德国耶拿弗里德里希·席勒大学Markus A. Schmidt团队研究了用于高精度纳米颗粒跟踪分析的3D纳米打印光纤接口空心波导。2025年5月15日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志发表了这一成果。
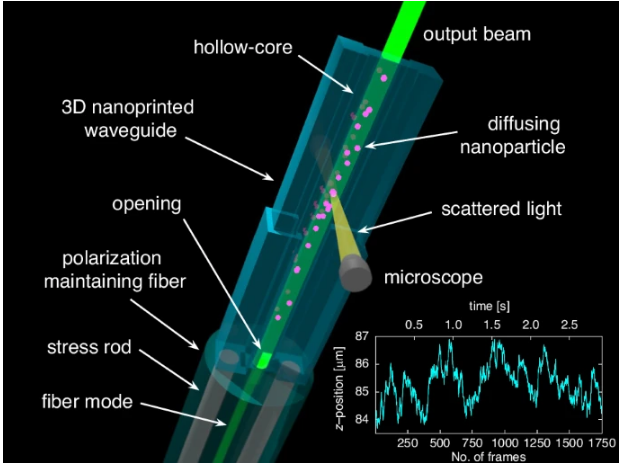
将功能元件集成到柔性光子环境中是集成光子学研究的一个关键领域,对高精度传感至关重要。研究组提出了一种将方芯空心波导与市售光纤相结合的新概念,并通过基于纳米科学的表征技术证明了其实际意义。详细而言,这一创新的概念产生了一个单片的、全光纤集成的设备,具有诸如无对准操作、高纯度基模激励、全偏振控制和独特的处理灵活性等关键优势。通过纳米粒子跟踪分析实验,首次证明了光纤界面波导在纳米尺度分析中的应用潜力。
这些实验包括跟踪和分析单个金纳米球在空心波导中的衍射,通过几乎无像差成像,延长观察时间和均匀的光线照明实现。该研究涵盖设计策略、实验实施、关键原理、光学特性及实际应用。光纤接口的空心波导概念在生物分析、环境科学、量子技术、光学操作和生命科学等领域具有巨大的应用潜力。它还为新型全光纤器件的开发铺平了道路,这些器件以适合灵活和远程应用的单片形式利用增强的光-物质相互作用。
附:英文原文
Title: 3D nanoprinted fiber-interfaced hollow-core waveguides for high-accuracy nanoparticle tracking analysis
Author: Pereira, Diana, Wieduwilt, Torsten, Hauswald, Walter, Zeisberger, Matthias, Ferreira, Marta S., Schmidt, Markus A.
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-15
Abstract: The integration of functional components into flexible photonic environments is a critical area of research in integrated photonics and is essential for high-precision sensing. This work presents a novel concept of interfacing square-core hollow-core waveguides with commercially available optical fibers using 3D nanoprinting, and demonstrates its practical relevance through a nanoscience-based characterization technique. In detail, this innovative concept results in a monolithic, fully fiber-integrated device with key advantages such as alignment-free operation, high-purity fundamental mode excitation, full polarization control, and a unique handling flexibility. For the first time, the application potential of a fiber-interfaced waveguide in nanoscale analysis is demonstrated by performing nanoparticle-tracking-analysis experiments. These experiments involve the tracking and analysis of individual gold nanospheres diffusing in the hollow core waveguide, enabled by nearly aberration-free imaging, extended observation times, and homogeneous light-line illumination. The study comprehensively covers design strategy, experimental implementation, key principles, optical characterization, and practical applications. The fiber-interfaced hollow-core waveguide concept offers significant potential for applications in bioanalytics, environmental sciences, quantum technologies, optical manipulation, and life sciences. It also paves the way for the development of novel all-fiber devices that exploit enhanced light-matter interaction in a monolithic form suitable for flexible and remote applications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01827-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01827-9
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
