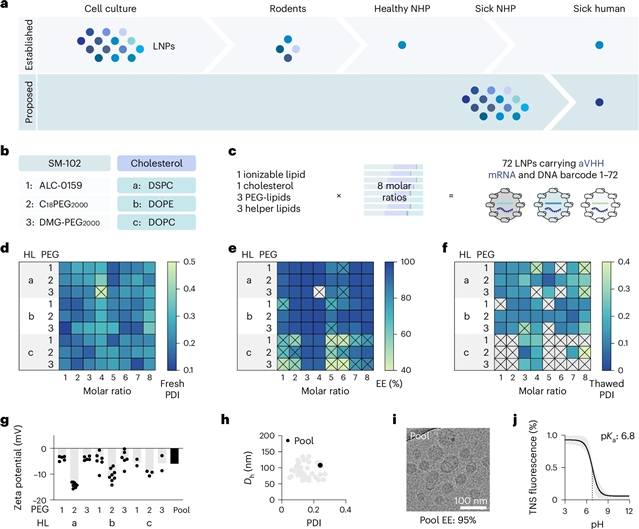
美国乔治亚理工学院James E. Dahlman小组的一项最新研究提出了脂质纳米颗粒筛选非人灵长类动物与最小的生命损失。相关论文于2025年6月26日发表在《自然—生物技术》杂志上。
为了最大限度地减少动物主题,课题组人员创建了一个无菌条形码LNPs池,这些LNPs被冷冻,引用并在生命终结的NHP(由于自动机疾病而独立安排安乐死的动物)可用时进行管理。然后,课题组研究人员将45种不同化学成分的LNP-aVHH mRNA通过静脉注射给小鼠和NHPs,观察到NHPs中aVHH的表达量高于小鼠。该课题组人员描述了LNP治疗的全身生理反应,包括47个临床相关变量,并分析了来自体内三种组织的单细胞递送的转录组反应。这些数据表明多种脂蛋白受体可能与输送有关。总之,生命末期NHPs减少了动物主题,可能是临床前模型的信息。
据了解,了解小鼠体内的传递如何预测非人灵长类动物(NHPs)的传递,可以使脂质纳米颗粒(LNP)的发现更有效。然而,很少有LNP-mRNA候选药物在NHPs中进行测试,部分原因是实验需要更多的动物,而不是被认为是道德的。
附:英文原文
Title: Lipid nanoparticle screening in nonhuman primates with minimal loss of life
Author: Zenhausern, Ryan, Jang, Bora, Schrader Echeverri, Elisa, Gentry, Kara, Calkins, Randi, Curran, Elizabeth H., Wood, Jennifer S., Stammen, Rachelle L., Loughrey, David, Chappa, Prasanthi, Koveal, Dorothy, Kim, Hyejin, Dahlman, James E.
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-26
Abstract: Understanding how well delivery in mice predicts delivery in nonhuman primates (NHPs) could make lipid nanoparticle (LNP) discovery more efficient. Yet, few LNP-mRNA drug candidates are tested in NHPs, in part because the experiments require more animals than is considered ethical. Here, to minimize animal use, we create a pool of sterile barcoded LNPs that are frozen, aliquoted and administered when an end-of-life NHP—an animal that is independently scheduled for euthanasia due to spontaneous disease—becomes available. We then administer this pool of 45 LNP-aVHH mRNAs with different chemistries intravenously to mice and NHPs and observe a higher amount of aVHH expression in NHPs than in mice. We characterize systemic physiological responses to LNP treatment using 47 clinically relevant variables and analyze the transcriptomic response alongside delivery in single cells from three tissues in vivo. These data suggest that multiple lipoprotein receptors may be associated with delivery. Altogether, end-of-life NHPs reduce animal use and may be informative preclinical models.
DOI: 10.1038/s41587-025-02711-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-025-02711-y
Nature Biotechnology:《自然—生物技术》,创刊于1996年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:68.164
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nbt/
投稿链接:https://mts-nbt.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
