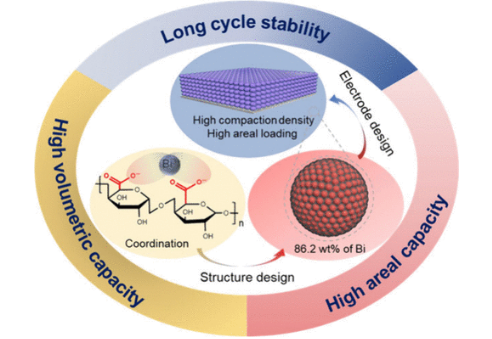
钠离子电池(SIB)是锂离子电池(LIB)在可持续能源存储方面的有前途的替代品,但其在紧凑型应用中的应用受到低体积能量密度(VED)或相对较差的结构不稳定性的阻碍。
研究组提出了一种nano-Bi@hard碳(nano-Bi@HC)复合材料,其特点是将均匀分散的Bi纳米颗粒(6-18 nm)密集排列的微球嵌入硬碳基体中,实现了385 Wh - 1的显著VED,具有出色的循环稳定性(在4000次循环中保持97%)。利用果胶的羧基官能团,Bi3+离子均匀配位,使炭化过程中铋含量高(86.2 wt %)而不团聚。nano-Bi@HC阳极在高面负载(12.3 mg cm-2)和压实密度(4.8 g cm-3)下具有无与伦比的1950 mAh cm-3的体积容量。
与Na3V(PO4)3阴极配对,整个电池在温度范围内表现出优异的性能,突出了其实用潜力。该研究建立了一种可扩展的策略,用于设计高VED和耐用的合金基阳极,弥合了SIB技术的关键空白。
附:英文原文
Title: Nano-Bi@Hard Carbon Composite Anode for Sodium-Ion Batteries with 385 Wh L–1 Volumetric Energy Density and Durability
Author: Zhiyu Lu, Haolei Yu, Yunhong Wei, Chengcheng Cao, Rong Liang, Guolei Cai, Song Jin, Hongchang Jin, Yong Ni, Yue Lin, Hengxing Ji
Issue&Volume: August 4, 2025
Abstract: Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) for sustainable energy storage, yet their adoption in compact applications is hindered by a low volumetric energy density (VED) or relatively poor structural instability. Herein, we present a nano-Bi@hard carbon (nano-Bi@HC) composite featuring densely packed microspheres with uniformly dispersed Bi nanoparticles (6–18 nm) embedded in a hard carbon matrix, achieving a remarkable VED of 385 Wh L–1, with exceptional cycling stability (97% retention over 4000 cycles). Utilizing pectin’s carboxyl functional groups, Bi3+ ions were homogeneously coordinated to enable a high Bi content (86.2 wt %) without agglomeration during carbonization. The nano-Bi@HC anode exhibits an unparalleled volumetric capacity of 1950 mAh cm–3 under a high areal loading (12.3 mg cm–2) and compaction density (4.8 g cm–3). Paired with a Na3V(PO4)3 cathode, the full cell demonstrates a superior performance across temperature ranges, highlighting its practical potential. This study establishes a scalable strategy for designing high-VED and durable alloy-based anodes, bridging critical gaps in SIB technology.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03507
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c03507
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
