|
|
|
|
|
FoAR 作为一种气候适应策略的城市几何形态对炎热沙漠气候条件下户外热舒适度的提升作用 |
|
|
论文标题:Urban geometry as a climate adaptation strategy for enhancing outdoor thermal comfort in a hot desert climate
期刊:Frontiers of Architectural Research
作者:Khaled Elkhayat, Mohamed Hssan Hassan Abdelhafez, Fatmaelzhraa Altaf, Steve Sharples, Mohammad A. Alshenaifi, Sultan Alfraidi, Ali Aldersoni, Ghazy Albaqawy, Ayman Ragab
发表时间:April 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foar.2024.08.004
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

FoAR是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 A&HCI / CSCD / Scopus / DOAJ / CSTPCD 收录
中国科技期刊卓越行动计划 英文领军期刊

01
论 文 题 目
Manuscript Title
Urban geometry as a climate adaptation strategy for enhancing outdoor thermal comfort in a hot desert climate
作为一种气候适应策略的城市几何形态对炎热沙漠气候条件下户外热舒适度的提升作用
02
作 者
Authors
Khaled Elkhayat (a), Mohamed Hssan Hassan Abdelhafez (a)(b)* , Fatmaelzhraa Altaf (b), Steve Sharples (c), Mohammad A. Alshenaifi (a), Sultan Alfraidi (a), Ali Aldersoni (a), Ghazy Albaqawy (a), Ayman Ragab (b)**
(a) Department of Architectural Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Hail, Hail, Saudi Arabia
(b) Department of Architectural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Aswan University, Aswan, Egypt
(c) School of Architecture, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom
03
论 文 摘 要
Abstract
This study aimed to assess the impact of varying street canyon geometries on outdoor thermal comfort in two Egyptian cities with distinct climates: Aswan, located in the southern desert region, and Alexandria, on the northern coast. The design of urban street canyons in Egypt often neglects the countrys diverse climatic regions. The investigation focused on four height-to-width aspect ratios and four principal street orientations in the two cities. Field data, ENVI-met microclimate software, and RayMan were utilized to analyze the impact of hypothesized scenarios on heat stress in the studied street canyons. Outdoor thermal comfort was evaluated using the physiologically equivalent temperature (PET). The findings demonstrated the effectiveness of aspect ratio and orientation in the respective cities. In Aswan, the aspect ratio had a greater influence on comfort, with aspect ratio of 2.5 providing the most favorable conditions and a ratio of 1 resulting in the