髓磷脂通过少突胶质细胞祖细胞的组成分化进行修复,这一成果由约翰斯·霍普金斯大学
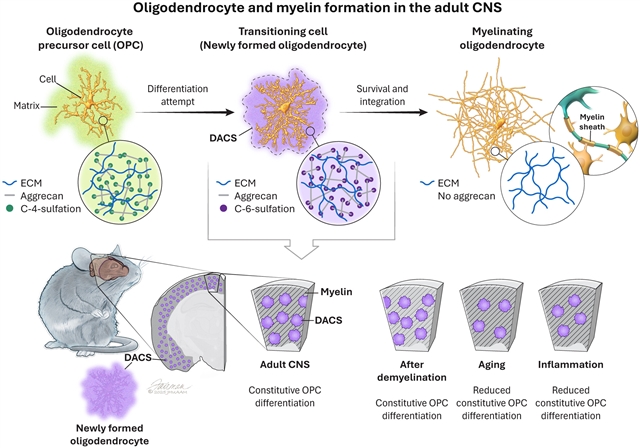
该课题组研究人员对单母脑中的OPCs进行了遗传询问和体内分析,以确定它们的分化动态。他们的研究结果表明,OPCs在整个成人中枢神经系统中具有空间和时间规律性的分化。分化率不受髓磷脂需求或少突胶质细胞损失的影响,并随年龄增长和急性炎症反应而下降。结果表明,OPC分化主要受构成过程控制,并可能受到衰老和炎症的负面影响。
研究人员表示,少突胶质细胞在轴突周围形成髓鞘,使神经回路中的快速信号传导成为可能。通过少突胶质前体细胞(OPCs)的分化产生新的少突胶质细胞,促进髓磷脂的可塑性和修复。
附:英文原文
Title: Myelin is repaired by constitutive differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitors
Author: Yevgeniya A. Mironova, Brendan Dang, Dongeun Heo, Yu Kang T. Xu, Angela Yu-Huey Hsu, Jaime Eugenin von Bernhardi, Gian Carlo Molina-Castro, Anya A. Kim, Jing-Ping Lin, Daniel S. Reich, Dwight E. Bergles
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-22
Abstract: Oligodendrocytes form myelin sheaths around axons to enable rapid signaling within neural circuits. The generation of new oligodendrocytes through differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) promotes myelin plasticity and repair in the adult brain. Here, we performed genetic interrogation and in vivo analysis of OPCs in the mouse brain to determine their differentiation dynamics. Our results show that OPCs attempt to differentiate throughout the adult central nervous system with spatial and temporal regularity. The differentiation rate was not influenced by myelin demand or oligodendrocyte loss and declined with age and in response to acute inflammation. The results suggest that OPC differentiation is governed primarily by constitutive processes and might be negatively influenced by aging and inflammation.
DOI: adu2896
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adu2896
