|
|
|
|
|
FMD 论文速览:人类疾病中铁死亡机制的微观解析与宏观洞察 |
|
|
论文标题:Zooming in and out of ferroptosis in human disease
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Xue Wang, Ye Zhou, Junxia Min, Fudi Wang
发表时间:15 Apr 2023
DOI:10.1007/s11684-023-0992-z
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
浙江大学医学部闵军霞教授和王福俤教授等在Frontiers of Medicine发表综述论文《人类疾病中铁死亡机制的微观解析与宏观洞察》(Zooming in and out of ferroptosis in human disease)。本文聚焦于铁死亡在人类疾病中的研究,阐释了其在多种疾病中的作用、治疗策略及未来方向,为疾病治疗提供了新的思路和潜在途径。
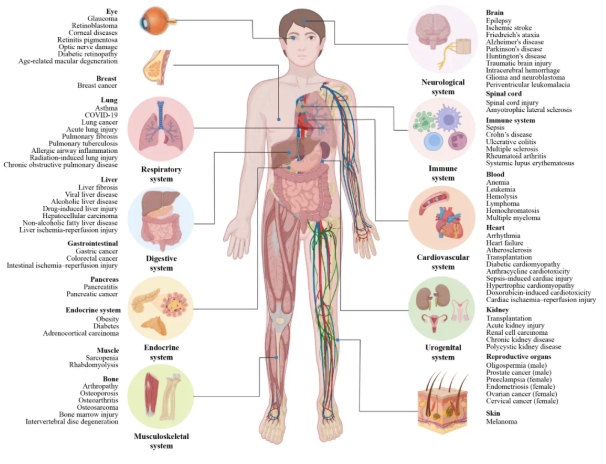
Ferroptosis is defined as an iron-dependent regulated form of cell death driven by lipid peroxidation. In the past decade, it has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases that together involve almost every organ of the body, including various cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, endocrine metabolic diseases, iron-overload-related diseases, orthopedic diseases and autoimmune diseases. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its regulatory pathways could provide additional strategies for the management of these disease conditions. Indeed, there are an expanding number of studies suggesting that ferroptosis serves as a bona-fide target for the prevention and treatment of these diseases in relevant pre-clinical models. In this review, we summarize the progress in the research into ferroptosis and its regulatory mechanisms in human disease, while providing evidence in support of ferroptosis as a target for the treatment of these diseases. We also discuss our perspectives on the future directions in the targeting of ferroptosis in human disease.
铁死亡,被定义为一种由脂质过氧化驱动的铁依赖性调节性细胞死亡形式。在过去十年中,铁死亡已被证明与多种疾病的发病机制相关,这些疾病广泛涉及人体的各个器官,涵盖多种癌症、神经退行性疾病、心血管疾病、肺部疾病、肝脏疾病、肾脏疾病、内分泌代谢疾病、铁过载相关疾病、骨科疾病以及自身免疫性疾病。了解铁死亡潜在的分子机制及其调控通路,能够为这些疾病的治疗提供更多策略。事实上,越来越多的研究表明,在相关临床前模型中,铁死亡可作为预防和治疗这些疾病的有效靶点。本综述系统梳理了铁死亡及其在人类疾病中调控机制的研究进展,同时通过详实的证据有力支持了铁死亡作为疾病治疗靶点的可行性。此外,对靶向铁死亡治疗人类疾病的未来研究方向进行了展望。
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
Zooming in and out of ferroptosis in human disease
作者
Xue Wang1,2, Ye Zhou3, Junxia Min1, Fudi Wang1,2
机构
1. The Second Affiliated Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital, Institute of Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310058, China
2. The First Affiliated Hospital, Basic Medical Sciences, School of Public Health, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China
3. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ningbo First Hospital, Ningbo 315000, China
通讯作者
Junxia Min, Fudi Wang
引用这篇文章
Xue Wang, Ye Zhou, Junxia Min, Fudi Wang. Zooming in and out of ferroptosis in human disease. Front. Med., 2023, 17(2): 173–206
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-023-0992-z
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-023-0992-z
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-023-0992-z
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。