least comfortable conditions. Conversely, in Alexandria, the street canyon orientation proved more advantageous, where a northwest-southeast orientation produced a significant decrease (10 K) in PET compared to the least favorable orientation. These results highlight the importance of considering local climatic factors in the design of urban street canyons to effectively mitigate outdoor heat stress.
本研究旨在评估不同街道峡谷几何形态对埃及两座气候迥异城市户外热舒适度的影响:一座是位于南部沙漠地区的阿斯旺,另一座是北部沿海的亚历山大。埃及城市街道峡谷的设计往往忽视了该国多样化的气候区域。研究聚焦于这两座城市中的四种建筑高宽比和四种主要街道走向。通过实地数据采集、ENVI-met 微气候软件以及 RayMan 工具,分析了假设情景对所研究街道峡谷热应力的影响。户外热舒适度采用生理等效温度(PET)进行评估。研究结果证实了高宽比和街道走向在不同城市的有效性差异。在阿斯旺,高宽比对热舒适度的影响更为显著,其中建筑高宽比为 2.5 时可以创造最有利的热环境条件,而建筑高宽比为 1:1 时则导致热舒适度最差。相反,在亚历山大,街道走向的优化更为关键,西北-东南走向的街道峡谷相较于最不利走向可使 PET 显著降低 10 开尔文。这些结果强调了在城市街道峡谷设计中考虑当地气候因素对有效缓解户外热应力的重要性。
04
关 键 词
Keywords
Street canyons / 都市峡谷
Heat stress / 热应激
Aspect ratio / 建筑长宽比
PET / 生理等效温度
ENVI-met / ENVI-met软件
Street orientation / 街道方向
05
章 节 标 题
Sections Title
1. Introduction / 引言
2. Study area and methodology / 研究领域和研究方法
2.1. Study area / 研究领域
2.2. Simulation software and input data for this study / 本研究的模拟软件和数据输入
2.3. Thermal comfort indices / 热舒适指数
2.4. Site measurements and validation process / 现场测量和验证过程
3. Results / 研究成果
3.1. Effect of aspect ratio on the microclimate thermal comfort / 建筑高宽比对小气候热舒适的影响
3.1.1. Thermal comfort analysis for A-R 1 / A-R 1 热舒适分析
3.1.2. Thermal comfort analysis for A-R 2 / A-R 2 热舒适分析
3.1.3. Thermal comfort analysis for A-R 3 / A-R 3 热舒适分析
3.1.4. Thermal comfort analysis for A-R 4 / A-R 4 热舒适分析
3.2. Effect of street canyon orientation on the microclimate thermal comfort / 街道峡谷走向对微气候热舒适度的影响
4. Discussion / 讨论
5. Conclusion / 结论
06
主 要 插 图
Illustrations
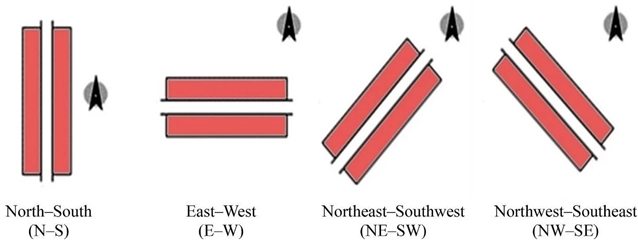
▲ 图一:街道走向场景的调研成果。©本文作者
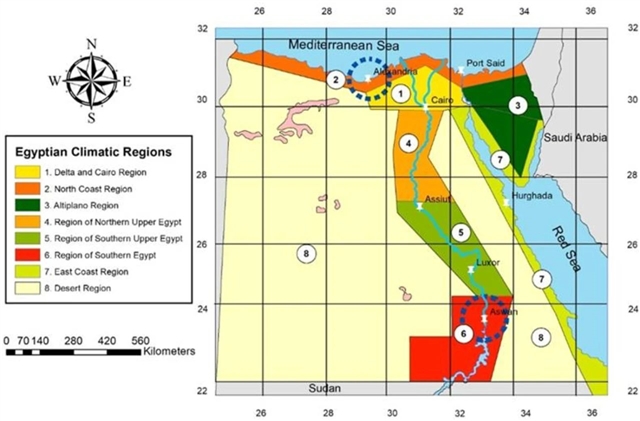
▲ 图二:案例城市区位及气候区域。两处蓝色虚线圈出了埃及境内案例城市的地理区位——亚历山大市和阿斯旺市。亚历山大市位于埃及北部沿海地区,而阿斯旺市位于埃及南部地区。©本文作者
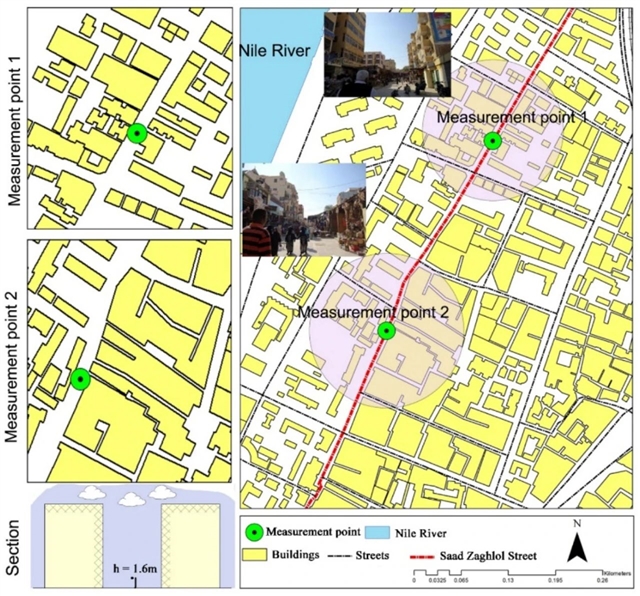
▲ 图三:两个测量点。©本文作者
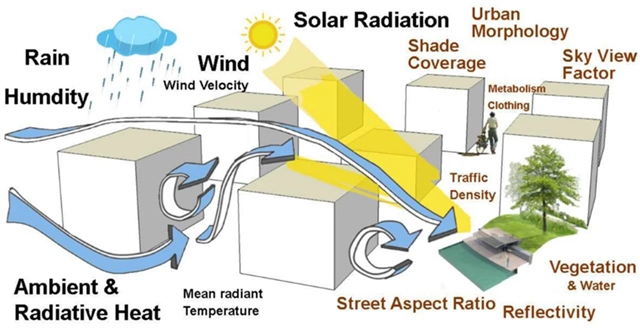
▲ 图四:城市热舒适因素(黑色标注为气候因素,棕色标注为设计因素)。©本文作者

▲ 图五:来自当地的现状照片展示了埃及的街道结构,其中包括一些几何元素。©本文作者
07
作 者 介 绍
Authors’ Information

Khaled Elkhayat
Professor
Department of Architectural Engineering
College of Engineering, University of Hail, Saudi Arabia
His main research directions cover energy, engineering, environmental science, sociology and other fields.

