (326/4548) of patients were detected to be ALK positive. On the basis of the adjusted VAF (adjVAF, VAF normalization for tumor purity) of four different threshold values (adjVAF < 50%, 40%, 30%, or 20%), the association of ALK subclonality with crizotinib efficacy was assessed. Nonetheless, no statistical association was observed between median progression-free survival (PFS) and ALK subclonality assessed by adjVAF, and a poor correlation of adjVAF with PFS was found among the 85 patients who received first-line crizotinib. Results suggest that the ALK VAF determined by hybrid capture-based NGS is probably unreliable for ITH assessment and targeted therapy efficacy prediction in NSCLC.
间变性淋巴瘤激酶(ALK)是非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中最常见的融合基因,ALK酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(ALK-TKIs)的应用已取得显著疗效。然而,其临床疗效存在高度异质性。已有研究表明,肿瘤内异质性(ITH)是导致治疗效果不佳以及对靶向治疗产生耐药的原因之一。本研究通过分析ALK融合的变异等位基因频率(VAFs),探讨其是否可用于评估ITH及预测靶向治疗的疗效。基于下一代测序技术(NGS),7.2%(326/4548)的患者被检测为ALK阳性。利用肿瘤纯度归一化校正的VAF(adjVAF)设定四种阈值(adjVAF <50%、40%、30%、20%),评估了ALK亚克隆与克唑替尼疗效的关联。然而,在85例接受一线克唑替尼治疗的患者中,经adjVAF评估后发现,中位无进展生存期(PFS)与ALK亚克隆变异之间未观察到统计学相关性,并且adjVAF与PFS之间的相关性较差。研究结果表明,通过基于杂交捕获的NGS技术测定的ALK VAF,在评估NSCLC的ITH以及预测靶向治疗疗效方面可能并不可靠。
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
Potential unreliability of ALK variant allele frequency in the efficacy prediction of targeted therapy in NSCLC
作者
Wei Rao1, Yutao Liu2, Yan Li1, Lei Guo1, Tian Qiu1, Lin Dong1, Jianming Ying1, Weihua Li1
机构
1. Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China
2. Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China
通讯作者
Jianming Ying, Weihua Li
引用这篇文章
Wei Rao, Yutao Liu, Yan Li, Lei Guo, Tian Qiu, Lin Dong, Jianming Ying, Weihua Li. Potential unreliability of ALK variant allele frequency in the efficacy prediction of targeted therapy in NSCLC. Front. Med., 2023, 17(3): 493–502 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0946-x
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-022-0946-x
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-022-0946-x
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。