中国科学院福建物构所陈浙宁团队近日揭示了具有面心立方结构的多组分Ru基合金在氢氧化电催化中具有高活性和CO容忍度。该项研究成果发表在2025年6月16日出版的《美国化学会志》上。
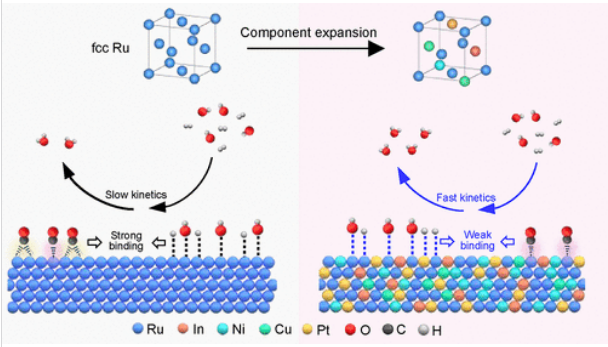
面心立方(fcc)Ru在碱性氢氧化反应(HOR)中表现出巨大的潜力,而实现高HOR活性和CO耐受性对实际燃料电池中的Ru催化剂构成了巨大的挑战,特别是在使用CO污染的H2,如灰色和蓝色氢气时。研究组提出了一种成分多样化策略,以创建14种fcc-Ru基合金,其中可调节的成分可以调节纳米结构,同时抵消单一Ru的局限性。
其中,五元RuInPtNiCu纳米晶体(NC)表现出5.36 a mgPGM–1的出色HOR活性,分别比商业Pt/C(0.338 a mgPGM-1)和单一Ru NC(1.88 a mgPGEM–1)高15.9倍和2.9倍。更重要的是,基于RuInPtNiCu的膜电极组件(MEA)在H2–O2中实现了1.72 W cm–2的高峰值功率密度和19.0 a mgPGM–1@0.65 V的显著质量活性,基于RuInPtNiCu的MEA可以在0.6 a cm–2下稳定运行100多个小时。
此外,RuInPtNiCu在旋转盘电极中暴露于含1000ppm CO的H2中8000秒后,保持了94.6%的HOR电流,并在燃料电池的CO毒性稳定性测试后保持了92.5%的电池电压,突显了其出色的CO耐受性。机理和计算研究证实,RuInPtNiCu的优化电子结构和原子构型削弱了表面物种(*H、*OH和CO)的吸附,改变了活性位点上的CO吸附模式,从而提高了HOR性能和CO耐受性。
附:英文原文
Title: Multicomponent Ru-Based Alloys with a Face-Centered Cubic Structure Achieve High Activity and CO Tolerance for Hydrogen Oxidation Electrocatalysis
Author: Qing Yao, Renjie Ren, Yuanmin Zhu, Wei Yan, Zhiyong Yu, Zhongliang Huang, Aiying Song, Haixin Lin, Lin Zhuang, Zhe-Ning Chen, Nanjun Chen, Xiaoqing Huang
Issue&Volume: June 16, 2025
Abstract: The face-centered cubic (fcc) Ru exhibits great potential for the alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR), while achieving high HOR activity and CO tolerance poses a formidable challenge for Ru catalysts in practical fuel cells, particularly when using CO-contaminated H2, such as gray and blue hydrogen. Here, we propose a compositional diversification strategy to create 14 types of fcc Ru-based alloys, in which adjustable compositions can tune the nanostructure while offsetting the limitations of single Ru. Among them, quinary RuInPtNiCu nanocrystals (NCs) exhibit an outstanding HOR activity of 5.36 A mgPGM–1, which is 15.9 and 2.9 times higher than those of commercial Pt/C (0.338 A mgPGM–1) and single Ru NCs (1.88 A mgPGM–1), respectively. More importantly, the RuInPtNiCu-based membrane electrode assembly (MEA) achieves a high peak power density of 1.72 W cm–2 and a remarkable mass activity of 19.0 A mgPGM–1@0.65 V in H2–O2, and the RuInPtNiCu-based MEA can be run stably at 0.6 A cm–2 for over 100 h. Moreover, the RuInPtNiCu retains 94.6% of the HOR current after exposure to H2 containing 1000 ppm CO for 8000 s in a rotating disk electrode and retains 92.5% of cell voltage after a CO-toxicity stability test in fuel cells, underscoring its exceptional CO tolerance. Mechanism and computation studies corroborate that the optimized electronic structure and atomic configuration of RuInPtNiCu weaken the adsorption of surface species (*H, *OH, and CO) and alter the CO adsorption mode on active sites, thus leading to enhanced HOR performance and CO tolerance.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c02339
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c02339
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
