|
|
|
|
|
长江学者刘昌俊教授团队:高活性Au/In2O3-ZrO2催化剂用于CO2选择性加氢制备甲醇 | MDPI Catalysts |
|
|
论文标题:A Highly Active Au/In2O3-ZrO2 Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2 to Methanol
期刊:Catalysts
作者:Zhe Lu et al.
发表时间:23 November 2020
DOI:10.3390/catal10111360
微信链接:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?biz=MzI1MzEzNjgxMQ==&mid=2649984877&idx=
1&sn=4d4f7f21542874f4fdc47d84d29a3027&chksm=f1de35a9c6a9bcbff22dce
6b94fbb250a06da096b86aec3d2eda85c0ee66488462cedbcca878&token=799446241&lang=zh_CN#rd
期刊链接:https://www.mdpi.com/journal/catalysts
原文通讯作者简介

刘昌俊教授
刘昌俊教授,国家杰出青年基金获得者、第十二、十三届全国政协委员;英国皇家化学会会士。
刘教授主要研究领域包括CO2化学利用、天然气转化、催化剂与纳米材料等离子体制备与应用研究等,在催化剂结构性能关系、CO2活化、甲烷转化、纳米金属组合材料等方面取得创新性研究成果。曾任国家自然科学基金委员会化学科学部第九、十、十二、十三届学科评审组成员、美国化学 (ACS) 燃料化学分会2010年程序主席、国际二氧化碳利用大会第十届大会主席、欧盟框架温室气体利用项目会评专家、中国力学会等离子体科学技术专业委员会副主任。现任中国化学会催化专业委员会委员。
文章导读
二氧化碳 (CO2) 加氢制甲醇是缓解温室效应与化石能源短缺的一种有效策略,越来越多研究者致力于开发具备高甲醇选择性与高CO2转化率的催化剂。含氧空位的In2O3催化剂近来被证明对于CO2加氢合成甲醇具有高选择性和高活性 [1,2]。后续研究发现负载活性金属在In2O3上能有效提高加氢能力。同时,ZrO2能稳定、优化In2O3氧空位,并能改进CO2吸附,从而提高In2O3催化剂活性 [3]。另一方面,Au催化剂是催化研究的热点课题,但通常Au催化剂对CO2加氢合成甲醇不具活性。来自天津大学的刘昌俊教授团队前期通过In2O3与Au相互作用,发现In2O3负载Au催化剂 (Au/In2O3) 对CO2加氢合成甲醇具有良好活性 [4]。在此研究基础上,团队进一步发现了一种铟锆固溶体负载Au催化剂 (Au/In2O3-ZrO2),通过Zr的掺杂,Au/In2O3催化剂的CO2加氢合成甲醇活性有了进一步提高 (图1)。在反应温度为573 K、反应压力为5 MPa、空速为21,000 cm3 h-1 gcat-1的条件下,Au/In2O3-ZrO2催化剂的CO2转化率、甲醇选择性、甲醇收率分别达到14.8%,70.1%和0.59 gMeOH h−1 gcat−1。
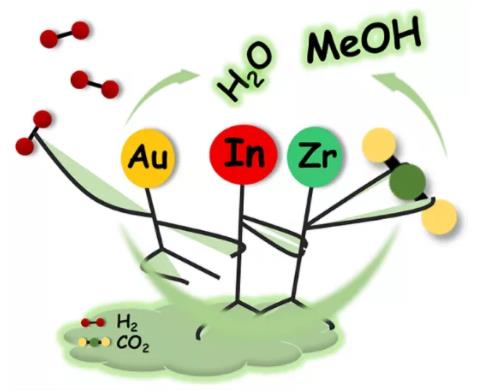
