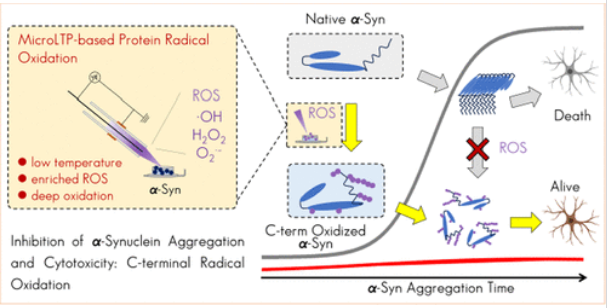
南开大学李功玉团队研究了C端自由基氧化通过氧化寡聚物破坏途径抑制α-突触核蛋白聚集和细胞毒性。2025年6月18日出版的《美国化学会志》发表了这项
α-Synuclein(α-Syn)聚集是帕金森病和其他神经退行性疾病的标志。研究组探讨了受控自由基氧化对α-Syn聚集和相关细胞毒性的影响。使用用于亚毫秒自由基氧化的微型低温等离子体装置,结合天然离子迁移率质谱和液相色谱串联质谱,他们证明了α-Syn C末端区域的自由基定向优先氧化。这种靶向氧化导致SH-SY5Y细胞中蛋白质聚集的抑制和细胞毒性的降低。机理分析表明,超快的C末端自由基氧化会损害α-Syn低聚倾向,这可能是通过阻止对形成稳定的无定形沉积物和有序纤维至关重要的构象转变来实现的。
值得注意的是,这种抑制作用特定于聚集前的单体氧化,而不是预成型纤维的氧化。该发现揭示了一种新的氧化寡聚化破坏途径,该途径调节α-Syn原纤维化行为,为神经退行性疾病中氧化应激和蛋白质聚集之间的复杂相互作用提供了新的见解。这项研究挑战了氧化应激在α-Syn病理中有害作用的传统观点,并提出了基于靶向氧化修饰的潜在神经保护策略。
附:英文原文
Title: C-Terminal Radical Oxidation Inhibits α-Synuclein Aggregation and Cytotoxicity via an Oxidative Oligomer-Disrupting Pathway
Author: Xiaoli Wang, Tingting Liang, Anran Jin, Chenao Zhang, Jiaxin Zhou, Mingrui Li, Ziyi Sun, Gongyu Li
Issue&Volume: June 18, 2025
Abstract: α-Synuclein (α-Syn) aggregation is a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. This study investigates the impact of controlled radical oxidation on α-Syn aggregation and associated cytotoxicity. Using a microscale low-temperature plasma device for submillisecond radical oxidation, combined with native ion mobility-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, we demonstrate radical-directed preferential oxidation of the α-Syn C-terminal region. This targeted oxidation leads to the inhibition of protein aggregation and reduced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Mechanistic analysis reveals that ultrafast C-terminal radical oxidation impairs α-Syn oligomerization propensity, likely by preventing conformational transitions critical for forming stable amorphous deposits and well-ordered fibers. Notably, this inhibitory effect is specific to monomer oxidation prior to aggregation rather than oxidation of preformed fibers. Our findings unveil a novel oxidative oligomerization-disrupting pathway that modulates α-Syn fibrillization behavior, offering new insights into the complex interplay between oxidative stress and protein aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases. This study challenges conventional views of the detrimental role of oxidative stress in α-Syn pathology and suggests potential neuroprotective strategies based on targeted oxidative modifications.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c06792
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c06792
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
