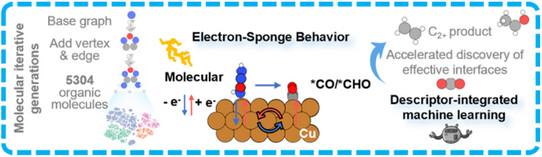
近日,湖南大学王双印团队实现了通过机器学习发现CO2电还原有机-金属界面上的电子海绵行为。相关论文于2026年1月19日发表在《德国应用化学》杂志上。
有机-金属界面的分子调控对于CO2电还原中的C─C偶联至关重要,直接影响多碳产物的生成。然而,电子、空间和拓扑分子描述符之间的非线性相互作用,阻碍了预测性定量构效关系的建立,限制了机理的深入理解。
研究组采用一种可解释的机器学习-QSAR框架,将分子特征与铜表面上C─C偶联的自由能垒联系起来,揭示了界面“电子海绵”行为的主导作用。机理上,修饰分子首先向铜捐赠电子,随后这些电子重新分配给*CO/*CHO中间体及分子自身,同时直接稳定了中间体。SHAP分析识别出关键的电子描述符,包括较低的最小局域电子亲和能、较窄的HOMO-LUMO能隙以及较高的HOMO能量。这些描述符主导了电子海绵机制,从而促进了ΔG‡的降低。
作为一个代表性分子,从5,304个图论衍生化合物库中筛选出的3,4-二氨基呋喃唑,其分子结构整合了具有给电子和反馈电子能力的氨基以及呋喃-唑类基序。实验验证表明,C2+产物的法拉第效率提升了1.8倍(从42%增至77%),证实了该QSAR框架的有效性。这一描述符驱动的方法进一步扩展到金和银体系,为设计下一代电催化剂提供了可扩展的途径。
附:英文原文
Title: Discovering Electron-Sponge Behavior at Organic-Metal Interfaces for CO2 Electroreduction via Machine Learning
Author: Haochen Shen, Bin Jiang, Xiaodong Yang, Ningce Zhang, Hao Jiang, Shuxuan Liu, Luoming Kang, Luhong Zhang, Xiaoming Xao, Yongli Sun, Xiaowei Tantai, Guobin Wen, Na Yang, Bohua Ren, Shuangyin Wang
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-19
Abstract: Molecular regulation at organic-metal interfaces is crucial for C─C coupling in CO2 electroreduction, directly influencing the formation of multi-carbon (C2+) products. However, the non-linear interplay of electronic, spatial, and topological molecular descriptors has hindered the establishment of predictive quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR), limiting mechanistic insight. Herein, we employed an interpretable machine learning (ML)-QSAR framework to link molecular features with the C─C coupling free energy barrier (ΔG) on Cu surfaces, uncovering the dominant role of interfacial “electron-sponge” behavior. Mechanistically, the modifier molecule donates electrons to Cu, which subsequently redistributes them to *CO/*CHO intermediates and the molecule itself, while also directly stabilizing the intermediates. Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) analysis identifies key electronic descriptors, including low minimal local electron affinity (LEAmin), narrow HOMO-LUMO gap and elevated HOMO energy. These descriptors govern the electron-sponge mechanism, facilitating the reduction of ΔG. As a representative molecule, 3,4-diaminofurazan (DAF), selected from a library of 5,304 graph-theory-derived compounds, incorporates electron-donating and back-donating amino and furan-azole motifs. Experimental validation shows a 1.8-fold increase in C2+ Faradaic efficiency, from 42% to 77%, confirming the QSAR framework's effectiveness. This descriptor-driven approach was further extended to Au and Ag systems, providing a scalable pathway for designing next-generation electrocatalysts.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202525751
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202525751
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
