|
|
|
|
|
Engineering工程管理论文合集(2024) |
|
|
标题:Engineering工程管理论文合集(2024)
期刊:Engineering
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
1.一种基于血液检测的诊断和预测HBV相关疾病的弹性方法 Article
Gege Hou, Yunru Chen, Xiaojing Liu, Dong Zhang, Zhimin Geng, Shubin Si
摘要:乙肝病毒(HBV)感染威胁着全球公共卫生安全,是导致肝脏相关疾病发病率和死亡率的主要原因。HBV持续感染引起的肝脏疾病检查方法包括实验室检测、超声、CT、核磁共振和肝活检等,重复的检查和多次诊断可能导致患者每次就医都面临高额费用。因此,迫切需要建立一种经济有效的诊断方法简化乙肝相关疾病的医疗流程。基于临床血液检测,我们构建复杂网络模型并定义功能恢复力评价指标,可以帮助医生评估患者的肝脏状况。其次,通过结合网络模型和动力学,发现导致患者向肝硬化或肝癌转化的关键血液指标及其相应的阈值,为进一步研究疾病临界状态和预防疾病恶化提供思路。结果表明功能恢复力的诊断宏观平均精度为84.74%,而在没有影像或活检辅助的情况下医生凭经验诊断的宏观平均精度为55.64%。从经济角度,与一般诊断方法相比,功能恢复力可以为大多数中国患者每次就诊节省至少30美元,为大多数美国患者节省至少400美元。在全球范围内,每年将节省至少105亿美元。因此,功能恢复力可以全面评估患者的肝脏状况,减少影像学检查的次数,避免肝病诊断过程中医疗资源的浪费。
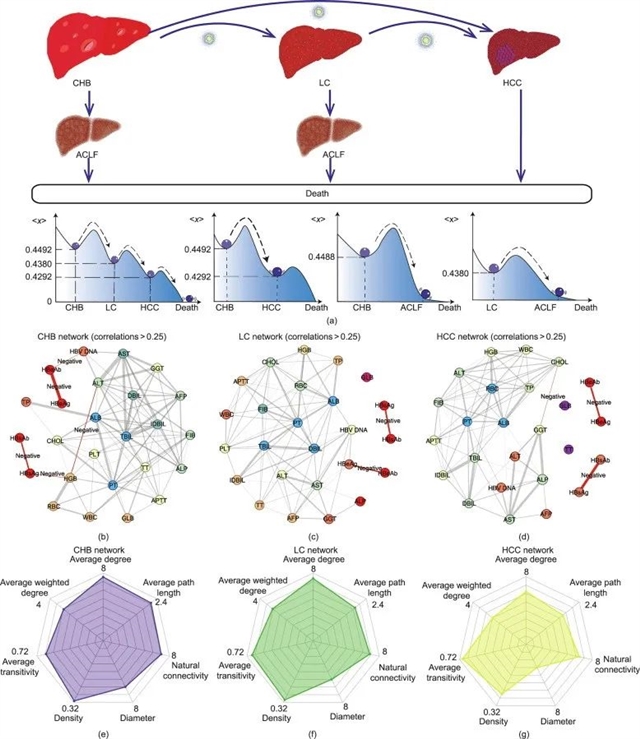
Cite this article
Gege Hou, Yunru Chen, Xiaojing Liu, Dong Zhang, Zhimin Geng, Shubin Si. A Resilience Approach for Diagnosing and Predicting HBV-Related Diseases Based on Blood Tests. Engineering, 2024, 32(1): 174–185 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.06.013
2.道路车辆主动悬架系统研究进展 Review
Min Yu, Simos A. Evangelou, Daniele Dini
摘要:主动悬架系统(ASS)已被提出并发展了几十年,由于对驾驶舒适性和安全性的高要求,以及ASS与汽车电气化和自动化的兼容性,现在再次成为学术界和工业界的热门话题。现有的关于ASS的综述论文主要涉及动力学建模和鲁棒控制;然而,学术研究成果和工业应用要求之间的差距尚未弥合,阻碍了大多数ASS研究知识向汽车公司转移。本文回顾了道路车辆ASS的研究进展,重点介绍了硬件结构和控制策略。特别是,详细讨论了最近在量产汽车中采用的最先进的ASS,包括梅赛德斯主动车身控制(ABC)和奥迪预测主动悬架的代表性解决方案;还介绍了可能成为替代方案的新概念,包括串联主动可变几何悬架和主动车轮对准系统。结构紧凑、质量增量小、功耗低、频率响应高、经济成本可接受、可靠性高的ASS更容易被汽车制造商采用。在控制策略方面,未来ASS的发展不仅旨在稳定底盘姿态和减弱底盘振动,而且使ASS能够配合汽车内的其他模块(如转向和制动)和传感器(如摄像头),甚至在整个交通系统中进行高层决策(如参考驾驶速度),这些策略将与快速发展的电动汽车和自动驾驶汽车兼容。
Cite this article
Min Yu, Simos A. Evangelou, Daniele Dini. Advances in Active Suspension Systems for Road Vehicles. Engineering. 2024, 33(2): 160-177 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.06.014
3.错失的温室气体减排机遇——被低估的生活垃圾填埋场甲烷排放量 Views & Comments
