近日,西湖大学杨汶醒团队研究了电化学CO2或CO还原过程中Cu自发重建的*CObridge的普遍形成、动力学和反应性。该项研究成果发表在2025年8月21日出版的《美国化学会志》上。
该研究对电化学CO2和CO还原反应(CO(2)RR)中自发Cu重构及其对CO(2)RR最重要的反应中间体表面吸附CO(*CO)的影响有了统一的认识。
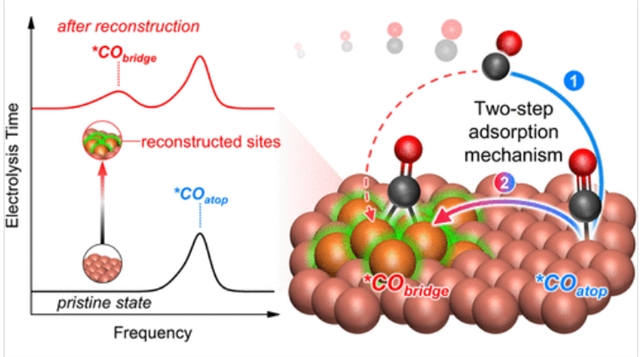
具体来说,通过使用各种原位拉曼和红外光谱技术,研究组发现除了在顶部位置吸附的CO (*COatop)外,在重建过程中还普遍逐渐形成桥型吸附CO (*CObridge)。这种现象在不同的铜催化剂和电解槽配置中都可以观察到。特别是,它也发生在Cu的CV测量中,为机制研究*CO的光谱表征提供了导管干扰。重构Cu上*CObridge的形成过程分为两个步骤:首先CO吸附形成*COatop,然后表面转化为*CObridge,而动力学研究表明*CObridge无活性,不利于催化转化。
最后,为了为未来的研究提供有价值的参考结果,研究组对广泛使用的Cu催化剂的*CO的线形和势相关数进行了基准测试,提出了精确测量所需的方案。总的来说,这些结果解释了为什么自发Cu重建会导致CO(2)RR活性降低、*CObridge的表面动力学和活性降低,以及如何准确表征*CO的机理研究。这些发现不仅促进了对铜基电催化剂的基本认识,而且为研究其他反应中电催化剂的动态重构提供了一个框架。
附:英文原文
Title: Universal Formation, Dynamics, and Reactivities of *CObridge Accompanying Spontaneous Reconstruction of Cu during Electrochemical CO2 or CO Reduction
Author: Qiliang Liu, Jianyang Zang, Wentao Ye, Ling Li, Chaochen Wang, Jiali Jin, Wenxing Yang
Issue&Volume: August 21, 2025
Abstract: This study demonstrates a unifying understanding of spontaneous Cu reconstruction during electrochemical CO2 and CO reduction reactions (CO(2)RR) and its influence on the surface-adsorbed CO (*CO), the most important reaction intermediate of CO(2)RR. Specifically, by employing various in situ/operando Raman and infrared spectroscopy techniques, we reveal a universal gradual formation of bridge-type adsorbed CO (*CObridge) accompanying the reconstruction in addition to CO adsorbed on the atop site (*COatop). This phenomenon is observed across diverse Cu catalysts and electrolyzer configurations. Especially, it also occurs during CV measurements of Cu, causing interference for spectroscopic characterization of *CO for mechanistic studies. The formation of *CObridge on reconstructed Cu is revealed to involve two steps: first, CO adsorption to form *COatop followed by its surface conversion to *CObridge, while kinetic studies show that *CObridge is inactive and detrimental to catalytic conversion. Finally, to provide reference results valuable for future studies, we benchmark the line shape and potential-dependent population of *CO for widely utilized Cu catalysts, proposing protocols necessary for accurate measurements. Collectively, these results explain why spontaneous Cu reconstruction would result in lower activities of CO(2)RR, the surface dynamics and activities of *CObridge, as well as how to accurately characterize *CO for future mechanistic studies. These insights not only advance the fundamental understanding of Cu-based electrocatalysts but also provide a framework for studying the dynamic reconstruction of electrocatalysts for other reactions.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03886
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c03886
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
