近日,南方科技大学陈树明团队揭示了胶体量子点的电泵浦面发射放大自发辐射。这一研究成果发表在2025年8月19日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
胶体量子点(QDs)是实现溶液可加工、波长可调、低成本激光二极管的有前景的增益材料。然而,在量子点中实现电泵浦放大自发发射(ASE)是激光的先决条件,受到低净光增益和二极管低电流注入的阻碍。
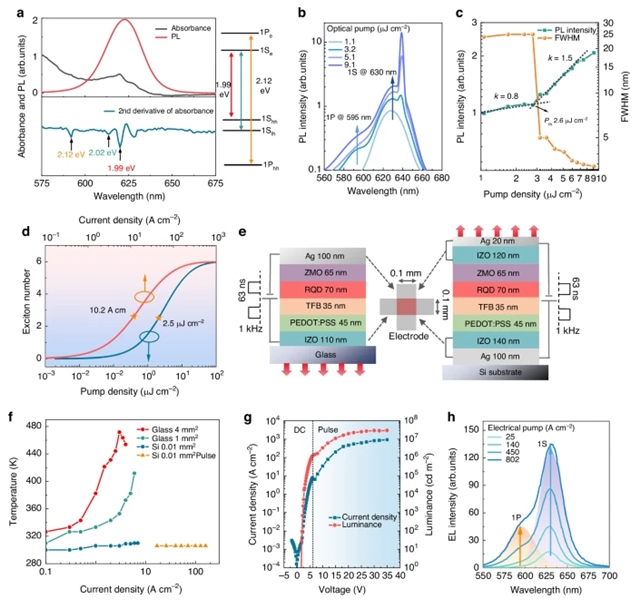
研究组通过电热光学共同设计一个具有高净光增益和高电流注入的量子点发光二极管(QLED),展示了量子点的电泵浦和表面发射ASE。通过构建具有Ag/铟锌氧化物(IZO)底部反射电极和IZO/Ag顶部半透明电极的顶发射腔,实现了量子点发射的有效共振;此外,不仅完全消除了金属电极引起的表面等离子激元极化子损耗,而且光场可以主要限制在量子点内,从而减少了损耗,增益提高了2倍。
因此,当使用100飞秒激光泵浦在77开尔文温度下工作时,该量子点发光二极管表现出阈值低至10微焦每平方厘米的面发射放大自发辐射。通过将量子点发光二极管直接构建在硅散热器上并采用纳秒脉冲电流源驱动,焦耳热得以有效散发,使其能在2000安培每平方厘米的高电流密度下稳定工作。在153开尔文温度和94安培每平方厘米的注入电流条件下,该器件展现出具有强方向性、高辐射强度及窄带宽特征的面发射放大自发辐射。所开发的QLED能够产生面发射ASE,为基于QD的垂直腔面发射激光二极管的发展铺平了道路。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrically pumped surface-emitting amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Author: Tian, Fengshou, Zhou, Tianhong, Zhang, Xuanyu, Chen, Rui, Chen, Shuming
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-19
Abstract: Colloidal quantum dots (QDs) are promising gain materials for realizing solution-processable, wavelength-tunable and low-cost laser diodes. However, achieving electrically pumped amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) in QDs, a prerequisite for lasing, is hampered by the low net optical gain and low current injection of the diodes. Here we demonstrate electrically pumped and surface-emitting ASE from QDs by electro-thermal-optically co-designing a quantum-dot light-emitting diode (QLED) with high net optical gain and high current injection. By developing a top-emitting cavity featuring a Ag/indium-zinc-oxide (IZO) bottom reflective electrode and a IZO/Ag top semi-transparent electrode, the QD emission is effectively resonated; moreover, not only are the surface plasmon polariton losses induced by the metallic electrodes completely eliminated, but also the optical field can be confined primarily within the QDs, resulting in a reduction in loss and a 2-fold enhancement in gain. As a result, the QLED exhibits surface-emitting ASE with a threshold of 10μJcm2 when pumped by a 100fs laser at 77K. By building the QLED directly on a Si heat sink and driving the QLED with an ns-pulsed current source, the Joule heat is effectively dissipated, allowing the QLED to operate stably even at a high current of 2000 A cm2. At 153K and an injection current of 94Acm2, the QLED demonstrates surface-emitting ASE with strong directionality, high intensity and narrow bandwidth. The developed QLED, capable of generating surface-emitting ASE, paves the way for the development of QD based vertical cavity surface-emitting laser diodes.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01972-1
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01972-1
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