Yao Wang, Chuanbin Zhou, Ziyang Lou, Houhu Zhang, Abid Hussain, Liangtong Zhan, Ke Yin, Mingliang Fang, Xunchang Fei
导读:本文件探讨了固体废物处理场(如填埋场)所产生的甲烷(CH4)排放量被低估的现象,强调了城市所承担的温室气体(GHG)排放责任,尤其是固体废物处理场对甲烷排放的贡献。甲烷的全球变暖潜力比二氧化碳强28倍,因此降低其排放在应对气候变化中至关重要。文件建议采用更准确的计算方法和更高效的管理策略,以抓住未被充分挖掘的减排机会,实现更有效的温室气体减排。
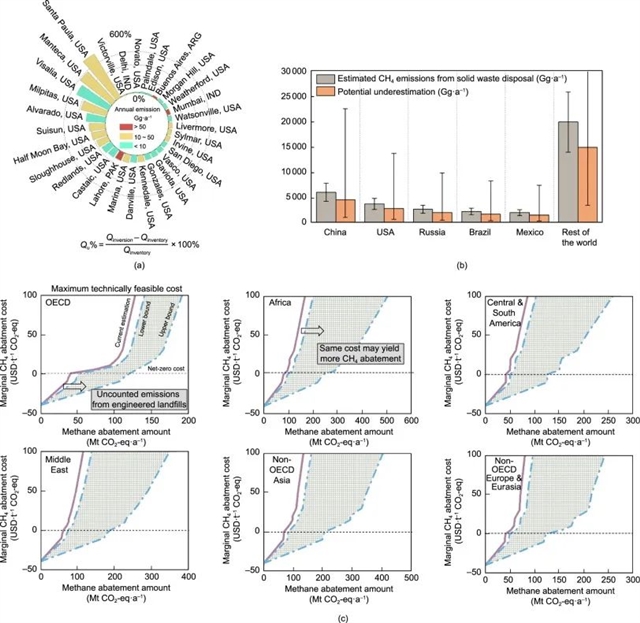
Cite this article
Yao Wang, Chuanbin Zhou, Ziyang Lou. Underestimated Methane Emissions from Solid Waste Disposal Sites Reveal Missed Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Opportunities. Engineering. 2024, 36(5): 12-15 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.12.011
4.工程管理背景下的无人机巡检路径调度优化 Article
Lu Zhen, Zhiyuan Yang, Gilbert Laporte, Wen Yi, Tianyi Fan
摘要:无人机(UAV)技术的蓬勃发展革新了各个领域的业态模式,使基于无人机的各类解决方案得以广泛应用。而在工程管理领域当中,基于无人机的巡检监测相较于传统的人工巡检方式有着巨大的优势,能够以较低的风险去高效识别高风险施工环境中的潜在隐患。在此背景下,本文研究了工程领域背景下的无人机巡检路径调度优化问题,在该问题中本文考虑了无人机飞行禁飞区、监测时间间隔以及多轮次巡检路径调度等因素。为高效求解该优化问题,本文提出了一种混合整数线性规划(MILP)模型用于优化无人机巡检任务分配、监测点巡检顺序调度以及无人机充电的三类决策。上述三类复杂因素的考虑使该巡检路径调度问题与传统的车辆调度问题(VRP)有着显著区别,同时模型的复杂程度也使得商业求解器难以在合理时间内高效求解上述模型。为此,本文基于变邻域搜索算法设计了定制化的元启发式算法来高效求解所提出的数学模型。大量的数值实验验证了本文设计算法的有效性,并证明了该算法在大规模算例和真实规模算例中的应用性。此外,本文还基于实际的工程项目开展了敏感性分析和案例研究,为工程管理人员在提高巡检工作效率方面提供了相关管理启示。
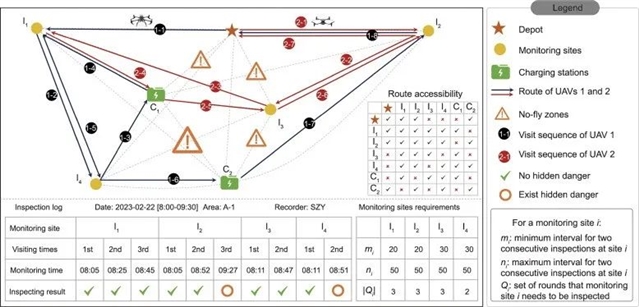
Cite this article
Lu Zhen, Zhiyuan Yang, Gilbert Laporte, Wen Yi, Tianyi Fan. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Inspection Routing and Scheduling for Engineering Management. Engineering, 2024, 36(5): 223–239 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.10.014
5.有向动态网络的自发恢复 Article
Xueming Liu, Xian Yan, H. Eugene Stanley
摘要:复杂网络系统涵盖了从自然界的生物系统到人工制造的基础设施系统的各个领域,在发生故障后可以表现出自发恢复的能力;例如,大脑在癫痫发作后可能会自发恢复正常,交通流量在堵塞后也可以再次变得顺畅。以往关于动态网络自发恢复的研究主要局限在无向网络上。然而,大多数现实中的网络是有向的。为了填补这一空白,我们建立了一个模型,其中节点可能交替发生故障和恢复,同时我们开发了一个理论工具来分析有向动态网络的恢复特性。该工具可以准确预测活跃节点的最终比例,预测准确性会随网络中双向边比例的增加而降低,这凸显了网络方向性的重要性。根据不同的初始状态,有向动态网络在相同的控制参数下可能显示出不同的稳定状态,呈现出滞后行为。此外,对于小规模网络,活跃节点的比例可能在高低状态之间震荡,模拟重复的故障恢复过程。这些发现有助于阐明系统恢复机制,并能更好地指导设计具有高韧性的网络系统。
