德克萨斯大学Philipp E. Scherer研究团队在研究中取得进展。他们报道了FGF21通过独立于生长抑制的代谢益处促进饮食引起的肥胖的寿命。2025年6月16日出版的《细胞—代谢》发表了这项成果。
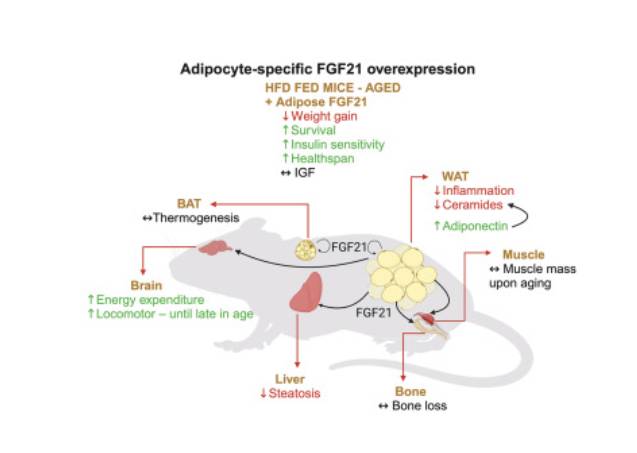
为了探索其在没有发育混杂因素的情况下的作用,研究人员从成年期开始培养了脂肪细胞特异性FGF21过表达的小鼠。当喂食高脂肪食物时,这些小鼠活了3.3年,抵抗体重增加,改善胰岛素敏感性,并显示出肝脏脂肪变性减少。衰老的转基因小鼠也显示出较低水平的炎症免疫细胞和内脏脂肪组织中的脂毒神经酰胺,即使在缺乏脂联素(一种已知的调节神经酰胺分解的激素)的情况下也会出现这种益处。这些结果表明,脂肪组织是FGF21有益作用的中心部位,并指出其在治疗代谢综合征和年龄相关疾病方面的潜力,通过促进饮食应激下更健康的代谢谱,延长健康寿命和寿命。
据了解,大约35%的65岁以上的美国成年人肥胖,这突出了针对年龄相关代谢问题的治疗需求。成纤维细胞生长因子21 (FGF21)是一种主要由肝脏产生的激素,可以促进新陈代谢,延长寿命。
附:英文原文
Title: FGF21 promotes longevity in diet-induced obesity through metabolic benefits independent of growth suppression
Author: Christy M. Gliniak, Ruth Gordillo, Yun-Hee Youm, Qian Lin, Clair Crewe, Zhuzhen Zhang, Bianca C. Field, Teppei Fujikawa, Megan Virostek, Shangang Zhao, Yi Zhu, Clifford J. Rosen, Tamas L. Horvath, Vishwa Deep Dixit, Philipp E. Scherer
Issue&Volume: 2025-06-16
Abstract: Approximately 35% of US adults over 65 are obese, highlighting the need for therapies targeting age-related metabolic issues. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a hormone mainly produced by the liver, improves metabolism and extends lifespan. To explore its effects without developmental confounders, we generated mice with adipocyte-specific FGF21 overexpression beginning in adulthood. When fed a high-fat diet, these mice lived up to 3.3 years, resisted weight gain, improved insulin sensitivity, and showed reduced liver steatosis. Aged transgenic mice also displayed lower levels of inflammatory immune cells and lipotoxic ceramides in visceral adipose tissue, benefits that occurred even in the absence of adiponectin, a hormone known to regulate ceramide breakdown. These results suggest that fat tissue is a central site for FGF21’s beneficial effects and point to its potential for treating metabolic syndrome and age-related diseases by promoting a healthier metabolic profile under dietary stress and extending healthspan and lifespan.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.05.011
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00267-0
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
