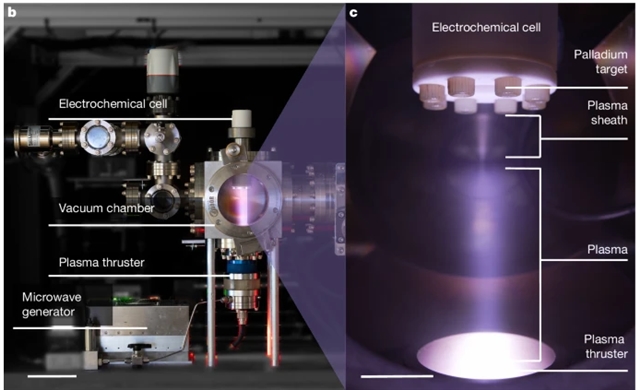
近日,加拿大英属哥伦比亚大学Berlinguette, Curtis P.团队报道了电化学加载提高了金属靶中的氘聚变速率。该研究于2025年8月20日发表在《自然》杂志上。
能源应用的核聚变研究旨在创造条件,释放比触发聚变过程所需的更多能量。为了产生有意义的能量,氘等燃料需要在空间上受到限制,以增加粒子的碰撞概率。
因此,研究组着手探讨用氘燃料电化学加载金属晶格是否会增加核聚变事件的概率。他们报告了一个台式聚变反应堆,实现了用氘离子轰击钯金属靶。这些氘离子在钯金属中发生氘-氘聚变反应。研究组发现,将氘原位电化学加载到钯靶中导致氘-氘聚变速率提高了15(2)%。该实验展示了金属靶在电子伏特能级上的电化学加载如何影响兆电子伏特能级上的核反应。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrochemical loading enhances deuterium fusion rates in a metal target
Author: Chen, Kuo-Yi, Maiwald, Jannis, Schauer, Phil A., Issinski, Sergey, Garcia, Fatima H., Oldford, Ryan, Egoriti, Luca, Higashino, Shota, Vakili, Aref E., Wen, Yunzhou, Koh, Joseph Z. X., Schenkel, Thomas, Stolar, Monika, Brown, Amanda K., Berlinguette, Curtis P.
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-20
Abstract: Nuclear fusion research for energy applications aims to create conditions that release more energy than required to initiate the fusion process1. To generate meaningful amounts of energy, fuels such as deuterium need to be spatially confined to increase the collision probability of particles2,3,4. We therefore set out to investigate whether electrochemically loading a metal lattice with deuterium fuel could increase the probability of nuclear fusion events. Here we report a benchtop fusion reactor that enabled us to bombard a palladium metal target with deuterium ions. These deuterium ions undergo deuterium–deuterium fusion reactions within the palladium metal. We showed that the in situ electrochemical loading of deuterium into the palladium target resulted in a 15(2)% increase in deuterium–deuterium fusion rates. This experiment shows how the electrochemical loading of a metal target at the electronvolt energy scale can affect nuclear reactions at the megaelectronvolt energy scale.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09042-7
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09042-7
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