Cite this article
Xueming Liu, Xian Yan, H. Eugene Stanley. Spontaneous Recovery in Directed Dynamical Networks. Engineering, 2024, 37(6): 224–230 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.12.007
6.基于物理引导深度学习的突发公共卫生事件期间城市轨道交通短时OD客流预测 Article
Shuxin Zhang, Jinlei Zhang, Lixing Yang, Feng Chen, Shukai Li, Ziyou Gao
摘要:Accurate origin-destination (OD) demand prediction is crucial for the efficient operation and management of urban rail transit (URT) systems, particularly during a pandemic. However, this task faces several limitations, including real-time availability, sparsity, and high-dimensionality issues, and the impact of the pandemic. Consequently, this study proposes a unified framework called the physics-guided adaptive graph spatial-temporal attention network (PAG-STAN) for metro OD demand prediction under pandemic conditions. Specifically, PAG-STAN introduces a real-time OD estimation module to estimate real-time complete OD demand matrices. Subsequently, a novel dynamic OD demand matrix compression module is proposed to generate dense real-time OD demand matrices. Thereafter, PAG-STAN leverages various heterogeneous data to learn the evolutionary trend of future OD ridership during the pandemic. Finally, a masked physics-guided loss function (MPG-loss function) incorporates the physical quantity information between the OD demand and inbound flow into the loss function to enhance model interpretability. PAG-STAN demonstrated favorable performance on two real-world metro OD demand datasets under the pandemic and conventional scenarios, highlighting its robustness and sensitivity for metro OD demand prediction. A series of ablation studies were conducted to verify the indispensability of each module in PAG-STAN.
