美国加州大学洛杉矶分校Demetrios N. Christodoulides团队近日研究了高多模系统中频率转换过程的光子-光子化学热力学。相关论文发表在2025年5月12日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
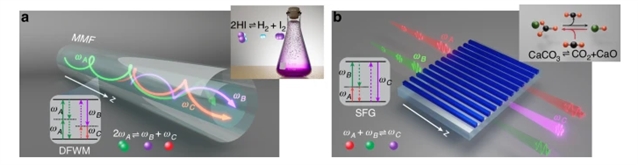
高度多模非线性光学系统中的频率产生本质上是一个复杂的过程,导致了极其复杂的演化动力学景观。虽然预测和控制这种非线性环境中的全局转换效率长期以来一直被认为是不可能的,但研究组正式解决了这一挑战,即使在涉及大量空间模式的情况下也是如此。通过利用光学统计力学的基本概念,他们开发了一个通用的理论框架,该框架有效地将所有频率分量视为化学反应物/产物,能够通过各种多波混合效应进行光学热力学反应。这些光子-光子反应受守恒定律的支配,守恒定律直接决定了每种频率物种的光学温度和随后化学平衡的化学势。
在此背景下,研究组开发了一个全面的化学计量模型,并正式推导出了一个表达式,该表达式将化学势与光学化学计量系数联系起来,其方式类似于原子/分子化学反应。这一进步释放了新的预测能力,可以促进高度多模光子排列中频率生成的优化,超越了仅依赖非线性光学动力学的传统方案的局限性。值得注意的是,研究组发现了瑞利-金斯热化的普遍机制,在接近零的光学温度下的光学反应可以促进光在目标频率下完全和熵不可逆地转换为基模。在二次谐波产生、和频产生和四波混频过程可以显现的环境中,该理论结果得到了数值模拟的证实。
附:英文原文
Title: Photon–photon chemical thermodynamics of frequency conversion processes in highly multimode systems
Author: Ren, Huizhong, Pyrialakos, Georgios G., Zhong, Qi, Wu, Fan O., Khajavikhan, Mercedeh, Christodoulides, Demetrios N.
Issue&Volume: 2025-05-12
Abstract: Frequency generation in highly multimode nonlinear optical systems is inherently a complex process, giving rise to an exceedingly convoluted landscape of evolution dynamics. While predicting and controlling the global conversion efficiencies in such nonlinear environments has long been considered impossible, here, we formally address this challenge even in scenarios involving a very large number of spatial modes. By utilizing fundamental notions from optical statistical mechanics, we develop a universal theoretical framework that effectively treats all frequency components as chemical reactants/products, capable of undergoing optical thermodynamic reactions facilitated by a variety of multi-wave mixing effects. These photon–photon reactions are governed by conservation laws that directly determine the optical temperatures and chemical potentials of the ensued chemical equilibria for each frequency species. In this context, we develop a comprehensive stoichiometric model and formally derive an expression that relates the chemical potentials to the optical stoichiometric coefficients, in a manner akin to atomic/molecular chemical reactions. This advancement unlocks new predictive capabilities that can facilitate the optimization of frequency generation in highly multimode photonic arrangements, surpassing the limitations of conventional schemes that rely exclusively on nonlinear optical dynamics. Notably, we identify a universal regime of Rayleigh–Jeans thermalization where an optical reaction at near-zero optical temperatures can promote the complete and entropically irreversible conversion of light to the fundamental mode at a target frequency. Our theoretical results are corroborated by numerical simulations in settings where second-harmonic generation, sum-frequency generation and four-wave mixing processes can manifest.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01856-4
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01856-4
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
