|
|
|
|
|
FMD 合并症患者接种灭活疫苗预防新冠感染的有效性:前瞻性队列研究 |
|
|
论文标题:Protection of inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections in patients with comorbidities: a prospective cohort study
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Kanchana Ngaosuwan, Kamonwan Soonklang, Chawin Warakul Chirayu Auewarakul, Nithi Mahanonda
发表时间:15 Oct 2023
DOI:10.1007/s11684-023-0995-9
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
泰国朱拉蓬皇家学院Kanchana Ngaosuwan等在Frontiers of Medicine发表研究论文《合并症患者接种灭活疫苗预防新冠感染的有效性:前瞻性队列研究》(Protection of inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections in patients with comorbidities: a prospective cohort study)。本文通过对泰国曼谷接种新冠灭活疫苗人群进行前瞻性随访发现,合并症患者感染新冠病毒的风险与健康人无显著差异,但自身免疫病患者的感染风险显著增加。本研究强调了免疫缺陷人群需优先考虑加强接种的重要性,有助于指导该类人群的疫苗接种和疫情防控策略。
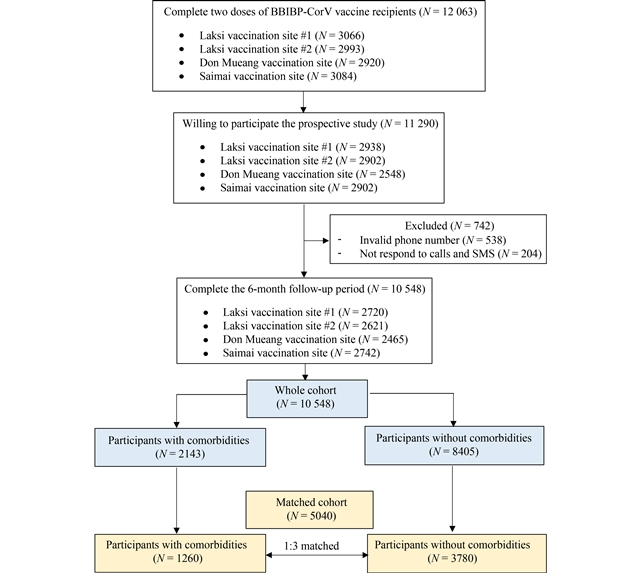
Protection against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection of inactivated vaccines is not well characterized in people with comorbidities, who are at high risk of severe infection. We compared the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection after complete vaccination with Sinopharm/BBIBP in people with comorbidities (e.g., autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disease, and diabetes) with healthy individuals using a Cox-proportional hazard model. In July–September 2021, a total of 10 548 people (comorbidities, 2143; healthy, 8405) receiving the complete primary series of vaccination with Sinopharm/BBIBP in Bangkok, Thailand were prospectively followed for SARS-CoV-2 infection through text messaging and telephone interviewing for 6 months. A total of 295 infections from 284 participants were found. HRs (95% CI) of individuals with any comorbidities did not increase (unadjusted, 1.02 (0.77–1.36), P = 0.89; adjusted, 1.04 (0.78–1.38), P = 0.81). HRs significantly increased in the subgroup of autoimmune diseases (unadjusted, 2.64 (1.09–6.38), P = 0.032; adjusted, 4.45 (1.83–10.83), P = 0.001) but not in cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disease, or diabetes. The protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection of the Sinopharm vaccine was similar in participants with any comorbidities vs. healthy individuals. However, the protection appeared lower in the subgroup of autoimmune diseases, which may reflect suboptimal immune responses among these people.
灭活疫苗对严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2型(SARS-CoV-2,简称新冠病毒)感染的防控作用在具有严重感染高危风险的合并症人群中尚未完全明确。本研究采用Cox比例风险模型,比较了合并症(如自身免疫性疾病、心血管疾病、慢性肺部疾病及糖尿病)人群与健康个体在完成国药集团/北京生物制品研究所(BBIBP)疫苗接种后的SARS-CoV-2感染风险。研究于2021年7月至9月在泰国曼谷开展,共有10 548名完成国药/BBIBP疫苗全称基础免疫接种的受试者(合并症组2143例,健康对照组8405例),通过短信及电话随访的方式进行了为期6个月的SARS-CoV-2感染前瞻性追踪。研究发现284名参与者发生了295次感染事件。总体合并症人群的风险比(HRs,95%置信区间)未显著升高(未校正时:1.02(0.77-1.36),P = 0.89;校正后:1.04(0.78-1.38),P = 0.81)。自身免疫性疾病亚组的HRs显著升高(未校正时:2.64(1.09-6.38),P = 0.032;校正后:4.45(1.83-10.83),P = 0.001),而心血管疾病、慢性肺部疾病或糖尿病患者未见统计学差异。研究表明,国药疫苗对合并症人群预防SARS-CoV-2感染的总体保护效力与健康个体相当,但在自身免疫性疾病亚组中保护力降低,这可能反映出这部分人群的免疫应答欠佳。
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine 专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
Protection of inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections in patients with comorbidities: a prospective cohort study
作者
Kanchana Ngaosuwan1, Kamonwan Soonklang2, Chawin Warakul1, Chirayu Auewarakul1, Nithi Mahanonda3
机构
1. Princess Srisavangavadhana College of Medicine, Chulabhorn Royal Academy, Bangkok 10210, Thailand
2. Data Management Unit, Centre of Learning and Research in Celebration of HRH Princess Chulabhorns 60th Birthday Anniversary, Chulabhorn Royal Academy, Bangkok 10210, Thailand
3. Chulabhorn Hospital, Chulabhorn Royal Academy, Bangkok 10210, Thailand
通讯作者
Kanchana Ngaosuwan
引用这篇文章
Kanchana Ngaosuwan, Kamonwan Soonklang, Chawin Warakul, Chirayu Auewarakul, Nithi Mahanonda. Protection of inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections in patients with comorbidities: a prospective cohort study. Front. Med., 2023, 17(5): 867–877 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-023-0995-9
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-023-0995-9
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-023-0995-9
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。