近日,新加坡南洋理工大学Ling, Tong团队报道了视网膜造影显示视紫红质激活后杆状光感受器快速运动。2026年1月7日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志发表了这项成果。
视杆细胞在昏暗光线下对视觉至关重要,但在视网膜退行性疾病中极易受损。
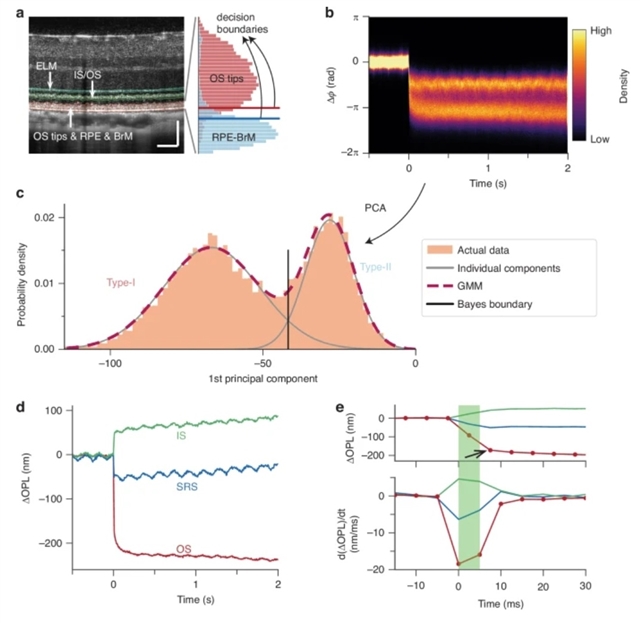
研究组证明人类和啮齿动物的视杆细胞在光异构化(光传导的第一步)时,其外节会发生微小而迅速的收缩。这种收缩被解释为视盘膜中产生的视杆细胞早期受体电位的一种电机械表现,而这种电位在电生理学中难以获取。通过超高分辨率点扫描光学相干断层扫描(OCT)系统,并结合无监督学习方法,将视杆细胞外节顶端的光诱发反应与视网膜色素上皮-布鲁赫膜复合体分开,从而实现了对啮齿动物视杆细胞中光诱发电活动的体内光学成像。
在人类中,自适应光学线扫描OCT有助于高速记录视杆细胞的活动。视紫红质激活的非侵入性体内光学成像扩展了视网膜光成像的诊断能力,并可能有助于对遗传性和年龄相关性黄斑变性中的视杆细胞功能障碍和视觉循环受损进行个性化、客观评估。
附:英文原文
Title: Optoretinography reveals rapid rod photoreceptor movement upon rhodopsin activation
Author: Li, Huakun, Weiss, Connor E., Pandiyan, Vimal Prabhu, Nanni, Davide, Liu, Teng, Kung, Pei Wen, Tan, Bingyao, Barathi, Veluchamy Amutha, Schmetterer, Leopold, Sabesan, Ramkumar, Ling, Tong
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-07
Abstract: Rod photoreceptors are essential for vision under dim light conditions and are highly vulnerable in retinal degenerative diseases. Here, we demonstrate that both human and rodent rods undergo a minute and rapid contraction of their outer segments upon photoisomerization, the first step of phototransduction. The contraction is explained as an electromechanical manifestation of the rod early receptor potential generated in the disk membranes, which is challenging to access in electrophysiology. The in vivo optical imaging of light-evoked electrical activity in rodent rods was facilitated by an ultrahigh-resolution point-scan optical coherence tomography (OCT) system, combined with an unsupervised learning approach to separate the light-evoked response of the rod outer segment tips from the retinal pigment epithelium-Bruch’s membrane complex. In humans, an adaptive optics line-scan OCT facilitated high-speed recordings in rods. The non-invasive in vivo optical imaging of rhodopsin activation extends the diagnostic capability of optoretinography, and may facilitate personalized, objective assessment of rod dysfunction and visual cycle impairment in inherited and age-related macular degeneration.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-02149-6
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-02149-6
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
