近日,美国哥伦比亚大学Kishalay De团队报道了仙女座星系中一颗大质量恒星由于黑洞的形成而消失。相关论文于2026年2月12日发表在《科学》杂志上。
当大质量恒星行至生命终点,其核心坍缩并释放中微子,驱动激波冲向恒星外层包层。足够强劲的激波会将包层抛射出去,产生超新星爆发。若激波未能成功抛射包层,理论预言包层将回落至坍缩的核心,形成恒星质量黑洞,并使恒星本身悄然湮灭。
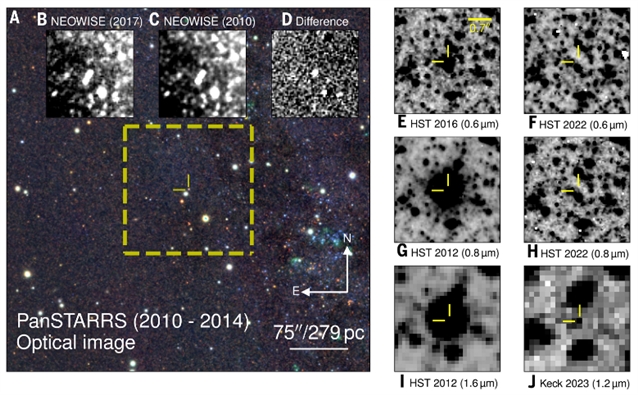
研究组报道了对仙女座星系中一颗贫氢超巨星M31-2014-DS1的观测。2014年,它在中红外波段增亮,随后从2017年至2022年,其可见光亮度衰减了10000倍(直至不可探测),总亮度衰减了10倍。研究组将这些观测结果,连同先前NGC 6946星系中类似事件的记录,共同解释为失败超新星形成恒星质量黑洞的证据。
附:英文原文
Title: Disappearance of a massive star in the Andromeda Galaxy due to formation of a black hole
Author: Kishalay De, Morgan MacLeod, Jacob E. Jencson, Elizabeth Lovegrove, Andrea Antoni, Erin Kara, Mansi M. Kasliwal, Ryan M. Lau, Abraham Loeb, Megan Masterson, Aaron M. Meisner, Christos Panagiotou, Eliot Quataert, Robert Simcoe
Issue&Volume: 2026-02-12
Abstract: When a massive star reaches the end of its lifetime, its core collapses and releases neutrinos that drive a shock into the outer layers (the stellar envelope). A sufficiently strong shock ejects the envelope, producing a supernova. If the shock fails to eject it, the envelope is predicted to fall back onto the collapsing core, producing a stellar-mass black hole (BH) and causing the star to disappear. We report observations of M31-2014-DS1, a hydrogen-depleted supergiant in the Andromeda Galaxy. In 2014, it brightened in the mid-infrared, then from 2017 to 2022, it faded by factors of ≥104 in optical light (becoming undetectable) and ≥10 in total light. We interpret these observations, and those of a previous event in NGC 6946, as evidence for failed supernovae forming stellar-mass BHs.
DOI: adt4853
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adt4853