Cite this article
Shuxin Zhang, Jinlei Zhang, Lixing Yang, Feng Chen, Shukai Li, Ziyou Gao. Physics Guided Deep Learning-Based Model for Short-Term Origin-Destination Demand Prediction in Urban Rail Transit Systems Under Pandemic. Engineering, 2024, 41(10): 276–296 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.04.020
7.认知城市轨道交通的韧性——概念、方法与趋势 Review
Yun Wei, Xin Yang, Xiao Xiao, Zhiao Ma, Tianlei Zhu, Fei Dou, Jianjun Wu, Anthony Chen, Ziyou Gao
摘要:As the scale of urban rail transit (URT) networks expands, the study of URT resilience is essential for safe and efficient operations. This paper presents a comprehensive review of URT resilience and highlights potential trends and directions for future research. First, URT resilience is defined by three primary abilities: absorption, resistance, and recovery, and four properties: robustness, vulnerability, rapidity, and redundancy. Then, the metrics and assessment approaches for URT resilience were summarized. The metrics are divided into three categories: topology-based, characteristic-based, and performance-based, and the assessment methods are divided into four categories: topological, simulation, optimization, and data-driven. Comparisons of various metrics and assessment approaches revealed that the current research trend in URT resilience is increasingly favoring the integration of traditional methods, such as conventional complex network analysis and operations optimization theory, with new techniques like big data and intelligent computing technology, to accurately assess URT resilience. Finally, five potential trends and directions for future research were identified: analyzing resilience based on multisource data, optimizing train diagram in multiple scenarios, accurate response to passenger demand through new technologies, coupling and optimizing passenger and traffic flows, and optimal line design.
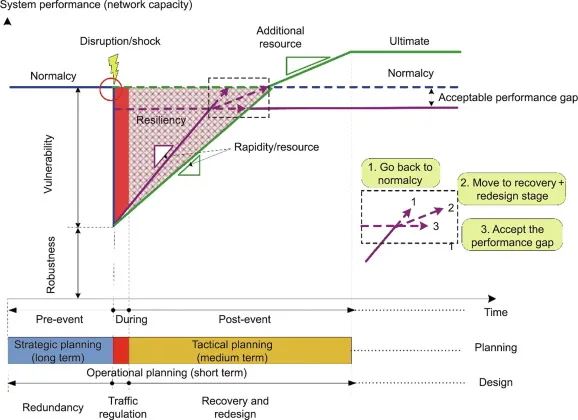
Cite this article
Yun Wei, Xin Yang, Xiao Xiao, Zhiao Ma, Tianlei Zhu, Fei Dou, Jianjun Wu, Anthony Chen, Ziyou Gao. Understanding the Resilience of Urban Rail Transit: Concepts, Reviews, and Trends. Engineering, 2024, 41(10): 7–18 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.01.022
8.工程设施管理数字孪生——综述、分析框架和未来方向 Review
Yongkui Li, Qinyue Wang, Xiyu Pan, Jian Zu, Jinying Xu, Yilong Han
摘要:Effective engineering asset management (EAM) is critical to economic development and improving livability in society, but its complexity often impedes optimal asset functionalities. Digital twins (DTs) could revolutionize the EAM paradigm by bidirectionally linking the physical and digital worlds in real time. There is great industrial and academic interest in DTs for EAM. However, previous review studies have predominately focused on technical aspects using limited life-cycle perspectives, failing to holistically synthesize DTs for EAM from the managerial point of view. Based on a systematic literature review, we introduce an analytical framework for describing DTs for EAM, which encompasses three levels: DT 1.0 for technical EAM, DT 2.0 for technical−human EAM, and DT 3.0 for technical−environmental EAM. Using this framework, we identify what is known, what is unknown, and future directions at each level. DT 1.0 addresses issues of asset quality, progress, and cost management, generating technical value. It lacks multi-objective self-adaptive EAM, however, and suffers from high application cost. It is imperative to enable closed-loop EAM in order to provide various functional services with affordable DT 1.0. DT 2.0 accommodates issues of human−machine symbiosis, safety, and flexibility management, generating managerial value beyond the technical performance improvement of engineering assets. However, DT 2.0 currently lacks the automation and security of human−machine interactions and the managerial value related to humans is not prominent enough. Future research needs to align technical and managerial value with highly automated and secure DT 2.0. DT 3.0 covers issues of participatory governance, organization management, sustainable development, and resilience enhancement, generating macro social value. Yet it suffers from organizational fragmentation and can only address limited social governance issues. Numerous research opportunities exist to coordinate different stakeholders. Similarly, future research opportunities exist to develop DT 3.0 in a more open and complex system.
