近日,德国多特蒙德马克斯·普朗克分子生理学研究所Herbert Waldmann团队研究了单价假天然产物通过其天然E3 KLHDC3增强IDO1的降解。这一研究成果于2026年1月7日发表在《自然-化学》杂志上。
靶向蛋白降解除了抑制酶活性或蛋白-蛋白相互作用外,还能调节蛋白功能。大多数降解药物通过直接介导新底物与被劫持的E3连接酶之间的接近来发挥作用。
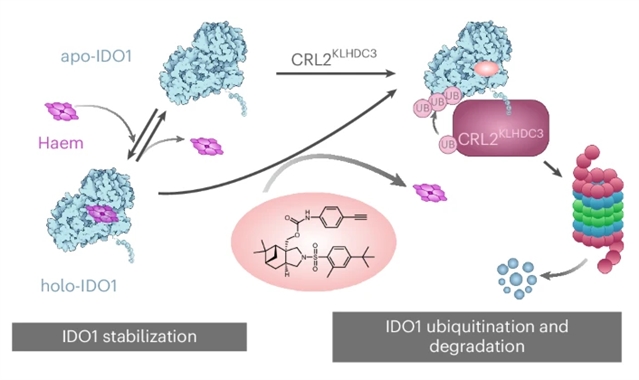
研究组鉴定了源自(-)-桃金娘醇的伪天然产物,称为iDegs,它们通过一种独特的机制抑制并诱导免疫调节酶吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶1(IDO1)的降解。iDegs通过cullin-RING E3连接酶CRL2KLHDC3促进IDO1的泛素化和降解,研究组确定该酶天然介导IDO1的泛素介导降解。因此,iDegs利用天然的蛋白水解途径增加IDO1的周转。与临床探索的IDO1抑制剂不同,iDegs通过抑制和诱导酶降解来减少犬尿氨酸的形成,从而也调节IDO1的非酶功能。这种独特的作用机制可能为癌症治疗开辟了除经典IDO1抑制之外的替代治疗机会。
附:英文原文
Title: Monovalent pseudo-natural products supercharge degradation of IDO1 by its native E3 KLHDC3
Author: Hennes, Elisabeth, Lucas, Beln, Scholes, Natalie S., Cheng, Xiu-Fen, Scott, Daniel C., Bischoff, Matthias, Reich, Katharina, Gasper, Raphael, Lucas, Mara, Xu, Teng Teng, Rossini, Sofia, Pulvermacher, Lisa-Marie, Dtsch, Lara, Imrichova, Hana, Brause, Alexandra, Fhrer, Siska, Naredla, Kesava Reddy, Sievers, Sonja, Kumar, Kamal, Janning, Petra, Orabona, Ciriana, Gersch, Malte, Murray, Peter J., Schulman, Brenda A., Winter, Georg E., Ziegler, Slava, Waldmann, Herbert
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-07
Abstract: Targeted protein degradation modulates protein function beyond the inhibition of enzyme activity or protein–protein interactions. Most degrader drugs function by directly mediating the proximity between a neosubstrate and a hijacked E3 ligase. Here we identify pseudo-natural products derived from ()-myrtanol, termed iDegs, that inhibit and induce degradation of the immunomodulatory enzyme indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) by a distinct mechanism. iDegs boost IDO1 ubiquitination and degradation by the cullin-RING E3 ligase CRL2KLHDC3, which we identified to natively mediate ubiquitin-mediated degradation of IDO1. Therefore, iDegs increase IDO1 turnover using the native proteolytic pathway. In contrast to clinically explored IDO1 inhibitors, iDegs reduce the formation of kynurenine by both inhibition and induced degradation of the enzyme and thus also modulate the non-enzymatic functions of IDO1. This unique mechanism of action may open up alternative therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of cancer beyond classical inhibition of IDO1.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02021-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-02021-5
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
