|
|
|
|
|
FESE | 前沿研究:严格的水资源管理促进了我国北方干旱区生态保护与经济发展间的协同 |
|
|
论文标题:Water resource conservation promotes synergy between economy and environment in China’s northern drylands (严格的水资源管理促进了我国北方干旱区生态保护与经济发展间的协同)
期刊:Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering
作者:Yali Liu1, Jianqing Du, Boyang Ding, Yuexian Liu, Wenjun Liu, Anquan Xia, Ran Huo, Qinwei Ran, Yanbin Hao, Xiaoyong Cui, Yanfen Wang
发表时间:21 Jun 2021
DOI:10.1007/s11783-021-1462-y
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

原文链接:
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fese/EN/10.1007/s11783-021-1462-y
文章出版:Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16(3): 28
原文信息
题目:
Water resource conservation promotes synergy between economy and environment in China’s northern drylands
作者:
Yali Liu1, Jianqing Du ( )2,3, Boyang Ding2, Yuexian Liu1, Wenjun Liu4, Anquan Xia2, Ran Huo5, Qinwei Ran1, Yanbin Hao2,3,6, Xiaoyong Cui2,3,6, Yanfen Wang (
)2,3, Boyang Ding2, Yuexian Liu1, Wenjun Liu4, Anquan Xia2, Ran Huo5, Qinwei Ran1, Yanbin Hao2,3,6, Xiaoyong Cui2,3,6, Yanfen Wang ( )1,3,6
)1,3,6
作者单位:
1 College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
2 College of Life Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Yanshan Earth Critical Zone and Surface Fluxes Research Station, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
5 Shandong Tudi Development Group Co., Ltd., Jinan 250101, China
6 CAS Center for Excellence in Tibetan Plateau Earth Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
关键词:
Water conservation (水资源保护);
Environmental protection (环境保护);
Industry transformation (产业转型);
Evenness (均衡);
Sustainable development (可持续发展);
Dryland (干旱区)
文章亮点
• 采用均衡度能更准确地评估可持续发展;
• 水资源管理政策推动了产业结构转型;
• 实现经济发展与环境保护协同发展;
• 围绕水资源的区域合作可以促进旱地的可持续发展。
背景介绍
水资源是干旱区发展的主要限制因素,在气候变化和人类不合理的开发利用下造成水资源短缺、土地退化、粮食短缺等,制约了其可持续发展。我国北方干旱区水资源占有量仅为全国的19%,却拥有全国1/3的人口数量,面临着巨大的水资源压力。以我国北方典型干旱区内蒙古为例,在过去的几十年间由于水资源的过度开发带来了一系列的社会-环境问题,例如干旱、沙尘暴、畜牧业倒退、贫困等,加剧了经济发展与生态环境之间的矛盾。以往的研究大都采用提高水资源利用效率、控制污染等措施来缓解上述矛盾。但是长期以来生态系统与社会经济系统之间的内在冲突,以及可能缓解二者冲突的举措却一直被忽视。
主要结论
气候变化加剧了人类发展与环境保护之间的用水冲突,而有效的水资源管理能够平衡经济发展与环境保护之间的矛盾。鉴于此,2008年3月内蒙古政府颁布了《内蒙古自治区取水许可和水资源费征收管理实施办法》,旨在缓解经济和环境之间的矛盾。然而,目前尚未开展系统评估来确定该严格的水资源管理政策能否以及如何缓解环境保护与经济发展之间的矛盾。针对以上问题,本研究主要从两个方面对上述水资源管理政策进行了定量评估,一是政策实施后内蒙古经济发展是否降低了对水资源的依赖程度,二是政策是否促进了环境保护与经济发展协同发展,并对城市发展提出了政策建议。
主要结论
研究结果显示严格的水资源管理政策促进了内蒙古的产业转型和可持续发展,其中煤炭和钢铁等对环境危害较大的产业比重逐渐下降,第三产业(主要是旅游业)比重不断上升,至2018年成为重要支柱产业,有效降低了经济发展对水资源的依赖,改善了环境质量,缓解了水资源压力。通过水资源调控,激发产业转型的内生动力,可以实现经济发展与环境保护的协同效应,促进干旱区可持续发展。此外,不同城市表现出不同的均衡-发展特点,因地制宜的适应性管理策略可助力可持续发展。首先,发展相对较好的城市-鄂尔多斯市,和相对欠发展但发展路径较理想的城市(如通辽、乌海、阿拉善),这类城市可以维持现状。其次,对于相对欠发展但不均衡且发展路径也不理想的盟市,包括巴彦淖尔、赤峰、乌兰察布,大多数都水资源匮乏且经济发展不理想。省政府的政策扶持就十分重要,包括畜牧业的生态补偿、减税等。最后,通过水交易来实现协同互补,如呼伦贝尔和兴安(经济欠发达、水资源相对丰富的地区)与呼和浩特和包头(经济发达、水资源压力较大的地区)之间的水贸易协定,使跨区域整体实现可持续发展的成为可能。
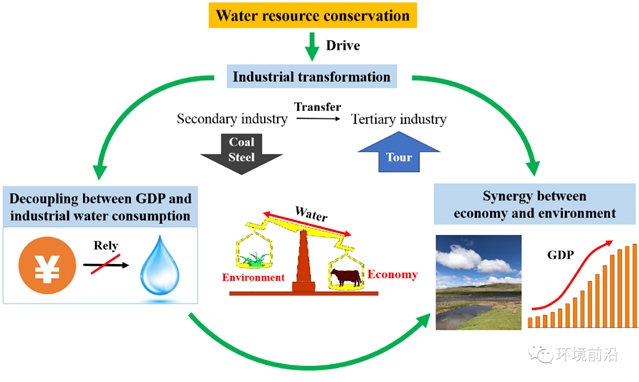
图1 摘要图
本研究通过对水资源管理政策实施前后进行对比分析,探索政策类管理办法能否促进经济发展和环境保护协同发展,并构建了可持续发展综合评价指数,结合数值模型制定适应性管理策略,提供了一种可复制的方法,可供其它地区参考。
摘要
Water resource availability is the major limiting factor for sustainable development in drylands. Climate change intensifies the conflicting water demands between people and the environment and highlights the importance of effective water resource management for achieving a balance between economic development and environmental protection. In 2008, Inner Mongolia, typical dryland in northern China, proposed strict regulations on water exploitation and utilization aimed at achieving sustainable development. Our study is the first to investigate the effectiveness and performance of these long-standing water conservation regulations. Our analyses found that the regulations drove industrial transformation, evidenced by the decreasing proportion of environmentally harmful industries such as coal and steel, and the increasing proportion of tertiary industries (especially tourism). Following industrial transformation, economic development decoupled from industrial water consumption and subsequently led to reduced negative environmental impacts. Based on these results, adaptive strategies were developed for 12 cities by revealing and integrating their development pathways and relative status in achieving sustainable development. Integration and cooperation between cities were proposed, e.g., a water trade agreement between eastern Inner Mongolia (an economically underdeveloped region with relatively abundant water resources) and central Inner Mongolia (an economically developed region with high water stress). Such an agreement may enable the holistic achievement of sustainable development across regions. By integrating the findings of our research, our study presents a reproducible framework for water-management-based sustainable development strategies in drylands.

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。