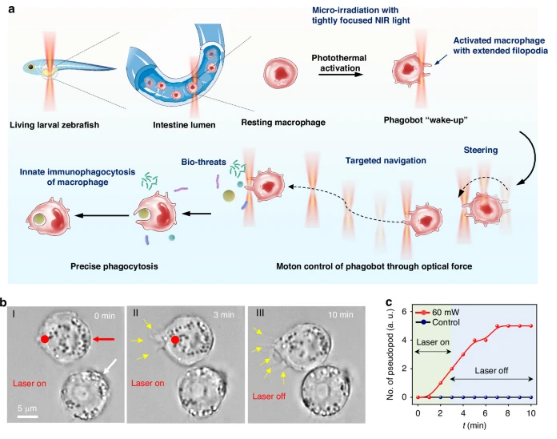
暨南大学辛洪宝团队近日研究了体内外光驱动吞噬巨噬细胞微机器人(phagobot)。2025年5月19日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志发表了这项成果。
基于免疫细胞的微/纳米机器人在解决具有挑战性的生物和生物医学条件方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,它们强大的先天免疫功能,特别是吞噬能力,仍然是充分利用当前基于免疫细胞的微型机器人设计的一大挑战。研究组报告了一种光动力吞噬巨噬细胞微机器人(phagobot),它能够机器人导航到特定的外来生物威胁,并在光控制下对这些目标实体进行精确的吞噬。
在没有对巨噬细胞进行基因改造或纳米工程的情况下,吞噬机器人的“唤醒”程序是通过紧密聚焦的近红外(NIR)光束直接激活静息状态的巨噬细胞来实现的。吞噬机器人表现出由激活巨噬细胞内延伸伪足的光学操纵控制的机器人转向和定向导航。它可以通过吞噬各种外来生物解冻物,包括纳米塑料、微生物和癌症细胞碎片,进一步执行靶向吞噬清除任务。
值得注意的是,噬菌体可以通过内源性巨噬细胞的光学激活和操纵在活体斑马鱼幼虫中构建,内源性巨噬细胞在体内也表现出可控的导航和靶向吞噬能力。凭借巨噬细胞的内在免疫功能,该光驱动吞噬机器人代表了一种新型的基于智能免疫细胞的微型机器人,为精确的免疫调节和治疗免疫相关疾病提供了许多新的可能性。
附:英文原文
Title: Light-powered phagocytic macrophage microrobot (phagobot): both in vitro and in vivo
Author: Li, Xing, Zhong, Shuhan, Pan, Ting, Xiong, Jianyun, Zhu, Guoshuai, Shi, Yang, Xin, Hongbao
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-19
Abstract: Micro/nanorobots based on immune cells show great potential for addressing challenging biological and biomedical conditions. However, their powerful innate immune functions, particularly the phagocytosis capabilities, remain a big challenge to fully leverage with the current designs of immune cell-based microrobots. Herein, we report a light-powered phagocytic macrophage microrobot (phagobot), which is capable of robotic navigation toward specific foreign bio-threats and executing precise phagocytosis of these targeted entities under light control. Without genetic modification or nanoengineering of macrophages, the phagobot’s “wake-up” program is achieved through direct activation of a resting-state macrophage by a tightly focused near-infrared (NIR) light beam. The phagobot exhibits robotic steering and directional navigation controlled by optical manipulation of the extended pseudopodia within the activated macrophage. It can further execute targeted phagocytic clearance tasks via engulfing various foreign bio-threats, including nanoplastics, microbials, and cancer cell debris. Notably, the phagobot can be constructed in a living larval zebrafish through optical activation and manipulation of the endogenous macrophage, which also exhibits controllable navigation and targeted phagocytic capabilities in vivo. With the intrinsic immune functions of macrophages, our light-powered phagobot represents a novel form of intelligent immune cell-based microrobots, holding many new possibilities for precise immune regulation and treatment for immune-related diseases.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01881-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01881-3
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
