杏仁核-肝脏信号协调应激下的血糖反应,这一成果由美国西奈山伊坎医学院S. A. Stanley研究团队经过不懈努力而取得。相关论文于2025年9月3日发表在《自然》杂志上。
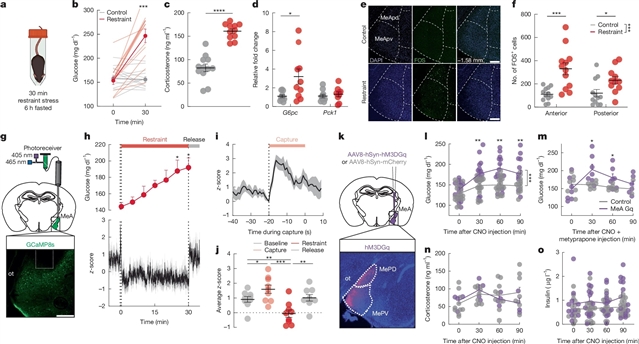
在这里,该团队发现急性应激激活内侧杏仁核(MeA)神经元,这些神经元支配下丘脑腹内侧(MeAVMH)神经元,从而导致高血糖和吞咽不足。MeAVMH神经元的降糖作用独立于肾上腺或胰腺糖调节激素。通过全身病毒追踪,课题组研究人员确定了MeA与肝脏之间的多突触连接,通过肝脏糖异生促进葡萄糖的快速合成。反复的应激暴露会破坏MeA对血糖的控制,导致类似糖尿病的葡萄糖稳态失调。他们的发现揭示了杏仁核-肝脏轴调节对压力的快速血糖适应,并将反复出现的压力与代谢功能障碍联系起来。
据介绍,对环境威胁的行为适应对生存至关重要,并且需要快速部署能源储备。杏仁核协调对威胁的行为适应,但对它在代谢适应中的作用知之甚少。
附:英文原文
Title: Amygdala–liver signalling orchestrates glycaemic responses to stress
Author: Carty, J. R. E., Devarakonda, K., OConnor, R. M., Krek, A., Espinoza, D., Jimenez-Gonzalez, M., Alvarsson, A., Hampton, R. F., Li, R., Qiu, Y., Petri, S., Shtekler, A., Rajbhandari, A., Conner, K., Bayne, M., Garibay, D., Martin, J., Lehmann, V., Wang, L., Beaumont, K., Kurland, I., Yuan, G. C., Kenny, P. J., Stanley, S. A.
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-03
Abstract: Behavioural adaptations to environmental threats are crucial for survival1,2 and necessitate rapid deployment of energy reserves3,4,5. The amygdala coordinates behavioural adaptations to threats6, but little is known about its involvement in underpinning metabolic adaptations. Here we show that acute stress activates medial amygdala (MeA) neurons that innervate the ventromedial hypothalamus (MeAVMH neurons), which precipitates hyperglycaemia and hypophagia. The glycaemic actions of MeAVMH neurons occur independently of adrenal or pancreatic glucoregulatory hormones. Using whole-body virus tracing, we identify a polysynaptic connection from MeA to the liver that promotes the rapid synthesis of glucose by hepatic gluconeogenesis. Repeated stress exposure disrupts MeA control of blood glucose, resulting in diabetes-like dysregulation of glucose homeostasis. Our findings reveal an amygdala–liver axis that regulates rapid glycaemic adaptations to stress and links recurrent stress to metabolic dysfunction.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09420-1
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09420-1
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
