乔治敦大学Samir N. Khleif课题组取得一项新突破。他们的研究认为PARP抑制通过转录和代谢重编程产生增强的CD8+中枢记忆T细胞。相关论文发表在2026年1月12日出版的《自然—免疫学》杂志上。
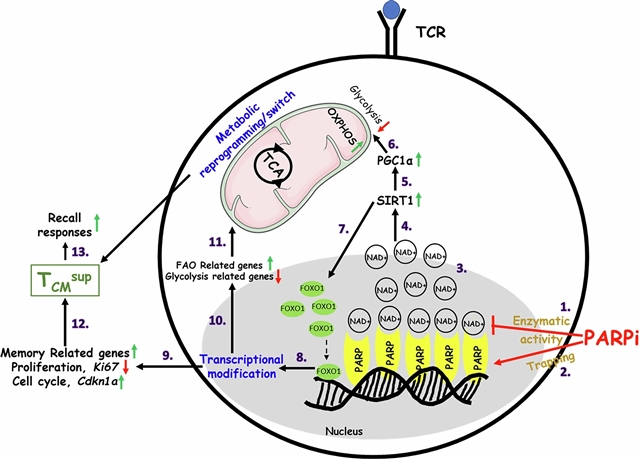
本研究表明,聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶(PARP)抑制通过激活SIRT-1-FOXO1途径,通过抑制酶活性和增强PARP捕获诱导代谢和转录开关,诱导CD8+ TCM细胞具有优越的记忆能力。总之,这导致细胞周期的抑制和记忆和脂肪酸氧化基因表达的上调,并将CD8+ T细胞重编程为具有增强代谢适应性和更高回忆能力的TCM细胞。PARP抑制剂治疗荷瘤小鼠导致肿瘤微环境中“高级中药”细胞数量增加,免疫介导的抗肿瘤反应增强。PARP抑制剂处理的CD8+ T细胞在过继细胞治疗中更有效。
此外,在接受PARP抑制剂治疗的癌症患者中,CD8+记忆T细胞的频率及其记忆标记物的表达增加。总之,这些数据表明PARP抑制直接重编程CD8+ T细胞,增强代谢适应性并产生高效的治疗性优越的记忆细胞。
据介绍,CD8+中枢记忆T (TCM)细胞比分化程度更高的效应记忆细胞提供更强的抗肿瘤免疫。
附:英文原文
Title: PARP inhibition generates enhanced CD8+ central memory T cells by transcriptional and metabolic reprogramming
Author: Traboulsi, Wael, Gaur, Pankaj, Kundu, Subhadip, Ramlaoui, Zainab, Priestley-Milianta, Christopher, Iyengar, Aishwariya, Shobaki, Nour, Sarhan, Dareen, Lee, Min-Jung, Lee, Jung-Min, Pavlakis, George N., Mkrtichyan, Mikayel, Valge-Archer, Viia E., Barry, Simon T., Verma, Vivek, Gupta, Seema, Khleif, Samir N.
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-12
Abstract: CD8+ central memory T (TCM) cells provide stronger antitumor immunity than more-differentiated effector memory counterparts. Here we show that poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibition induces CD8+ TCM cells with superior memory by activating the SIRT-1–FOXO1 pathway and inducing metabolic and transcriptional switches through inhibition of enzymatic activity and enhanced PARP trapping. Together, this results in suppression of the cell cycle and upregulation of memory and fatty acid oxidation gene expression, and reprogramming CD8+ T cells into TCM cells with enhanced metabolic fitness and substantially higher recall capabilities. PARP inhibitor treatment of tumor-bearing mice resulted in an increase in the number of ‘superior TCM’ cells within the tumor microenvironment and enhanced immune-mediated antitumor responses. PARP inhibitor-treated CD8+ T cells were more effective in adoptive cell therapy. Furthermore, the frequency of CD8+ memory T cells and the expression of their memory markers was increased in patients with cancer treated with PARP inhibitor. Together, these data show that PARP inhibition directly reprograms CD8+ T cells, enhancing metabolic fitness and generating highly effective therapeutically superior memory cells.
DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02383-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-025-02383-5
Nature Immunology:《自然—免疫学》,创刊于2000年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:31.25
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ni/
投稿链接:https://mts-ni.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
