近日,北京理工大学黄佳琦团队研究了锂硫电池中锂金属阳极的电偶腐蚀。该研究于2025年9月16日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
锂硫(Li–S)电池因其超高的理论能量密度而成为下一代可充电电池。然而,它们的循环寿命受到锂金属阳极稳定性差的阻碍。主要的挑战在于锂金属阳极上严重的锂多硫化物腐蚀。
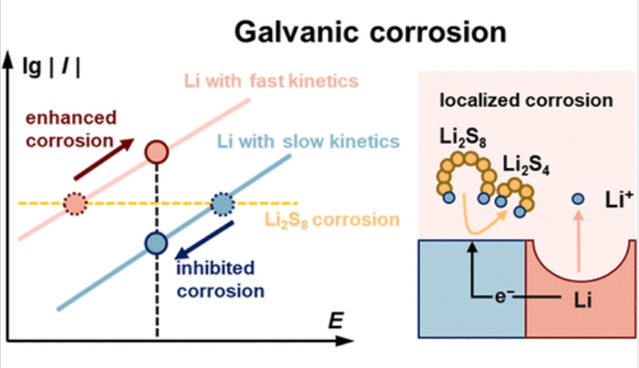
研究组认为,LiPSs引起的电偶腐蚀是Li–S电池工作过程中锂离子沉积和溶解不均匀的主要原因。具体而言,根据腐蚀动力学,LiPSs不断腐蚀锂金属阳极,从而不同程度地增加其电极电位。具有不同腐蚀动力学的锂金属的电连接引起电偶腐蚀,并导致在严重腐蚀部位选择性沉积锂。因此,空间异质性的锂离子电池腐蚀最终导致局部锂离子利用,锂离子分布不均匀,加速电池失效。为了减轻电偶腐蚀,预先构建了富含氟化锂的固体电解质界面,以钝化锂金属,抑制LiPS腐蚀,并将Li–S电池在恶劣工作条件下的循环寿命延长57%。这项工作确定了电偶腐蚀机制下不均匀锂沉积的化学性质,并强调了钝化锂金属阳极对实现长循环锂电池的重要性。
附:英文原文
Title: Galvanic Corrosion of Lithium Metal Anodes in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
Author: Chen-Xi Bi, Yu-Jie Zhu, Xi-Yao Li, Jin Ma, Xue-Qiang Zhang, Meng Zhao, Bo-Quan Li, Jia-Qi Huang
Issue&Volume: September 16, 2025
Abstract: Lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries are promising next-generation rechargeable batteries due to their ultrahigh theoretical energy density. However, their cycling lifespan is hindered by the poor stability of Li metal anodes. The main challenge lies in the severe Li polysulfide (LiPS) corrosion on Li metal anodes. Herein, galvanic corrosion induced by LiPSs is identified as the main cause of nonuniform Li deposition and dissolution in working Li–S batteries. Concretely, LiPSs continuously corrode the Li metal anode and thereby increase its electrode potential to different extents according to the corrosion kinetics. The electrical connection of the Li metals with different corrosion kinetics causes galvanic corrosion and consequent selective Li deposition in severely corroded locations. Consequently, spatially heterogeneous LiPS corrosion eventually induces localized Li utilization, uneven Li distribution, and accelerated cell failure. To alleviate the galvanic corrosion, a Li fluoride-rich solid electrolyte interphase is preconstructed to passivate Li metal, suppress LiPS corrosion, and extend the cycling lifespan of Li–S batteries by 57% under harsh working conditions. This work identifies the chemical nature of nonuniform Li deposition following the galvanic corrosion mechanism and highlights the importance of passivating Li metal anodes to realize long-cycling Li–S batteries.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09705
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c09705
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
