|
|
|
|
|
低成本笑脸式腕带可监测紫外线辐射,还能根据肤色定制 |
|
|
论文标题:Skin color-specific and spectrally-selective naked-eye dosimetry of UVA, B and C radiations
期刊:Nature Communications
作者:Wenyue Zou, Ana González, Deshetti Jampaiah, Rajesh Ramanathan, Mohammad Taha, Sumeet Walia, Sharath Sriram, Madhu Bhaskaran, José M. Dominguez-Vera, Vipul Bansal
发表时间:2018/09/25
数字识别码:10.1038/s41467-018-06273-3
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-06273-3?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-MixedBrand-multijournal-Multidisciplinary-China&utm_campaign=ORG_USG_JRCN_RL_article_promotion_sciencenet_Oct_2nd
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lE9zsJdXYJewCJmqMu-37g
《自然-通讯》论文Skin color-specific and spectrally-selective naked-eye dosimetry of UVA, B and C radiations介绍了一种裸眼探测紫外线辐射(UVR)的低成本、高灵敏度传感器的全新制造方法。这种纸基的可穿戴传感器能让用户对日常生活中的UVR影响进行监管。
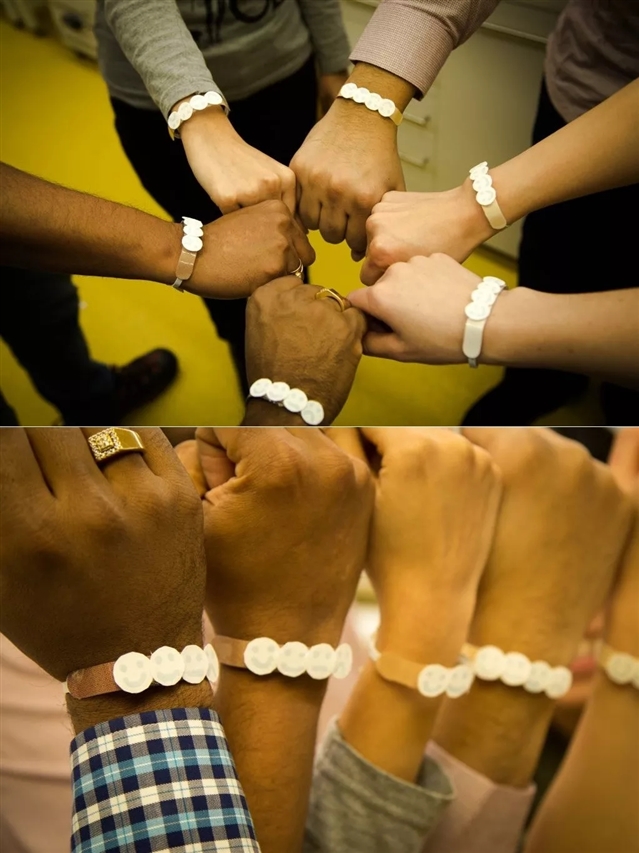

图1:个性化的可穿戴式UV传感器适用于肤色不同的人群。图源:Kiralee Greenhalgh
UVR可根据波长分为UVA、UVB和UVC。要监测不同UV辐射的影响,就需要低成本的光谱选择性UV传感器。但目前的传感器由于造价高、制造工序复杂,很难实现大规模部署。

图2:纸基UV传感器示意图。图源:Zou等
澳大利亚皇家理工大学的Vipul Bansal和同事设计出了一种具有光谱选择性的高灵敏度UV传感器的制造方法。他们的设计秘诀在于创造出了一种基于多金属氧酸盐的隐形墨水。这种墨水具有光谱选择性UV感应的特殊性能,与低成本的现成部件(如滤纸、透明膜或钢笔)结合后,就能制造出一种纸基的低成本可穿戴UV传感器。
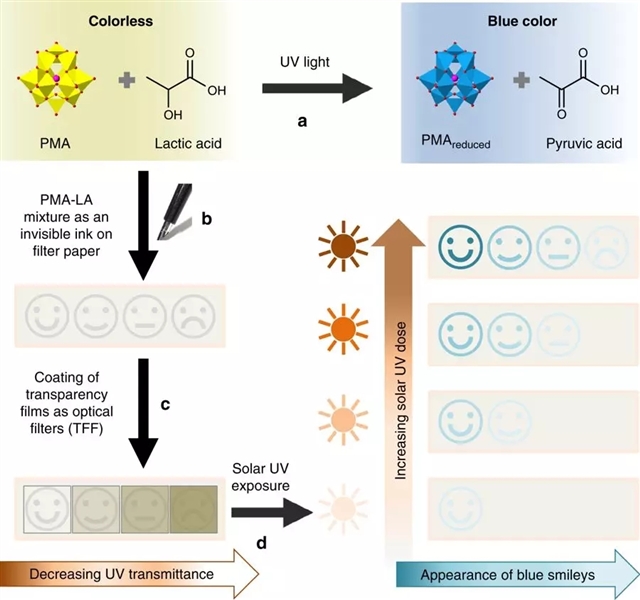
图3:一种可穿戴腕带式的纸基UV传感器原型,暴露在不同级别的可允许太阳紫外线阈值下。 表情符号最初是看不见的,但在特定个体的安全紫外线照射限值的25%,50%,75%和100%的照射量下,它们从左到右变为蓝色。图源:Ms Wenyue Zou
作者通过一个定制的纸基笑脸式UV传感器展示了这项新技术的适用性,该传感器可以针对6种不同皮肤类型对每种UVR的最大允许照射量阈值进行实时照射剂量监测。这一结果表明,光谱选择性UV传感器或有潜力投入大规模生产,并对特定皮肤类型进行定制。
摘要:Spectrally–selective monitoring of ultraviolet radiations (UVR) is of paramount importance across diverse fields, including effective monitoring of excessive solar exposure. Current UV sensors cannot differentiate between UVA, B, and C, each of which has a remarkably different impact on human health. Here we show spectrally selective colorimetric monitoring of UVR by developing a photoelectrochromic ink that consists of a multi-redox polyoxometalate and an e− donor. We combine this ink with simple components such as filter paper and transparency sheets to fabricate low-cost sensors that provide naked-eye monitoring of UVR, even at low doses typically encountered during solar exposure. Importantly, the diverse UV tolerance of different skin colors demands personalized sensors. In this spirit, we demonstrate the customized design of robust real-time solar UV dosimeters to meet the specific need of different skin phototypes. These spectrally–selective UV sensors offer remarkable potential in managing the impact of UVR in our day-to-day life.
阅读论文全文请访问:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-06273-3?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-MixedBrand-multijournal-Multidisciplinary-China&utm_campaign=ORG_USG_JRCN_RL_article_promotion_sciencenet_Oct_2nd
期刊介绍:Nature Communications (https://www.nature.com/ncomms/) is an open access journal that publishes high-quality research from all areas of the natural sciences. Papers published by the journal represent important advances of significance to specialists within each field.
The 2017 journal metrics for Nature Communications are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 12.353
•5-year impact factor: 13.691
•Immediacy index: 1.829
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.92656
•Article Influence Score: 5.684
•2-year Median: 8
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。