近日,中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所胡萍团队报道了外泌体-中性粒细胞纳米偶联剂阻断肿瘤转移。这一研究成果于2026年1月15日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
大多数恶性肿瘤患者的死亡源于癌细胞转移,其中肿瘤来源外泌体通过介导预转移微环境形成发挥关键作用——绝大多数肿瘤外泌体通过外周血液循环将细胞因子、核酸、脂质等肿瘤特异性生物分子运抵远端器官。因此,阻断肿瘤外泌体在血管系统中的迁移是一种极具前景的抗转移策略;然而现有治疗方案效果有限。
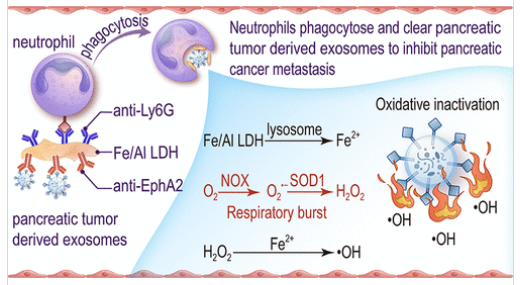
研究组提出一种外泌体-中性粒细胞结合策略:利用产生活性氧的纳米耦联器,通过中性粒细胞的内吞作用清除血管内外泌体。研究组以胰腺导管腺癌(因其高转移潜能)为范式,研究胰腺肿瘤来源外泌体的清除机制。具体而言,通过在铁铝层状双氢氧化物纳米片一侧修饰靶向中性粒细胞的Ly6G抗体,另一侧修饰靶向外泌体的EphA2抗体,构建出能将胰腺肿瘤外泌体锚定于中性粒细胞膜表面的纳米耦联系统。
该系统通过中性粒细胞的吞噬活性清除外周血中的肿瘤外泌体,同时借助铁铝层状双氢氧化物增强的中性粒细胞呼吸爆发效应,对胞内外泌体内的肿瘤特异性生物分子产生氧化损伤,最终抑制胰腺导管腺癌的转移。该研究针对肿瘤外泌体这一关键转移驱动因子提出创新清除策略,以胰腺癌为范式为侵袭性恶性肿瘤的转移阻断提供了具有临床转化潜力的新途径。
附:英文原文
Title: Cancer Metastasis Blockage by Exosome-Neutrophil Nanocoupler
Author: Yuedong Guo, Jianlin Shi, Ping Hu
Issue&Volume: January 15, 2026
Abstract: Most malignancy patients die of cancer cell metastasis, in which tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs) play a critical role by priming premetastatic niche formation, since most TDEs carry cancer-specific biomolecules such as cytokines, nucleic acids, and lipids through the peripheral blood to distant organs. Thus, blocking the TDEs' migration in the vascular system is an especially promising antimetastasis strategy; unfortunately, however, existing treatments have shown limited efficacy. In this study, we present an exosome-neutrophil binding strategy using a reactive oxygen species-producing nanocoupler to eliminate intravascular exosomes via neutrophil endocytosis. As a paradigm, we investigated the clearance of pancreatic tumor-derived exosomes (PTDEs) due to the high metastatic potential of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Specifically, a PTDEs-neutrophils nanocoupler has been obtained by asymmetrically modifying one side of an iron–aluminum layered double hydroxide (Fe/Al LDH) nanosheet with Ly6G antibody targeting neutrophils, and the opposite side with EphA2 antibody targeting PTDE, which binds PTDEs onto the membranes of neutrophils. Resultantly, PTDEs in peripheral blood can be eliminated through the phagocytic activity of neutrophils together with the oxidative damage against cancer-specific biomolecules within PTDEs by the Fe/Al LDH-enhanced neutrophil respiratory burst, ultimately inhibiting the metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. This study introduces a novel strategy for eliminating TDEs as key metastatic drivers, offering a promising approach for blocking metastasis in aggressive malignancies, with pancreatic cancer as the paradigm, with promising potential for clinical translation.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15070
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c15070
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
