近日,英国牛津大学Junjie Liu团队研究了分子磁体中量子自旋-电耦合的化学调谐。相关论文于2025年8月27日发表在《自然-化学》杂志上。
控制量子自旋以电场而不是磁场为主题,有望为发展量子技术带来实质性的架构优势。在这种情况下,分子磁体中的自旋通过合理的化学设计提供了自旋-电耦合(SECs)的可调性。
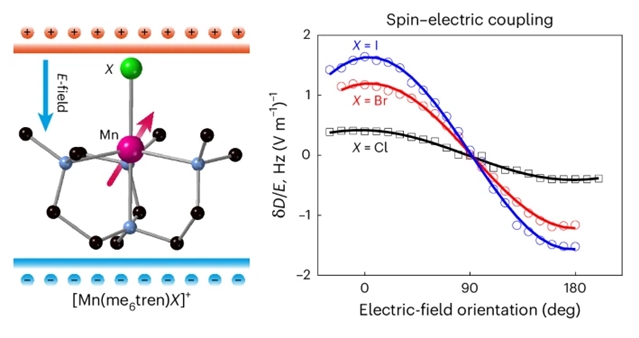
研究组通过改变自旋中心的配位环境,证明了一类Mn(II)-分子中SEC的系统控制。具有C3对称的三角双锥体(tbp)分子结构导致了与其磁各向异性直接相关的大量分子电偶极矩。这两个特征之间的相互作用产生了实验观察到的SEC,可以通过波函数理论计算来合理化。该发现为开发用于量子技术的可控分子自旋量子比特提供了指导策略。
附:英文原文
Title: Chemical tuning of quantum spin–electric coupling in molecular magnets
Author: Vaganov, Mikhail V., Suaud, Nicolas, Lambert, Franois, Cahier, Benjamin, Herrero, Christian, Guillot, Rgis, Barra, Anne-Laure, Guihry, Nathalie, Mallah, Talal, Ardavan, Arzhang, Liu, Junjie
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-27
Abstract: Controlling quantum spins using electric rather than magnetic fields promises substantial architectural advantages for developing quantum technologies. In this context, spins in molecular magnets offer tunability of spin–electric couplings (SECs) by rational chemical design. Here we demonstrate systematic control of SECs in a family of Mn(II)-containing molecules by varying the coordination environment of the spin centre. The trigonal bipyramidal (tbp) molecular structure with C3 symmetry leads to a substantial molecular electric dipole moment that is directly connected to its magnetic anisotropy. The interplay between these two features gives rise to experimentally observed SECs, which can be rationalized by wavefunction theoretical calculations. Our findings guide strategies for the development of electrically controllable molecular spin qubits for quantum technologies.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01926-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01926-5
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
