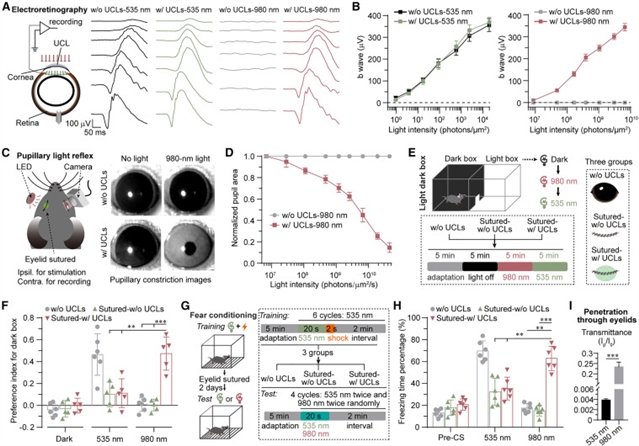
中国科学技术大学薛天研究小组在研究中取得进展。他们报道了上转换隐形眼镜使人类的近红外时空色觉成为可能。相关论文于2025年5月22日发表在《细胞》杂志上。
研究人员报道可穿戴的近红外(NIR)上转换隐形眼镜(UCLs)具有合适的光学特性、亲水性、柔韧性和生物相容性。UCLs小鼠能够识别近红外时空信息并做出行为决策。
此外,佩戴UCLs的人类参与者可以区分近红外信息,包括时间编码和空间图像。值得注意的是,研究人员已经开发了三色UCLs (tUCLs),使人类能够区分近红外光的多个光谱,这些光谱可以作为三基色,从而实现人类近红外光的时空色觉。他们的研究开辟了可穿戴聚合物材料用于非侵入性近红外视觉的潜力,帮助人类感知和传输近红外光的时间、空间和颜色维度。
研究人员表示,由于光子探测视蛋白的物理热力学性质,人类无法感知红外光。然而,用肉眼检测不可见的多光谱红外光的能力是非常可取的。
附:英文原文
Title: Near-infrared spatiotemporal color vision in humans enabled by upconversion contact lenses
Author: Yuqian Ma, Yunuo Chen, Sheng Wang, Zi-Han Chen, Yuanwei Zhang, Ling Huang, Xinxin Zhang, Fei Yin, Yunxuan Wang, Mingzhu Yang, Zhanjun Li, Kai Huang, Xin Fang, Zishuo Li, Minghong Wang, Wenhui Liu, Jia-Nan Li, Longfei Li, Hang Zhao, Min Wei, Yiming Shi, Rong Liu, Mei Zhang, Jutao Chen, Jiawei Shen, Jianjun Meng, Yupeng Yang, Fan Zhang, Xinglong Gong, Gang Han, Tian Xue
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-22
Abstract: Humans cannot perceive infrared light due to the physical thermodynamic properties of photon-detecting opsins. However, the capability to detect invisible multispectral infrared light with the naked eye is highly desirable. Here, we report wearable near-infrared (NIR) upconversion contact lenses (UCLs) with suitable optical properties, hydrophilicity, flexibility, and biocompatibility. Mice with UCLs could recognize NIR temporal and spatial information and make behavioral decisions. Furthermore, human participants wearing UCLs could discriminate NIR information, including temporal coding and spatial images. Notably, we have developed trichromatic UCLs (tUCLs), allowing humans to distinguish multiple spectra of NIR light, which can function as three primary colors, thereby achieving human NIR spatiotemporal color vision. Our research opens up the potential of wearable polymeric materials for non-invasive NIR vision, assisting humans in perceiving and transmitting temporal, spatial, and color dimensions of NIR light.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.04.019
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)00454-4