图1. Au, In2O3和ZrO2的结合实现高选择性的CO2加氢制甲醇。
催化剂反应性能
图2为In2O3, Au/In2O3, Au/In2O3-ZrO2 催化剂活性对比,Au/In2O3-ZrO2 催化剂表现出最高的活性与选择性。特别是,573 K下,Au/In2O3-ZrO2催化剂的甲醇选择性超过70%。这突出反映了Au/In2O3-ZrO2催化剂在CO2加氢高选择性合成甲醇方面的优势。
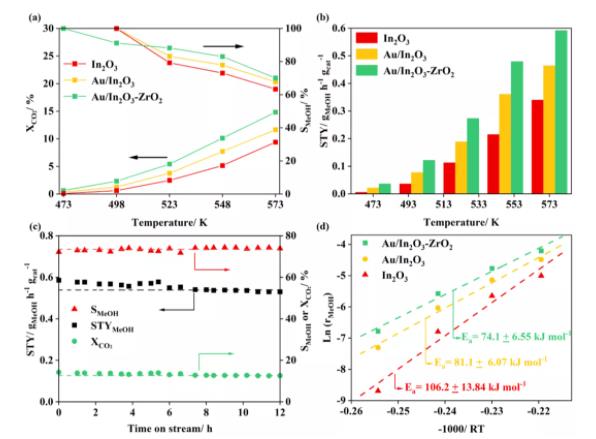
图2. In2O3, Au/In2O3和Au/In2O3-ZrO2催化剂活性对比。
催化剂结构特性
根据XRD、TEM、SEM-EDX分析结果 (图3) 可知,共沉淀制备的In2O3-ZrO2载体为固溶体结构,通过沉积沉淀方法负载的Au纳米颗粒很好地分散在载体表面上。拉曼表征 (图4) 进一步表明,Au/In2O3-ZrO2样品在氢还原前后都表现出比Au/In2O3更多的氧空位。另外,Zr、Au的引入均有利于提升In2O3在还原性气氛下的稳定性。
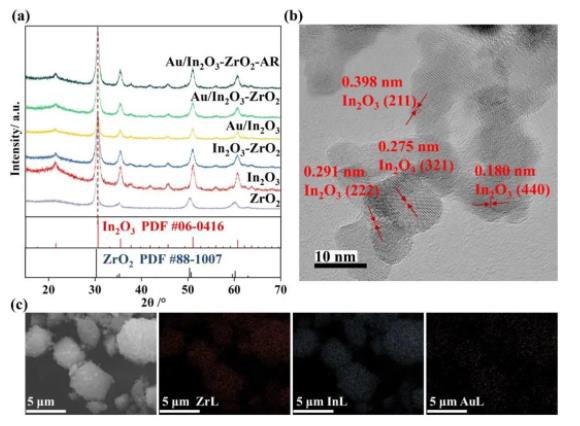
图3. (a) 样品XRD图谱;Au/In2O3-ZrO2样品的 (b) TEM图像与 (c) SEM-EDX图像。
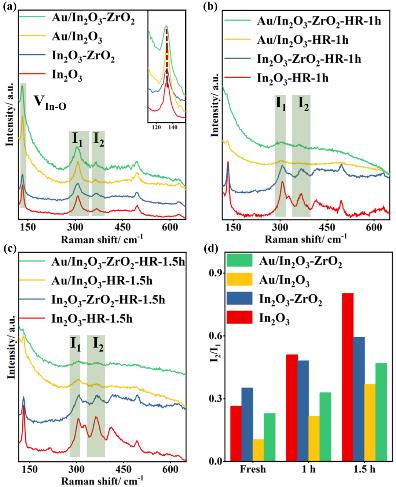
图4. (a) 制备样品与 (b-c) 还原样品的拉曼光谱以及 (d) 氧空位相对量的比较。
H2-TPR表征进一步验证了掺杂Zr对In2O3结构的稳定性 (图5)。同时,Au纳米颗粒与催化剂表面存在强相互作用,从而实现了增强的H2活化。CO2-TPD与原位DRIFTS表征 (图6) 证明Zr的加入有利于提升催化剂的CO2吸附能力。
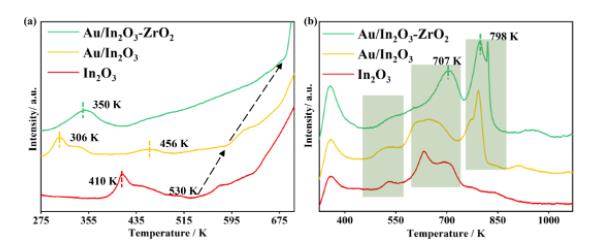
图5. 不同催化剂上的 (a) H2-TPR和 (b) CO2-TPD曲线。
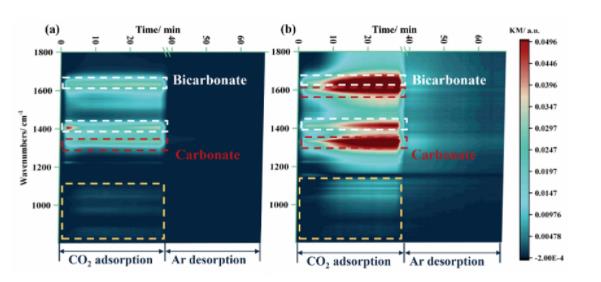
图6. 323 K下 (a) CO2化学吸附与 (b) Ar脱附的原位DRIFTS谱图。
结论
基于以上讨论,Au和In2O3-ZrO2固溶体之间存在强相互作用,这种形态下的Au纳米颗粒增强了H2的解离。同时,Zr掺入In2O3晶格后会导致氧空位增加,并增强CO2的吸附。与载体强烈相互作用的Au纳米颗粒解离的H原子可以溢流到氧空位上,并与在氧空位上活化的CO2分子反应,从而促进了CO2转化为甲醇。Zr的存在主要表现出四个作用:(1) 降低表观活化能;(2) 稳定In2O3的结构;(3) 增加氧空位的数量;(4) 增强CO2吸附。这项工作不仅扩展了Au催化剂在CO2加氢上的利用,也促进了CO2转化和Au催化剂基础研究的发展。
参考文献
1. Ye, J.; Liu, C.-J.; Mei, D.; Ge, Q. Active Oxygen Vacancy Site for Methanol Synthesis from CO2 Hydrogenation on In2O3(110): A DFT Study. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1296-1306.
