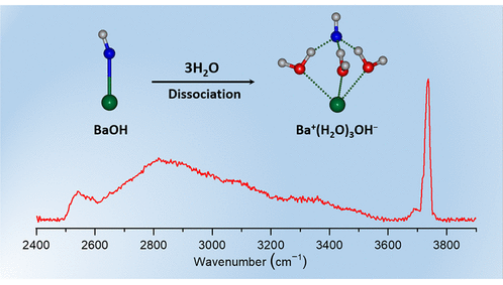
近日,中国科学院大连化学物理研究所李刚团队报道了水合BaOH的IR-VUV光电离光谱揭示生长水团中的碱解离。2026年1月13日出版的《美国化学会志》发表了这项成果。
研究碱在微水合环境中的解离过程对于揭示多种基础物理化学机制具有重要意义。
研究组结合量子化学计算与从头算分子动力学模拟,采用尺寸特异性红外-真空紫外光电离光谱技术对中性开壳层BaOH(H2O)n(n=1–5)团簇进行了表征。结果表明,当n=1和2时Ba–OH键未发生解离;从n=3开始,体系自发出现由接触离子对向溶剂共享离子对的转变。研究结果澄清了先前关于BaOH在n=5时仍无明显解离迹象的争议,揭示了碱溶解过程的微观机制,为相关体系的更广泛应用奠定了坚实基础。
附:英文原文
Title: IR-VUV Photoionization Spectra of Hydrated BaOH Reveal Base Dissociation in Growing Water Clusters
Author: Wenhui Yan, Shuai Jiang, Shangdong Li, Jianxing Zhuang, Ailin Wang, Hua Xie, Gang Li, Ling Jiang
Issue&Volume: January 13, 2026
Abstract: Investigating the dissociation of base in a microhydration environment is important for revealing various fundamental physical and chemical processes. In this study, neutral open-shell BaOH(H2O)n (n = 1–5) clusters were characterized by size-specific infrared-vacuum ultraviolet photoionization spectroscopy combined with quantum chemical calculations and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. The results show that the Ba–OH bond is undissociated for n = 1 and 2, and the transition from contact ion pair (CIP) to solvent-shared ion pair (SIP) spontaneously starts at n = 3. The present findings clarify the previous debate that BaOH shows no sign of dissociation even at n = 5. This work reveals the microscopic mechanisms of base dissolution processes and lays a solid foundation for broader application across systems.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15032
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c15032
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
