近日,中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所李驰麟团队报道了调节电解液的化学硬度以实现高压可逆氟离子电池的柔软性平衡。2025年9月2日出版的《德国应用化学》杂志发表了这项成果。
氟离子电池作为一种极具发展前景的下一代高能量密度储能技术,受到了广泛的关注。然而,开发一种理想的氟离子电解质,抑制β-H的提取 (由强路易斯碱度F电解液的分解)仍然具有挑战性。
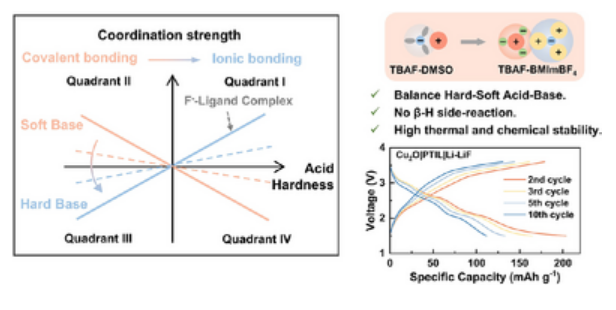
为了解决这一瓶颈,研究组设计了一种基于商用四丁基氟化铵(TBAF)盐和1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑四氟硼酸盐(BMImBF4)离子液体溶剂的电解质体系,通过阴离子-阳离子配位工程和硬-软酸碱(HSAB)平衡调制,揭示了其减轻界面寄生反应和提高金属阳极稳定性的多尺度机制。实验与理论分析表明,软酸 BMIm+会参与硬碱氟离子的溶剂化结构,有效阻断 β-H 消除路径,并将电化学窗口拓宽至 4.5 V。
这种基于离子液体的电解质即便在原位聚合后,60 °C 时的离子电导率仍可达 5.0×10-3 S cm-1。耦合了嵌入与转化反应的 Cu2O 正极能够缓解 Cu2O||Li–LiF 高压氟离子电池的体积形变与容量衰减,该电池具有 2.91 V 的高静置电压和 589.9 mAh g-1 的高初始容量。Cu2O||Pb–PbF2氟离子电池在 200 mA g-1 的电流密度下循环 800 次后,仍能保持 243.6 mAh g-1的高可逆容量。该研究为高压可逆氟离子电池建立了一种全新的电解质设计范式。
附:英文原文
Title: Adjusting Chemical Hardness–Softness Balance of Electrolyte to Enable High-Voltage Reversible Fluoride Ion Batteries
Author: Guyue Li, Huiyan Zha, Decheng Li, Meng Lei, Xiuting Wu, Chilin Li
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-02
Abstract: Fluoride ion batteries (FIBs), as a promising next-generation high-energy-density storage technology, have attracted significant attention. However, developing an ideal fluoride-ion electrolyte that suppresses the β-H abstraction (caused by strong Lewis-basicity F) and electrolyte decomposition remains challenging. To address this bottleneck, we design an electrolyte system based on commercial tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) salt and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BMImBF4) ionic liquid solvent through anion–cation coordination engineering and hard–soft-acid–base (HSAB) balance modulation, unveiling its multiscale mechanisms for mitigating interfacial parasitic reaction and enhancing metal anode stability. Experimental and theoretical analyses reveal that the soft-acid BMIm participates in the solvation structure of hard-base fluoride ions, effectively blocking the β-H elimination pathway and expanding the electrochemical window to 4.5 V. The ionic conductivity of this ionic liquid based electrolyte reaches 5.0 × 103 S cm1 at 60 °C even after in situ polymerization. The Cu2O cathode coupling insertion and conversion reactions can alleviate the volume deformation and capacity decay of Cu2O||Li–LiF high-voltage FIBs, with a high resting voltage (2.91 V) and a high initial capacity of 589.9 mAh g1. The Cu2O||Pb–PbF2 FIBs maintain a high reversible capacity of 243.6 mAh g1 even after 800 cycles under 200 mA g1. The work establishes a novel electrolyte design paradigm for high-voltage reversible FIBs.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202512401
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202512401
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
