近日,华中科技大学董建绩团队研究了扩展端到端片上光子神经的网络推理。这一研究成果于2025年9月17日发表在《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
光神经网络在带宽和能源效率方面具有明显的优势,正在成为电子网络的竞争替代品。尽管有这些好处,扩展端到端推理的片上光学神经网络仍面临着重大挑战。首先,网络深度受到光学非线性激活函数的弱级联性的限制。其次,输入尺寸受光学矩阵尺度的限制。
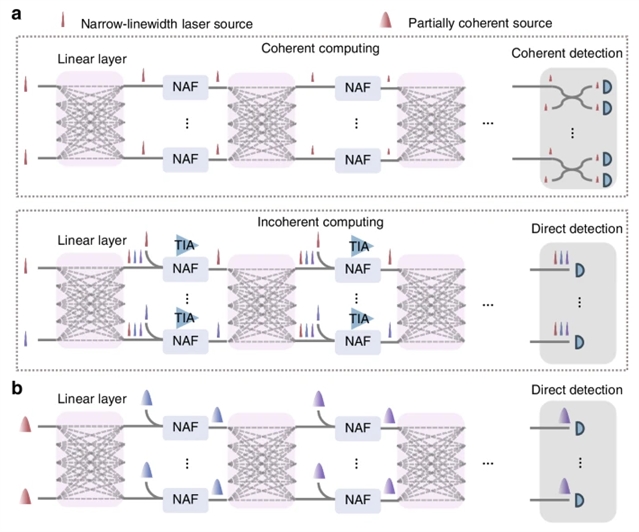
研究组提出了一种称为部分相干深度光神经网络(PDONNs)的扩展策略。通过利用基于光电转换的片上非线性激活函数,PDONN使网络深度扩展具有正净增益。此外,卷积层实现了快速降维,从而允许增加可容纳的输入大小。部分相干光强度的应用大大减少了对窄线宽激光二极管和相干检测的依赖。由于其更广泛的频谱特性和更简单的实现,这些特性更易于访问和兼容可扩展集成。
得益于这些创新,研究组设计并制造了一个具有最大输入尺寸和最深网络深度的单片集成光学神经网络,包括大小为64的输入层,两个卷积层和两个完全连接层。他们成功地演示了端到端流行图像的两类分类和手写体数字的四类分类,准确率分别为96%和94%。值得注意的是,在部分相干照明下,性能保持得很好。该体系结构是实现节能、可扩展和可广泛访问的光学计算的关键一步。
附:英文原文
Title: Scaling up for end-to-end on-chip photonic neural network inference
Author: Wu, Bo, Huang, Chaoran, Zhang, Jialong, Zhou, Hailong, Wang, Yilun, Dong, Jianji, Zhang, Xinliang
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-17
Abstract: Optical neural networks are emerging as a competitive alternative to their electronic counterparts, offering distinct advantages in bandwidth and energy efficiency. Despite these benefits, scaling up on-chip optical neural networks for end-to-end inference is facing significant challenges. First, network depth is constrained by the weak cascadability of optical nonlinear activation functions. Second, the input size is constrained by the scale of the optical matrix. Herein, we propose a scaling up strategy called partially coherent deep optical neural networks (PDONNs). By leveraging an on-chip nonlinear activation function based on opto-electro-opto conversion, PDONN enables network depth expansion with positive net gain. Additionally, convolutional layers achieve rapid dimensionality reduction, thereby allowing for an increase in the accommodated input size. The use of a partially coherent optical source significantly reduces reliance on narrow-linewidth laser diodes and coherent detection. Owing to their broader spectral characteristics and simpler implementation, such sources are more accessible and compatible with scalable integration. Benefiting from these innovations, we designed and fabricated a monolithically integrated optical neural network with the largest input size and the deepest network depth, comprising an input layer with a size of 64, two convolutional layers, and two fully connected layers. We successfully demonstrate end-to-end two-class classification of fashion images and four-class classification of handwritten digits with accuracies of 96% and 94%, respectively, using an in-situ training method. Notably, performance is well maintained with partially coherent illumination. This proposed architecture represents a critical step toward realizing energy-efficient, scalable, and widely accessible optical computing.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-02029-z
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-02029-z
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
