近日,中国科学院物理研究所杜世萱团队研究了精确区分异构体和表面非常相似分子的两阶段机器学习框架。这一研究成果于2025年9月18日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
准确检测和识别表面有机异构体和非常相似的分子对于监测化学反应过程和分析各种反应机理和分子性质至关重要。尽管它很重要,但纳米和表面科学界仍然缺乏一种高效、机械、精确和自动化的表面异构体和高度相似分子的检测方法。
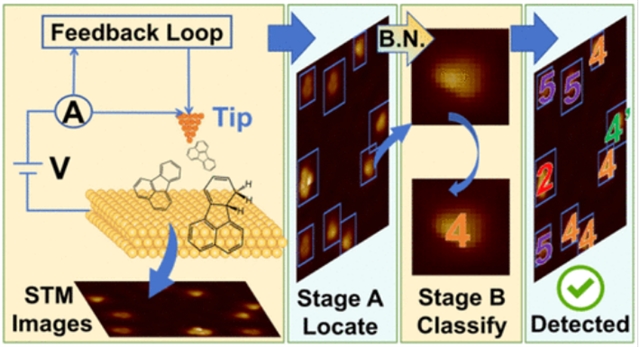
研究组提出了ReSTOLO,一个基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的框架,用于精确检测和识别表面上多种稀疏分布的分子,特别设计用于扫描隧道显微镜(STM)图像,其中包含许多具有模拟分子特征的分子。为应对分子形状与尺寸相似性带来的挑战,研究组采用了包含两个卷积神经网络模型的双阶段框架:YOLO v5.m用于分子定位,ResNet-101则负责分类任务。
该框架通过应用框规范化连接,最佳地利用了这两种模型的优点。研究组通过将其应用于分析涉及六个具有几乎相同STM特征的分子的表面反应过程来证明该框架的有效性。训练过程采用单分子STM图像数据库,外加物理和实验工具构建应用标准化图像盒。与传统框架相比,这种两阶段方法在性能指标上实现了大约20%的改进,包括精度、召回率和准确性。在复杂的表面反应中,该框架具有自动、有效地精确定位和区分具有相似构型的分子种类的能力。这种自动分子鉴别器在促进STM尖端操纵的表面化学反应方面取得了重大进展。
附:英文原文
Title: Two-Stage Machine Learning Framework for Accurate Discrimination of Isomers and Very-Similar Molecules on Surfaces
Author: Zixuan Wei, Qigang Zhong, Jinbo Pan, Fang Han Lim, Lifeng Chi, Shixuan Du
Issue&Volume: September 18, 2025
Abstract: The accurate detection and discrimination of on-surface organic isomers and very similar molecules are crucial for monitoring chemical reaction processes and analyzing various reaction mechanisms and molecular properties. Despite its importance, nano- and surface science communities still lack an efficient, robust, precise, and automated detection approach for on-surface isomers and highly similar molecules. Here, we present ReSTOLO, a convolution neural network (CNN)-based framework for precise detection and identification of multiple types of sparsely distributed molecules on surfaces, particularly designed for scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) images containing numerous molecules with analogous features. To address challenges arising from molecular shape and size similarities, we implemented a two-stage framework comprising two CNN models: YOLO v5.m was used for molecular localization, and ResNet-101 for classification. The framework optimally harnesses the advantages of both models by applying a box normalization connection. We demonstrated the framework’s effectiveness by applying it to analyze a surface reaction process involving six molecules with nearly identical STM signatures. The training process employed an STM image database of single molecules augmented with physical and experimental tools constructed using standardized image boxes. This two-stage approach achieved approximately ~20% improvements in performance metrics, including precision, recall, and accuracy, compared to conventional frameworks. The framework exhibits robust capabilities in automatically and efficiently pinpointing and discriminating between molecular species with similar configurations in complex surface reactions. This automated molecular discriminator represents a significant advance in facilitating STM tip-manipulated chemical reactions on surfaces.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03730
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c03730
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
