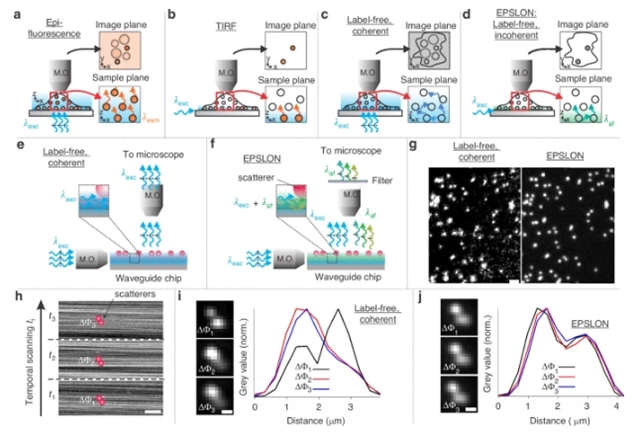
近日,挪威北极大学Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh团队开发出基于芯片的无标签非相干超分辨率光学显微镜。2025年8月4日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志发表了这项成果。
荧光分子的光动力学使其能够绕过远场衍射极限。尽管其潜力巨大,但标记样品的必要性可能会对正在调查的微妙生物学产生不利影响。因此,需要持续的开发努力来超越远场无标签衍射势垒。样品在无标记模式下散射光的统计相似性或有限相干性阻碍了现有基于非相干荧光成像的超分辨率方法的应用。
研究组介绍了一种物理学策略,通过利用氮化硅波导的光致发光(PL)对未标记样品进行近场照明来规避这一挑战。该技术缩写为EPSLON,即倏逝衰减光致发光散射技术,可实现无标签光学纳米显微镜。研究组证明,这种照明具有模拟纳米级荧光分子的光动力学特性,即,这种照明允许来自样品平面上不同位置的散射场之间的不相干。因此,该照明方案能够开发出一种远场无标签非相干成像系统,该系统强度呈线性且随时间稳定,从而允许在无标签模式下应用结构照明显微镜(SIM)和基于强度波动的光学纳米镜(IFON)等技术,以绕过衍射极限。
在这个概念验证工作中,研究组观察到SIM180在不同的生物样品上,用它们的河环相关(FRC)定量主题化,在超分辨纳米球上的分辨率提高了1.9× ~ 2.8×。研究组相信EPSLON是在非相干远场无标记超分辨率显微镜领域向前迈出的一步,它是研究生物系统在自然状态下不需要外源标记的关键。
附:英文原文
Title: Chip-based label-free incoherent super-resolution optical microscopy
Author: Jayakumar, Nikhil, Villegas-Hernndez, Luis E., Zhao, Weisong, Mao, Hong, Dullo, Firehun T., Tinguely, Jean-Claude, Sagini, Krizia, Llorente, Alicia, Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-04
Abstract: The photo-kinetics of fluorescent molecules have enabled the circumvention of the far-field optical diffraction limit. Despite its enormous potential, the necessity to label the sample may adversely influence the delicate biology under investigation. Thus, continued development efforts are needed to surpass the far-field label-free diffraction barrier. The statistical similarity or finite coherence of the scattered light off the sample in label-free mode hinders the application of existing super-resolution methods based on incoherent fluorescence imaging. In this article, we present physics and propose a methodology to circumvent this challenge by exploiting the photoluminescence (PL) of silicon nitride waveguides for near-field illumination of unlabeled samples. The technique is abbreviated EPSLON, Evanescently decaying Photoluminescence Scattering enables Label-free Optical Nanoscopy. We demonstrate that such an illumination has properties that mimic the photo-kinetics of nano-sized fluorescent molecules, i.e., such an illumination permits incoherence between the scattered fields from various locations on the sample plane. Thus, the illumination scheme enables the development of a far-field label-free incoherent imaging system that is linear in intensity and stable over time, thereby permitting the application of techniques like structured illumination microscopy (SIM) and intensity-fluctuation-based optical nanoscopy (IFON) in label-free mode to circumvent the diffraction limit. In this proof-of-concept work, we observed a two-point resolution of sim180nm on super-resolved nanobeads and resolution improvements between 1.9× to 2.8× over the diffraction limit, as quantified using Fourier Ring Correlation (FRC), on various biological samples. We believe EPSLON is a step forward within the field of incoherent far-field label-free super-resolution microscopy that holds a key to investigating biological systems in their natural state without the need for exogenous labels.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01914-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01914-x
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
