研究利用天然自上而下的质谱技术揭示隐藏的蛋白质修饰,这一成果由牛津大学Carol V. Robinson团队经过不懈努力而取得。相关论文于2025年9月29日发表于国际顶尖学术期刊《自然—方法学》杂志上。
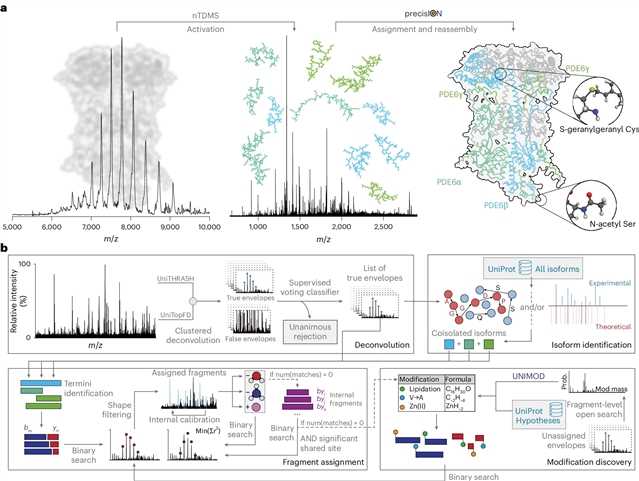
为了解决这一差距,研究人员引入了精确和准确的原生蛋白质形态识别(precisION),这是一个交互式的端到端软件包,利用强大的、数据驱动的片段级开放搜索来检测、定位和量化完整蛋白质复合物中的“隐藏”修饰。应用precisION分析它们的治疗相关靶点-PDE6、 ACE2、骨桥蛋白(SPP1)和GABA转运蛋白(GAT1) -研究团队发现了未记录的磷酸化,糖基化和脂化,并在GAT1的电子冷冻显微镜图中解决了以前无法解释的密度。作为一个开放式的软件包,precisION提供了一种直观的方法来解释复杂的蛋白质碎片数据。该工具将使社区能够释放天然自上而下质谱法的潜力,推进综合结构生物学,分子病理学和药物开发。
据悉,蛋白质修饰通过调节生物分子相互作用驱动动态细胞过程,然而在其天然结构背景下捕获这些修饰仍然是一个重大挑战。原生自顶向下质谱法有望保留修饰和相互作用之间的关键联系。然而,目前的方法往往无法检测到未表征或低丰度的修饰,从而限制了对蛋白质种类多样性的了解。
附:英文原文
Title: Uncovering hidden protein modifications with native top-down mass spectrometry
Author: Bennett, Jack L., El-Baba, Tarick J., Zouboulis, Konstantin C., Kirschbaum, Carla, Song, Haigang, Butroid, Frances I., Benesch, Justin L. P., Lutomski, Corinne A., Robinson, Carol V.
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-29
Abstract: Protein modifications drive dynamic cellular processes by modulating biomolecular interactions, yet capturing these modifications within their native structural context remains a significant challenge. Native top-down mass spectrometry promises to preserve the critical link between modifications and interactions. However, current methods often fail to detect uncharacterized or low-abundance modifications, limiting insights into proteoform diversity. To address this gap, we introduce precise and accurate Identification Of Native proteoforms (precisION), an interactive end-to-end software package that leverages a robust, data-driven fragment-level open search to detect, localize and quantify ‘hidden’ modifications within intact protein complexes. Applying precisION to four therapeutically relevant targets—PDE6, ACE2, osteopontin (SPP1) and a GABA transporter (GAT1)—we discover undocumented phosphorylation, glycosylation and lipidation, and resolve previously uninterpretable density in an electron cryo-microscopy map of GAT1. As an open-source software package, precisION offers an intuitive means for interpreting complex protein fragmentation data. This tool will empower the community to unlock the potential of native top-down mass spectrometry, advancing integrative structural biology, molecular pathology and drug development.
DOI: 10.1038/s41592-025-02846-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02846-5
Nature Methods:《自然—方法学》,创刊于2004年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:47.99
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nmeth/
投稿链接:https://mts-nmeth.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