2. Sun, K.; Fan, Z.; Ye, J.; Yan, J.; Ge, Q.; Li, Y.; He, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, C.-J. Hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol over In2O3 catalyst. J. CO2 Util. 2015, 12, 1-6.
3. Frei, M.S.; Mondelli, C.; Cesarini, A.; Krumeich, F.; Hauert, R.; Stewart, J.A.; Curulla Ferré, D.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Role of zirconia in indium oxide-catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation to methanol. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1133–1145.
4. Rui, N.; Zhang, F.; Sun, K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Stavitski, E.; Senanayake, S.D.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Liu, C.-J. Hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol on a Auδ+–In2O3–x catalyst. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 11307–11317.
期刊简介
Catalysts (ISSN 2073-4344; IF 3.520) 是一个国际型开放获取期刊,期刊主题涵盖催化剂和催化反应等相关研究领域。目前已被SCIE、Scopus、Inspec (IET)等重要数据库收录。Catalysts采取单盲同行评审,文章平均处理周期为30天,一审周期约为11天,文章从接收到发表仅需2.9天。
摘要:
Abstract
A novel gold catalyst supported by In2O3-ZrO2 with a solid solution structure shows a methanol selectivity of 70.1% and a methanol space–time yield (STY) of 0.59 gMeOH h−1 gcat−1 for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol at 573 K and 5 MPa. The ZrO2 stabilizes the structure of In2O3, increases oxygen vacancies, and enhances CO2 adsorption, causing the improved activity.
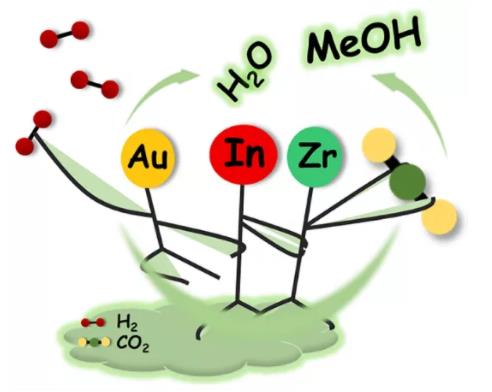
Figure 1. Graphical Abstract
Results
The activity test of CO2 hydrogenation to methanol was conducted in a vertical fixed-bed reactor. The products were analyzed with an online gas chromatograph (Agilent 7890A). For all catalysts, methanol and CO are the main products. Trace methane can be detected at reaction temperatures over 548 K. The carbon balance is better than 99%. As shown in Figure 2, the Au/In2O3-ZrO2 catalyst exhibits the highest catalytic performance among these three catalysts. The CO2 conversion of the Au/In2O3-ZrO2 catalyst is 14.8%, with a methanol selectivity of 70.1% at 573 K and 5 MPa. The methanol STY reaches 0.59 gMeOH h−1 gcat−1, which is much higher than that over the Au/In2O3 catalyst (0.47 gMeOH h−1 gcat−1) and other Au-based catalysts.
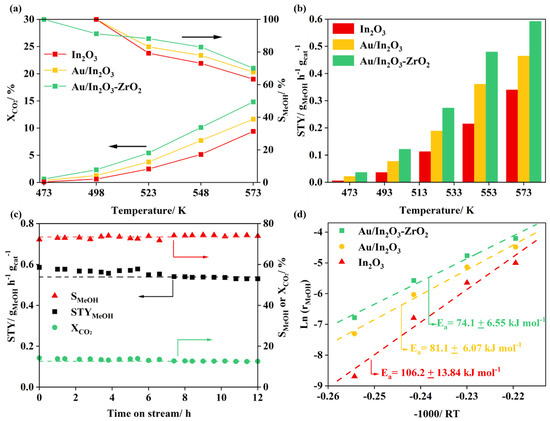
Figure 2. Comparison of (a) CO2 conversion and methanol selectivity, and (b) methanol space–time yield (STY) over the In2O3, Au/In2O3, and Au/In2O3-ZrO2 catalysts as a function of temperature; (c) CO2 conversion, methanol selectivity, and methanol STY versus time of the Au/In2O3-ZrO2 catalyst on stream (TOS); (d) Arrhenius plots for methanol production over the In2O3, Au/In2O3, and Au/In2O3-ZrO2 catalysts. (Reaction conditions: 5.0 MPa, H2/CO2/N2 = 76/19/5, GHSV = 21,000 cm3 h−1 gcat−1.).
