题目: Copper-surface-mediated synthesis of acetylenic carbon-rich nanofibers for active metal-free photocathodes
作者:Tao Zhang et al.
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41467-018-03444-0
发表日期: 2018/3/19
摘要:The engineering of acetylenic carbon-rich nanostructures has great potential in many applications, such as nanoelectronics, chemical sensors, energy storage, and conversion, etc. Here we show the synthesis of acetylenic carbon-rich nanofibers via copper-surface-mediated Glaser polycondensation of 1,3,5-triethynylbenzene on a variety of conducting (e.g., copper, graphite, fluorine-doped tin oxide, and titanium) and non-conducting (e.g., Kapton, glass, and silicon dioxide) substrates. The obtained nanofibers (with optical bandgap of 2.51 eV) exhibit photocatalytic activity in photoelectrochemical cells, yielding saturated cathodic photocurrent of ca. 10 µA cm−2 (0.3–0 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode). By incorporating thieno[3,2-b]thiophene units into the nanofibers, a redshift (ca. 100 nm) of light absorption edge and twofold of the photocurrent are achieved, rivalling those of state-of-the-art metal-free photocathodes (e.g., graphitic carbon nitride of 0.1–1 µA cm−2). This work highlights the promise of utilizing acetylenic carbon-rich materials as efficient and sustainable photocathodes for water reduction
炔属富碳纳米结构材料在纳米电子学,化学传感器,能量的存储和转换等很多方面都有很大的应用前景。近日发表在《自然-通讯》的一项研究Copper-surface-mediated synthesis of acetylenic carbon-rich nanofibers for active metal-free photocathodes则描述了炔属富碳纳米材料在光电领域的应用。
来自德国德累斯顿工业大学的冯新亮教授及同事们向我们展示了在一系列导电基质(例如铜,石墨,氟掺杂二氧化锡,钛等)和不导电基质(例如聚酰亚胺,玻璃,二氧化硅等)上,通过铜表面介导进行1,3,5-三乙炔基苯的格拉泽缩聚反应,来合成炔属富碳纳米纤维。获得的纳米纤维(2.51eV光学带隙)在光电化学电池中展现出了光催化活性,可产生大约10μA/cm2(0.3-0 V vs.可逆氢电极)的饱和阴极光电流。通过将噻吩并[3,2-b]噻吩单元结合到纳米纤维中,实现了红移(约100nm)的光吸收边缘,并有两倍于现有效能最高的无金属光电阴极(例如,0.1-1μA/cm2石墨氮化碳)能得到的光电流。本研究使利用炔属富碳材料制备高效可持续光电阴极进行水还原反应成为可能。
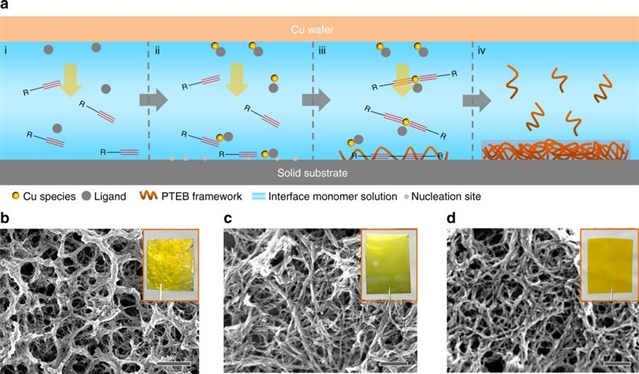
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-03444-0(来源:科学网)