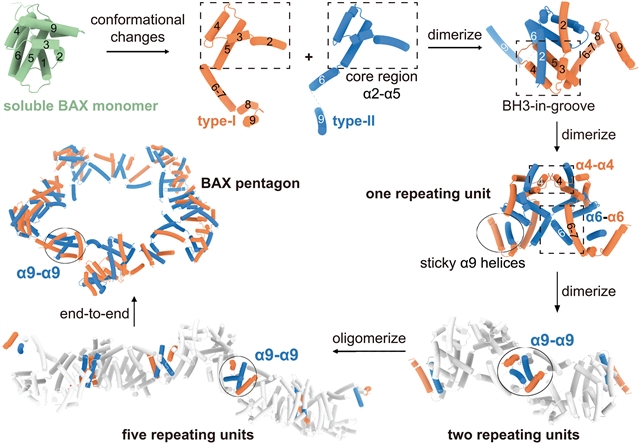
课题组研究人员确定了BAX二聚体的二聚体作为其各种低聚形式的基本重复单元:弧,线和环。BAX重复单元在3.2埃分辨率下的低温电子显微镜结构揭示了二聚体内部和之间的相互作用。通过突出的α9对将重复单元端到端堆叠,可以得到线、弧、多边形和环。该研究组在结构上表征了四边形、五边形、六边形和七边形,它们分别包含16、20、24和28个BAX原聚体。BAX原聚体间界面的错义突变破坏孔隙形成并削弱其促凋亡功能。本文报道的各种BAX低聚物的组装原理为BAX渗透膜提供了结构基础。
据悉,在细胞凋亡过程中,胞质BAX单体被转移到线粒体,使外膜通透。
附:英文原文
Title: Structural basis of BAX pore formation
Author: Ying Zhang, Lu Tian, Gaoxingyu Huang, Xiaofei Ge, Fang Kong, Pengqi Wang, Yige Xu, Yigong Shi
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-26
Abstract: During apoptosis, cytosolic BAX monomers are translocated to the mitochondria to permeabilize the outer membrane. Here, we identified a dimer of BAX dimers as the basic repeating unit of its various oligomeric forms: arcs, lines, and rings. Cryo–electron microscopy structure of the BAX repeating unit at 3.2-angstrom resolution revealed the interactions within and between dimers. End-to-end stacking of the repeating units through the protruding α9 pairs yielded lines, arcs, polygons, and rings. We structurally characterized the tetragon, pentagon, hexagon, and heptagon, which comprise 16, 20, 24, and 28 BAX protomers, respectively. Missense mutations at the BAX inter-protomer interface damage pore formation and cripple its proapoptotic function. The assembly principle of the various BAX oligomers reported here provides the structural basis of membrane permeabilization by BAX.
DOI: adv4314
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adv4314
