|
|
|
|
|
FIE Highlights:夜光——探索利用生物发光浮游生物作为自然光源的的机遇与挑战 |
|
|
论文标题:Glow-in-the-dark: Exploring the opportunities and challenges of bioluminescent plankton as a natural light source
期刊:Frontiers in Energy
作者:Siti Hamisah Tapsir , Siew Moi Phang , Nor Aieni Mokhtar , Swee Sen Teo , Lai Huat Lim , Kah Hou Teng , Swee Pin Yeap
发表时间:02 Oct 2024
DOI:10.1007/s11708-024-0966-0
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

近日,马来西亚思特雅大学Siti Hamisah Tapsir教授团队在《Frontiers in Energy》发表了题为“Glow-in-the-dark: Exploring the opportunities and challenges of bioluminescent plankton as a natural light source”的Highlights文章。该论文深入探讨了利用生物发光浮游生物作为天然光源的潜力与挑战,为未来绿色照明和能源技术提供了新视角。
# 文章主要内容#
生物发光浮游生物是一类能够通过体内化学反应发出蓝色光芒的海洋生物,其发光现象俗称“蓝眼泪”,目前广泛应用于生态、海洋和生物学研究,而在能源和照明领域的应用仍处于探索阶段。其发光原理基于荧光素酶-荧光素反应,可产生高效“冷光”,能量损耗极低,部分培养体系甚至能够达到100瓦白炽灯的亮度。
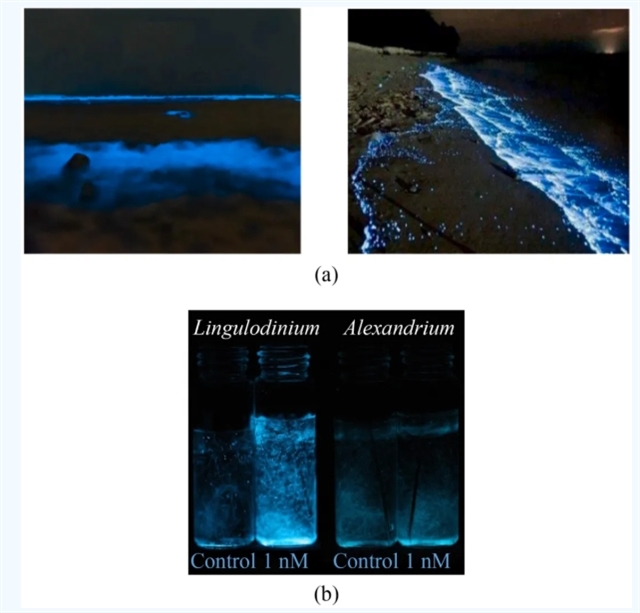
Fig.1 “Blue tears” phenomenon
与传统光源相比,生物发光技术有望实现独立于电网的天然照明,减少碳排放并提升能源利用效率。然而,这项技术面临多个挑战,包括如何实现生物的高效分离和大规模室内培养、稳定控制发光输出、筛选安全菌株以及优化发光强度等。此外,发光受昼夜节律影响,需要外部刺激维持稳定性。未来研究方向包括开发智能化培养体系、提取发光物质用于医药和商业领域,以及通过基因工程拓展应用场景。尽管存在技术和经济挑战,生物发光浮游生物作为可持续发展的一部分,展现出巨大的应用潜力。
# 原文信息 #

Abstract:
Bioluminescent plankton are marine organisms capable of emitting visible light through chemical reactions in their bodies. This unique biochemical trait is attributed to a luciferin-luciferase reaction, which produces a striking blue light. This fascinating phenomenon, often referred to as the “blue tears” effect, has become a major attraction for tourist attractions in many countries. Since their discovery, most investigations related to these marine organisms have primarily focused on the fields of biology, ecology, oceanography, and microbiology. However, there has been limited to almost no study of their potential applications in the area of energy or lighting. This paper provides viewpoints on the opportunities for using these marine organisms and their light-emitting characteristics as an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly lighting solution, rather than just as a tourist attraction. Additionally, it addresses the challenges associated with sustaining the growth of bioluminescent plankton collected from the marine environment, the importance of establishing suitable protocols for in-house cultivation, challenges in stimulating the light-production at desired time, constraint imposed by the circadian rhythm, the toxicity of certain bioluminescent plankton, and the capacity of their luminous intensity.
Cite this article:
Siti Hamisah Tapsir, Siew Moi Phang, Nor Aieni Mokhtar, Swee Sen Teo, Lai Huat Lim, Kah Hou Teng, Swee Pin Yeap. Glow-in-the-dark: Exploring the opportunities and challenges of bioluminescent plankton as a natural light source. Front. Energy, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-024-0966-0

识别二维码,下载全文

欢迎了解期刊更多信息
主编团队

期刊特点
1. 国际化投审稿平台ScholarOne方便快捷。
2. 严格的同行评议(Peer Review)。
3. 免费语言润色,有力保障出版质量。
4. 不收取作者任何费用。
5. 不限文章长度。
6. 审稿周期:第一轮平均30天,投稿到录用平均60天
7. 在线优先出版(Online First)。
8. 通过Springer Link平台面向全球推广。
在线浏览
http://journal.hep.com.cn/fie(国内免费开放)
https://link.springer.com/journal/11708
在线投稿
https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/fie
联系我们
FIE@sjtu.edu.cn, (86) 21-62932006
qiaoxy@hep.com.cn, (86) 10-58556482

小提示:Frontiers in Energy为国产英文刊,不属于瑞士Frontiers系列。瑞士Frontiers系列相关期刊为Frontiers in Energy Research。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。