As shown in Figure 3, the results of XRD, TEM and SEM-EDX indicate that the supported Au NPs and Zr are highly dispersed before and after the reaction. These results further confirm the excellent dispersion of Au NPs and the conclusion that In2O3-ZrO2 is in a solid solution state.
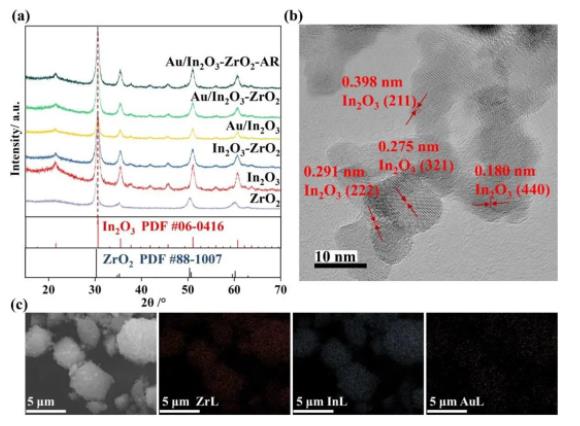
Figure 3. (a) XRD patterns of various oxides and Au-supported oxides; (b) HRTEM image of Au/In2O3-ZrO2; (c) scanning electron microscope (SEM) image and corresponding energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) mapping of Au/In2O3-ZrO2.
To further understand the factors responsible for the enhanced catalytic performance, Raman analyses were performed (Figure 4).
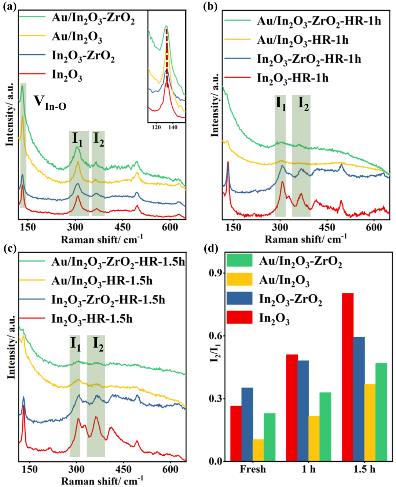
Figure 4. Visible Raman spectra of fresh samples (a) with the inset showing the enlargement of Raman spectra around 140 cm−1, and the samples after hydrogen reduction for 1 h (b) and 1.5 h (c); the comparison of the relative amount of the oxygen vacancies according to I2/I1 value (d). (H2 reduction conditions: 473 K, 0.1 MPa, 10% H2/Ar.)
H2 temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR) was employed to investigate the reduction behaviors of the catalysts (Figure 5).
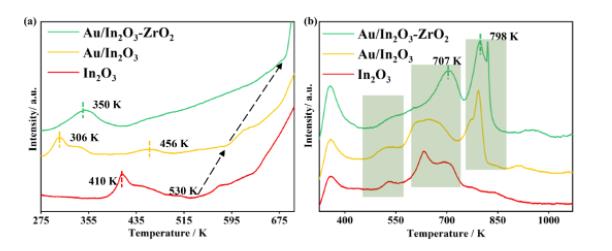
Figure 5. H2-TPR profiles (a) and CO2-TPD profiles (b) of In2O3 and Au-supported oxides.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have shown that the integration of Au, In2O3, and ZrO2enables the high selectivity for methanol synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation. The Au/In2O3-ZrO2 catalyst shows a CO2 conversion of 14.8% with a methanol STY of 0.59 gMeOH h−1 gcat−1 at 573 K and 5 MPa. Such an outstanding activity indicates that the addition of Zr remarkably improves the activity of the Au/In2O3 catalyst. The catalyst characterizations demonstrate that Au NPs are well dispersed on the surface of the In2O3-ZrO2 solid solution. Further investigation through Raman spectra, H2-TPR, and CO2-TPD indicates that the enhanced H2 activation is achieved by the Au NPs strongly interacting with catalysts surface due to the SMSI effect. The presence of Zr mainly exhibits four effects: (1) reducing the apparent activation energy, (2) stabilizing the structure of In2O3, (3) increasing the amount of oxygen vacancies, and (4) enhancing the CO2 adsorption. This work not only extends the utilization of gold catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation but also promotes the fundamental studies for CO2 conversion.


特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。