江南大学刘天西团队实现了金属-聚合物桥接界面上的选择性质量积累用于氨和硝酸锌电池的高效硝酸盐电还原。相关论文发表在2025年6月11日出版的《美国化学会志》上。
工业废水和受污染的地下水中常见的氮源硝酸盐(NO3-)的电化学转化为氨(NH3),意味着废水处理和NH3生产的方法。然而,其在低NO3-浓度和工业电流密度下的选择性和活性受到电极周围有限的质量传输的限制。
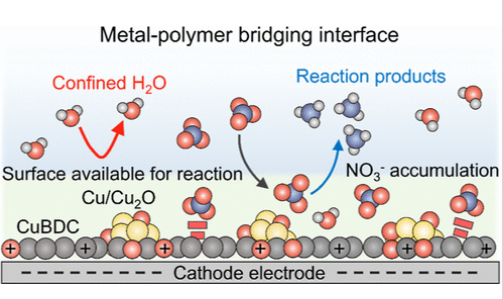
研究组报告了一个金属-聚合物桥接接口,通过将Cu/Cu2O纳米粒子固定在二维(2D)基于Cu的二碳酸苯(CuBDC)协调聚合物上,通过现场电还原(称为E-CuBDC)构建。该接口削弱了静电阻力,并调节了NO3和H2O的分布/迁移,在催化剂表面附近创建了一个富NO3和贫H2O的Janus域。
原位特征和理论模拟表明,金属 - 聚合物桥接接口有选择地积累NO3- 并降低了将*NH2OH减少为*NH2的能量屏障,克服了低NO3- 浓度的质量转移限制。E-CuBDC在广泛的NO3- 浓度(7.1-100 mM NO3- )和高应用电压中具有超过90%的高法拉代效率(FE)。
此外,它在安培电流密度下实现了超过100小时的稳定NH3生产。当应用于Zn-NO3- 系统时,这种新开发的E-CuBDC催化剂显示出用于NH3生产的出色功率密度和FE,展示了其在大规模电化学转换和存储系统中的巨大潜力。这项研究提出了构建金属 - 聚合物接口以调节接口质量传输的可推广策略。
附:英文原文
Title: Selective Mass Accumulation at the Metal–Polymer Bridging Interface for Efficient Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia and Zn-Nitrate Batteries
Author: Guojie Chao, Wei Zong, Jiexin Zhu, Haifeng Wang, Kaibin Chu, Hele Guo, Jian Wang, Yuhang Dai, Xuan Gao, Longxiang Liu, Fei Guo, Ivan P. Parkin, Wei Luo, Paul R. Shearing, Longsheng Zhang, Guanjie He, Tianxi Liu
Issue&Volume: June 11, 2025
Abstract: The electrochemical conversion of nitrate (NO3–), a common nitrogen source in industrial wastewater and contaminated groundwater, into ammonia (NH3), signifies an approach to wastewater treatment and NH3 production. Nevertheless, its selectivity and activity at low NO3– concentrations and industrial current densities are constrained by limited mass transfer around the electrode. Here, we report a metal–polymer bridging interface constructed by anchoring Cu/Cu2O nanoparticles onto a two-dimensional (2D) Cu-based benzene dicarboxylate (CuBDC) coordination polymer via in situ electroreduction (denoted as E-CuBDC). This interface weakens the electrostatic repulsion and regulates the distribution/migration of NO3– and H2O, creating a Janus NO3–-rich and H2O-poor domain near the catalyst surface. Operando characterizations and theoretical simulations indicate that the metal–polymer bridging interface selectively accumulates NO3– and reduces the energy barrier toward the reduction of *NH2OH to *NH2, overcoming the mass transfer limitations at a low NO3– concentration. E-CuBDC exhibits a high Faradaic efficiency (FE) of over 90% across wide NO3– concentrations (7.1–100 mM NO3–) and high applied voltages. Additionally, it achieved stable NH3 production over 100 h at ampere-level current densities. When applied in a Zn–NO3– system, this newly developed E-CuBDC catalyst demonstrates an outstanding power density and FE for NH3 production, showcasing its great potential for large-scale electrochemical conversion and storage systems. This study presents a generalizable strategy for constructing metal–polymer interfaces to regulate interfacial mass transport.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c00400
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jacs.5c00400
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
