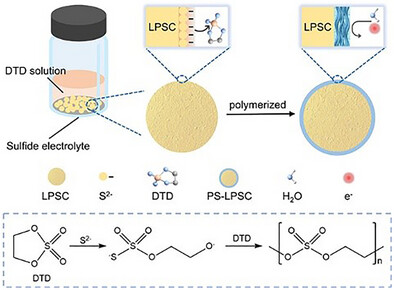
近日,武汉大学艾新平团队报道了一种解决硫化物固态电解质水分和氧化不稳定性的表面无损改性策略。相关论文于2025年12月29日发表在《德国应用化学》杂志上。
硫化物固体电解质因其高离子电导率和优异的界面贴合性,成为全固态电池的理想候选材料。然而,其固有的氧化不稳定性和高湿敏性阻碍了实际应用。
研究组提出了一种原位、非破坏性的硫化物电解质 Li6PS5Cl 表面改性策略:利用其表面亲核的 S2-阴离子引发 1,3,2-二氧硫杂环戊烷-2,2-二氧化物(乙烯硫酸酯,DTD)的开环聚合,从而形成均匀致密的聚硫酸酯改性层。该层能有效隔绝电解质与湿度和高压正极的直接接触,显著提升了材料的耐湿性和氧化稳定性。采用改性后的 PS-LPSC 电解质、高镍正极 LiNi0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 及LiIn 负极组装的全固态电池表现出优异的电化学性能:在室温下,0.2 C、1 C、10 C 和 20 C 倍率下的放电容量分别为 231.6、208.1、138.3 和 98.5 mA h g-1。
值得注意的是,电池在室温 10 C 倍率下循环 36,000 次后容量保持率达 70.0%,在苛刻条件(50 C 倍率、60 °C)下循环 20,000 次后仍保持 62.4% 的容量,展现出卓越的长周期循环稳定性和实用潜力。该研究为提升硫化物固体电解质的氧化与湿度稳定性提供了一条简便高效的表面改性路径。
附:英文原文
Title: A Surface Non-Destructive Modification Strategy Addressing Moisture and Oxidation Instabilities of Sulfide Solid-State Electrolytes
Author: Yicheng Deng, Guo Tang, Gengzhong Lin, Kean Chen, Hui Li, Yuliang Cao, Yongjin Fang, Jiangfeng Qian, Hanxi Yang, Xinping Ai
Issue&Volume: 2025-12-29
Abstract: Sulfide solid electrolytes are promising candidates for all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs), owing to their high ionic conductivity and excellent interfacial conformability. However, their practical application is hindered by inherent oxidative instability and high moisture sensitivity. Herein, we propose an in situ, non-destructive modification strategy for sulfide electrolyte Li6PS5Cl (LPSC) by leveraging the nucleophilic S2 anions on its surface to initiate the ring-opening polymerization of 1,3,2-dioxathiolane 2,2-dioxide (ethylene sulfate, DTD), thus forming a uniform and dense poly(sulfate) (PS) modification layer. This layer effectively shields the electrolyte from direct exposure to moisture and high-voltage cathodes, greatly enhancing both moisture tolerance and oxidation stability. ASSBs fabricated with the modified PS-LPSC electrolyte, a high-nickel LiNi0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 (NCM955) cathode and a LiIn anode, exhibit excellent electrochemical performance, delivering capacities of 231.6, 208.1, 138.3, and 98.5 mA h g1 at 0.2, 1, 10, and 20 C, respectively, at room temperature. Remarkably, the cells retain 70.0% capacity after 36,000 cycles at 10 C under room temperature, and 62.4% after 20,000 cycles even under harsh conditions (50 C and 60 °C), demonstrating exceptional long-term cycling stability and practical applicability. This study provides a facile and efficient surface modification route to enhance the oxidation and moisture stability of sulfide solid electrolytes.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202520531
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202520531
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
