近日,上海交通大学张礼知团队研究了
泛素水(H2O)均解离解成自由基是驱动化学、生物、地球科学和环境领域反应的关键;然而,它在切断主O-H键和防止自由基重组方面面临着重大挑战。
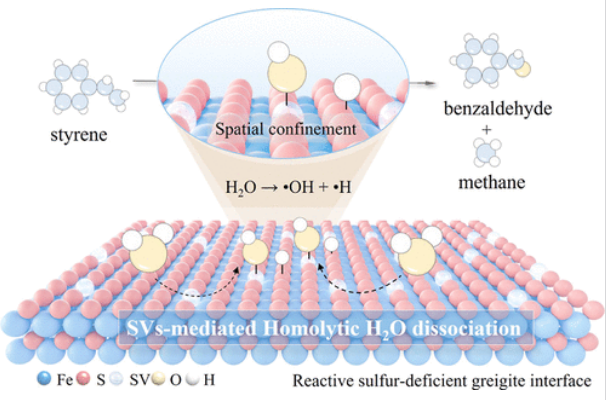
研究组证明了具有硫空位(SVs)的灰长岩可以以化学计量学的方式将水解离成活性羟基(OH)和氢(H)自由基。Fe3S4的反尖晶石结构促进了这一过程,其中高自旋铁原子的反平行排列将电子定位在SVs上,使得O-H键能够无阻碍地裂解生成OH和H。同时,相邻的具有明显刘易斯碱度的S原子有效地稳定了生成的H,促进了其与限制在SV上的OH的空间分离。这个有趣的水均解方案,其特点是同步生成-OH和-H,通过自由基途径触发苯乙烯及其衍生物高效和选择性水合成高附加值的醛和高能量的甲烷。
附:英文原文
Title: Homolytic H2O Dissociation into Hydroxyl and Hydrogen Radicals on Sulfur-Deficient Greigite for Efficient Hydration Reactions
Author: Cancan Ling, Hao Li, Yaling Li, Long Zhao, Sicong Ma, Yi Liu, Meiqi Li, Jincai Zhao, Lizhi Zhang
Issue&Volume: July 7, 2025
Abstract: Homolytic dissociation of ubiquitous water (H2O) into radical species is pivotal in driving reactions across chemical, biological, geoscientific, and environmental domains; yet, it faces substantial challenges in cleaving the robust O–H bond and preventing radical recombination. Herein, we demonstrate that greigite with sulfur vacancies (SVs) can ambiently dissociate H2O into reactive hydroxyl (OH) and hydrogen (H) radicals in a stoichiometric manner. This process is facilitated by the inverse-spinel structure of Fe3S4, where the antiparallel arrangement of high-spin Fe atoms localizes electrons at SVs, enabling barrierless cleavage of the O–H bond to yield OH and H. Concurrently, adjacent S atoms with pronounced Lewis basicity effectively stabilize the generated H, promoting its spatial separation from the OH confined on SVs. This interesting water homolysis scheme, characterized by synchronous OH and H generation, triggers efficient and selective hydrations of styrene and its derivatives to high-value-added aldehydes and energy-rich methane via a radical pathway.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c08801
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c08801
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
