江苏省中医药防治肿瘤协同创新中心程海波课题组在研究中取得进展。他们报道了去甲斑蝥素促进M1巨噬细胞极化,抑制结直肠癌生长。相关论文发表在2025年5月20日出版的《中国药理学报》杂志上。
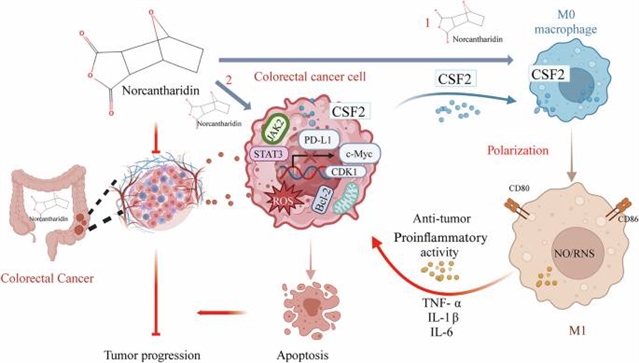
在本研究中,研究人员探讨了NCTD对结直肠癌的抗肿瘤作用及其机制。以motheme结直肠癌细胞系CT26为主题的balb/c小鼠和以人结直肠癌细胞系HCT116为主题的balb/c裸鼠分别建立CRC皮下模型。给小鼠注射NCTD(2 or 4 mg·kg−1·d−1, i.p.)14天。该团队发现NCTD剂量依赖性地降低了两种CRC模型中的肿瘤生长。
此外,在两种结直肠癌模型中,NCTD均显著增加肿瘤组织中M1巨噬细胞的浸润。在THP-1细胞源性和RAW264.7巨噬细胞模型中,通过流式细胞术和qPCR检测证实了NCTD诱导的巨噬细胞M1极化。研究团队证明NCTD (20,40 μM)剂量依赖性地增加CRC细胞和巨噬细胞的CSF2分泌,并抑制CRC细胞中JAK2/STAT3信号通路。同时,NCTD (10-40 μM)剂量依赖性地抑制结直肠癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移。综上所述,本研究为NCTD对CRC的作用提供了新的证据,并通过CSF2介导的巨噬细胞M1极化和抑制CRC细胞中JAK2/STAT3磷酸化重塑炎症微环境,阐明了NCTD的抗肿瘤机制。
据悉,结直肠癌(CRC)的特点是免疫抑制和炎症微环境,它们对治疗的反应很差。先前的研究表明,去甲斑蝥素(NCTD)是一种源自Mylabris的去甲基化斑蝥素(CTD),对治疗多种癌症有很高的疗效。
附:英文原文
Title: Norcantharidin promotes M1 macrophage polarization and suppresses colorectal cancer growth
Author: Wei, Xiao-man, Lu, Si-cheng, Li, Liu, Gao, Ying-jie, Wang, Jun-yi, Xi, Song-yang, Ye, Ling-yu Linda, Shen, Wei-xing, Wu, Mian-hua, Duan, Dayue Darrel, Cheng, Hai-bo
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-20
Abstract: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is characterized by an immunosuppressive and inflammatory microenvironment, thus responds poorly to therapy. Previous studies show that norcantharidin (NCTD), a demethylated cantharidin (CTD) derived from Mylabris, exerts high efficacy in treating various cancers. In this study we investigated the antitumor effects of NCTD against CRC and the underlying mechanisms. Subcutaneous CRC models were established in balb/c mice using mouse colorectal cancer cell line CT26 and in balb/c nude mice using human colorectal cancer cell line HCT116. The mice were administered NCTD (2 or 4mg·kg1·d1, i.p.) for 14 days. We showed that NCTD dose-dependently reduced the tumor growth in both the CRC models. Furthermore, NCTD markedly increased M1 macrophage infiltration in tumor tissue in both the CRC models. NCTD-induced macrophage M1 polarization was confirmed by flow cytometry and qPCR assays in both THP-1 cell-derived and RAW264.7 macrophage models in vitro. We demonstrated that NCTD (20, 40μM) dose-dependently increased CSF2 secretion from CRC cells and macrophages, and suppressed the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in CRC cells. Concurrently, NCTD (10–40μM) dose-dependently inhibited CRC cell proliferation, invasion and migration in vitro. In conclusion, this study provides new evidence for the effects of NCTD against CRC and elucidates its antitumor mechanisms through remodeling the inflammatory microenvironment via CSF2-mediated macrophage M1 polarization and inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation in CRC cells.
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-025-01578-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41401-025-01578-8
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica:《中国药理学报》,创刊于1980年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:8.2
官方网址:http://www.chinaphar.com/
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/aphs