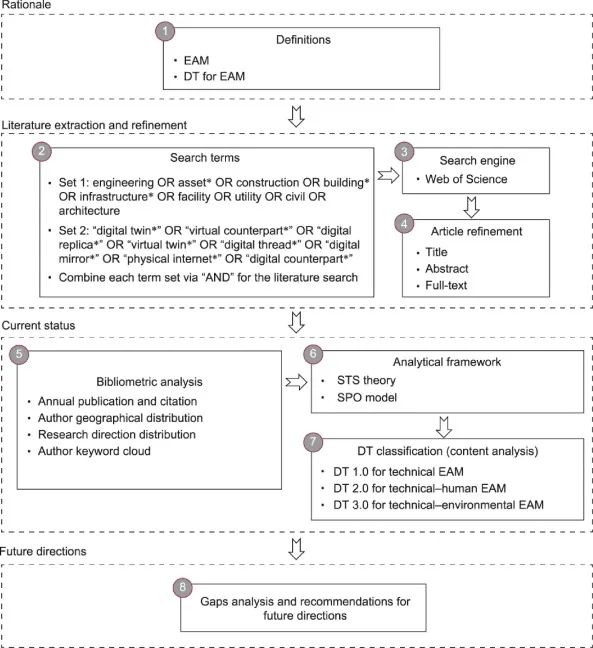
Cite this article
Yongkui Li, Qinyue Wang, Xiyu Pan, Jian Zuo, Jinying Xu, Yilong Han. Digital Twins for Engineering Asset Management: Synthesis, Analytical Framework, and Future Directions. Engineering, 2024, 41(10): 261–275 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.12.006
9.人工智能赋能情景规划——构建智慧与韧性城市视角 Review
Haiyan Hao, Yan Wang, Jiayu Chen
摘要:Scenario planning is a powerful tool for cities to navigate uncertainties and mitigate the impacts of adverse scenarios by projecting future outcomes based on present-day decisions. This approach is becoming increasingly important given the growing call for building resilient cities to face adverse future scenarios posed by emerging disruptive technologies and climate change. However, conventional scenario planning practices predominantly rely on expert knowledge and judgment, which may be limited in accounting for the complexity of future scenarios. Therefore, we explored the potential integration of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to assist scenario planning practices. We synthesized related studies from various disciplines (e.g., engineering, computer science, and urban planning) to identify the potential applications of AI in the three key components of scenario planning: plan generation, scenario generation, and plan evaluation. We then discuss the challenges and possible solutions for integrating AI into the scenario planning process and highlight the critical role of planning experts in this process. We conclude by outlining future research opportunities in this context. Ultimately, this study contributes to the advancement of scenario planning practices and aids the creation of more resilient cities that can thrive in an uncertain future.
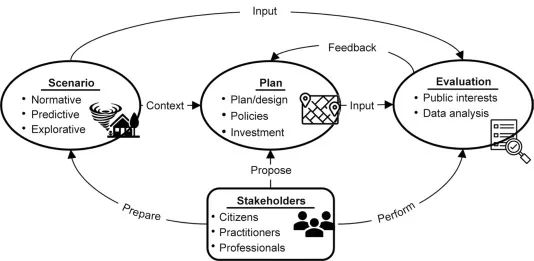
Cite this article
Haiyan Hao, Yan Wang, Jiayu Chen. Empowering Scenario Planning with Artificial Intelligence: A Perspective on Building Smart and Resilient Cities. Engineering, 2024, 43(12): 272–283 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.06.012
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。