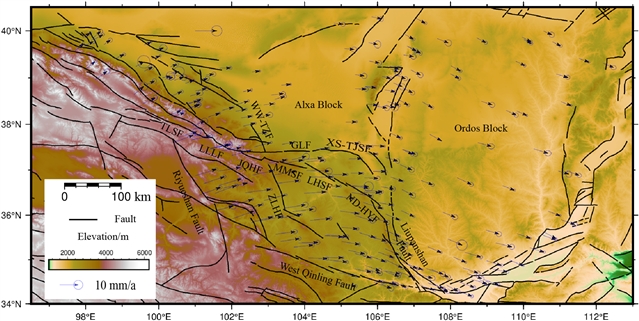
近日,武汉大学刘洋团队研究了基于精细块体模型和GPS数据的青藏高原东北部海原断裂带滑动速率和锁定程度。相关论文于2025年4月29日发表在《大地测量与地球动力学》杂志上。
海原断裂带是青藏高原东北部的一条主要断裂带,对了解区域变形具有重要意义。针对不同研究得出的滑动速率和锁定程度的差异,研究组构建了一个精细的块体模型(包括祁连、阿拉善、鄂尔多斯、西宁、海原和兰州块体),并使用网格搜索和模拟退火方法反演海原断带滑动速率和锁紧程度的GPS数据。
结果表明:(1)西段、中段和东段的左旋滑动速率分别为4.93-5.22 mm/a、1.52-4.94 mm/a和0.43-1.18 mm/a,总体上向东递减,而压缩速率分别为0.45-1.26 mm/a、0.58-2.62 mm/a和3.52-4.48 mm/a,整体上向东递增。(2)西段闭锁深度向东从约5km增加到约20km;中段向东先减小后增大;东段集中在约20km处(PHI约为0.86)。(3)冷龙岭、金强河、毛毛山和六盘山断层的滑动赤字相对较高(20公里内平均约为3.42 mm/a、4.16 mm/a、4.23 mm/a和3.43 mm/a)。(4)祁连、阿拉善、西宁、兰州和海原地块顺时针旋转,鄂尔多斯地块逆时针旋转。
此外,通过比较不同的区块模型,海原区块应独立考虑。海原断裂带调整了周边地块运动,在构造上抬升了六盘山。研究结果可为了解区域地震风险和变形机制提供重要参考。
附:英文原文
Title: Slip rate and locking degree of Haiyuan fault zone, northeastern Qinghai-Xizang plateau, based on refined block model and GPS data
Author: Yang Liu a b
Issue&Volume: 2025/04/29
Abstract: As a major fault in the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, the Haiyuan fault zone is important for understanding the regional deformation. Aiming at the differences in the slip rate and locking degree obtained from different studies, this study constructs a refined block model (including Qilian, Alxa, Ordos, Xining, Haiyuan, and Lanzhou blocks) and uses the grid search and simulated annealing methods to invert GPS data for slip rate and locking degree of the Haiyuan fault zone. The results are as follows: (1) The sinistral slip rates in the western, middle, and eastern segments are 4.93–5.22 mm/a, 1.52–4.94 mm/a, and 0.43–1.18 mm/a, decreasing eastward on the whole, while the compression rates are 0.45–1.26 mm/a, 0.58–2.62 mm/a, and 3.52–4.48 mm/a, increasing eastward on the whole. (2) The locking depth of the western segment increases from about 5 km to about 20 km eastward; the middle segment decreases and then increases eastward; the eastern segment concentrates at about 20 km (PHI is about 0.86). (3) The slip deficit is relatively higher in the Lenglongling, Jinqianghe, Maomaoshan, and Liupanshan faults (averaging about 3.42 mm/a, 4.16 mm/a, 4.23 mm/a, and 3.43 mm/a within 20 km). (4) The Qilian, Alxa, Xining, Lanzhou, and Haiyuan blocks rotate clockwise, while the Ordos block rotates counterclockwise. Additionally, by comparing different block models, the Haiyuan block should be considered independently. The Haiyuan fault zone adjusts surrounding block movements and uplifts Liupanshan mountain tectonically. The results can provide important references for understanding the regional earthquake risk and deformation mechanism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.geog.2025.02.005
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674984725000266
Geodesy and Geodynamics:《大地测量与地球动力学》,创刊于2010年。隶属于爱思唯尔出版集团,最新IF:2.4
官方网址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/geodesy-and-geodynamics
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/geog/default2.aspx