Mohamed Hssan Hassan Abdelhafez
Professor
Department of Architectural Engineering
Faculty of Engineering, Aswan University, Egypt
The current research interests include the built environment and its mutual effect with outdoor-indoor climate conditions with regards to passive systems to assess their thermal impact on comfort provision, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions which means to some extent sustainability. In addition, Environmental design of buildings; Thermal comfort & Energy efficiency in hot climates; Natural ventilation as a passive cooling strategy; and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling.
Fatmaelzhraa Altaf
Department of Architectural Engineering
Faculty of Engineering, Aswan University, Egypt

Steve Sharples
Professor
School of Architecture
University of Liverpool, United Kingdom
Professor Steve Sharples has been appointed a Fellow of the RSA (Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce). The award was made in recognition of Steve’s many years of research and teaching activities, which the RSA said had been "instrumental in examining the intersection between design and sustainability, centring practical policy solutions to the environmental crisis in the field of architecture". Steve’s work is in line with the RSAs Regenerative Futures programme, and the socially-driven ethos underpinning the RSA’s Student Design Awards.

Mohammad A. Alshenaifi
Phd Student
Department of Architectural Engineering
College of Engineering, University of Hail, Saudi Arabia

Sultan Alfraidi
Assistant Professor
Department of Architectural Engineering
College of Engineering, University of Hail, Saudi Arabia

Ali Aldersoni
Department of Architectural Engineering
College of Engineering, University of Hail, Saudi Arabia

Ghazy Albaqawy
Department of Architectural Engineering
College of Engineering, University of Hail, Saudi Arabia

Ayman Ragab
Associate Professor
Department of Architectural Engineering
Faculty of Engineering, Aswan University, Egypt
Ayman Ragab, an architect and urban planner with a masters degree from Assiut University and a doctorate from Aswan University, is a full-time Associate Professor of Architectural Engineering and Urban Planning at Aswan University in Egypt. Since 2016, he has worked as an Expert on Housing and Urban Planning for Egypts General Organization for Physical Planning GOPP.
08
原 文 阅 读
Download Link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
▼ 点击下方词条 | 往期精彩不容错过
#期刊快讯#系列
1/ 主编王建国院士团队荣获国家科技进步奖一等奖
2/ JCR最新|FoAR 2023年度影响因子3.1,两项评价指标均位列WoS核心合集建筑类第一
3/ 最新|FoAR 2023 CiteScore 指数上升为6.2
4/ 最新|FoAR 被中国科技论文与引文数据库(CSTPCD)收录
5/ 最新|FoAR 再次入选中国国际影响力优秀学术期刊
6/ 最新|FoAR 荣获科爱十大优秀期刊奖
7/ 最新|FoAR进入2023年中国科学院分区表一区
8/ 最新|FoAR 入选"中国科技期刊卓越行动计划"英文领军期刊
9/ 最新|FoAR 2025中国科学院分区表大类小类保持一区
10/ 最新|FoAR 进入 EI 工程索引数据库
#年度报告#系列
1/ FoAR|2021年度报告
2/ FoAR|2022年度报告
3/ FoAR|2023年度报告
4/ FoAR|2024年度报告
#新刊上线#系列
2025年第一期
2025年第二期
#FoAR投稿指南#系列
1/ 投稿流程
2/ Guide for Author中文版
3/ 审稿流程及发表流程
4/ 如何提交修改稿
5/ 录用文章出版流程
#期刊知识科普#系列
1/ SCI之父尤金·加菲尔德的传奇人生
2/ 国际核心期刊数据库大解析
3/ 手把手教你如何使用最强工具Web of Science
4/ 如何发现一本好期刊
5/ 国内核心期刊有哪些
6/ 版面费与期刊影响力
#精彩文章#系列精选
01/ 城市设计实践发展的多元维度——基于UAL的案例研究
02/ 从智慧城市到共情城市
03/ 传统阿拉伯伊斯兰城市居住区形态学:以传统城市大马士革为例
04/ 建筑遗产预防性保护的意大利视角
05/ 生物与建筑:将科学知识与设计实践相结合的六家法国建筑事务所项目案例研究
06/ 颇具争议的渐进式改造:Elemental建筑事务所金塔蒙罗伊公屋居住区项目的15年
07/ 联合眼动实验和SD法的传统商业街区视觉效果感知评价
08/ 历史的层次:古城堡遗迹中的新建筑改造
09/ 通过空间句法检验帕拉第奥别墅平面中的控制性、中心性和灵活性
10/ 自1931年柯布西耶的Salubra色卡问世后其建筑色彩的偏好:一种跨文化的分析
11/ 建筑师身份的描绘:1920年代末的中国美术建筑师——刘既漂
12/ 探索暴露于风影响下织物的表达与功能
13/ 绿色屋顶能否在地中海气候条件下显著节约能源?基于不同案例的批判性评估
14/ 芬兰近期落成的原木建筑的建构及建筑品质:相关建筑师的解读
15/ 新加坡高校教室光环境品质研究
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。