近日,美国罗切斯特大学Guo, Chunlei团队报道通过飞秒激光光谱工程和热管理,太阳能热电发电机性能提高15倍。这一研究成果于2025年8月12日发表在《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
太阳能热电发电机(STEGs)近年来受到越来越多的关注。然而,由于缺乏高效的热电材料和紧凑的散热器来有效散热,它们的广泛采用受到限制。
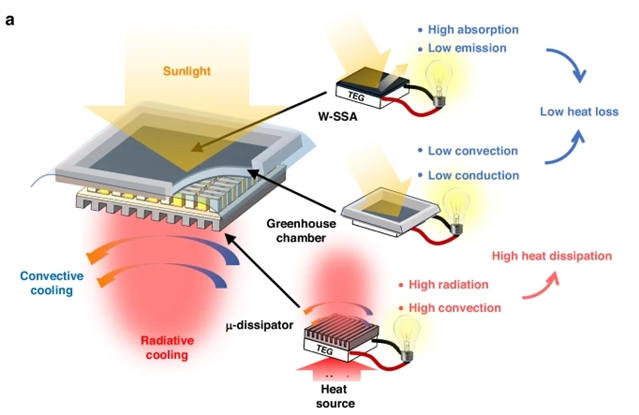
为了解决这些问题,研究组开发了一种光谱工程和热管理策略,可以将STEG发电量显著提高15倍,而重量仅增加25%。在热侧,研究组通过飞秒(fs)激光加工技术将普通钨(W)转变为选择性太阳能吸收剂(W-SSA),增强了太阳吸收,同时最小化了红外发射率,在高温下获得了80%的吸收效率。
研究组还为W-SSA设计了一个温室室,实现了对流热损失减少40%。在冷侧,他们采用fs激光加工将普通铝(Al)转变为超高容量微结构散热片(μ-耗散片),通过辐射和对流两种方式提高冷侧散热,散热性能是普通铝散热片的两倍。这些光谱工程和热管理增加了STEG的温差,从而大大增加了输出功率。高效STEG可以找到广泛的应用,如无线传感器网络,可穿戴电子产品和医疗传感器。
附:英文原文
Title: 15-Fold increase in solar thermoelectric generator performance through femtosecond-laser spectral engineering and thermal management
Author: Xu, Tianshu, Wei, Ran, Singh, Subhash C., Guo, Chunlei
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-12
Abstract: Solar thermoelectric generators (STEGs) have recently gained increasing attention. However, their widespread adoption has been limited due to the lack of high-efficiency thermoelectric materials and compact heat sinks for effective heat dissipation. To address these issues, we develop a spectral engineering and thermal management strategy that significantly increases STEG power generation by 15 times with only a 25% increase in weight. At the hot side, we transform a regular tungsten (W) to a selective solar absorber (W-SSA) through a femtosecond (fs)-laser processing technique, which enhances the solar absorption while minimizing the IR emissivity, obtaining >80% absorption efficiency at elevated temperatures. We also design a greenhouse chamber for W-SSA and achieved >40% reduction in convective heat loss. At the cold side, we apply the fs laser processing to transform a regular aluminum (Al) to a super-high-capacity micro-structured heat dissipator (μ-dissipator), which improves the cold-side heat dissipation through both radiation and convection, achieving twice the cooling performance of a regular Al heat dissipator. These spectral engineering and thermal management increase the temperature difference across the STEG, resulting in a substantial increase in output power. The high-efficiency STEG can find a wide range of applications, such as wireless sensor networks, wearable electronics, and medical sensors.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01916-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01916-9
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
