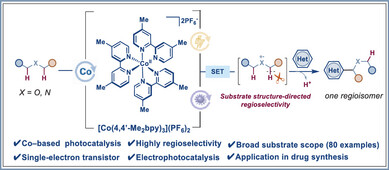
近日,浙江工业大学李坚军团队报道了钴多吡啶通过光电催化实现含N,O脂肪族化合物的高区域选择性α-杂芳基化。2025年9月1日出版的《德国应用化学》杂志发表了这项成果。
在几乎相同的化学环境中,C─H键的区域选择性功能化仍然是合成化学中的一个关键挑战。虽然传统的氢原子转移(HAT)策略主导了当前的方法,但它们在选择性上的局限性推动了对替代机制的追求。
研究组报道了一个由聚吡啶基钴催化剂介导的光电化学协同催化系统,使醚、醇和酰胺的α-杂芳化具有高度的区域选择性。与之前的钴基系统不同,在这些系统中,键的形成独立于钴金属中心,催化剂的功能是作为光催化剂,通过单电子转移(SET)过程直接氧化底物。该策略避开了传统的HAT途径,对大多数底物实现了极佳的α-位点选择性,同时表现出对不同杂芳烃的广泛适应性。随后的衍生化研究,包括氧化、水解、还原和氯甲基化,验证了获取医药中间体的合成实用性。
附:英文原文
Title: Cobalt Polypyridyl-Enabled Highly Regioselective α-Heteroarylation of N,O-Containing Aliphatics Through Photoelectrocatalysis
Author: Wen Lin, Ting Lv, Zhizi Wang, Jintong Xie, Jie Sun, Wenjian Wang, Chaodong Wang, Jianjun Li
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-01
Abstract: The regioselective functionalization of C─H bonds at positions with nearly identical chemical environments remains a pivotal challenge in synthetic chemistry. While conventional hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) strategies dominate current methodologies, their limitations in selectivity drive the pursuit of alternative mechanisms. Here, we report a photoelectrochemically cooperative catalytic system mediated by a polypyridyl cobalt catalyst, enabling highly regioselective α-heteroarylation of ethers, alcohols, and amides. Unlike previous cobalt-based systems in which bond formation occurs independently of the cobalt metal center, the catalyst functions as a photocatalyst to directly oxidize substrates via a single-electron transfer (SET) process. This strategy eschews traditional HAT pathways, achieving exclusive α-site selectivity for most substrates while exhibiting broad adaptability to diverse heteroarenes. Subsequent derivatization studies, including oxidation, hydrolysis, reduction, and chloromethylation, validate the synthetic utility for accessing pharmaceutical intermediates.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202515935
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202515935
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
