近日,美国退伍军人事务帕洛阿尔托医疗保健系统和帕洛阿尔托退伍军人研究所教授Eugene C. Butcher及其研究团队报道了SSTR2-生长抑素趋化轴驱动T细胞祖细胞归巢到肠道。相关论文于2025年3月26日发表于国际顶尖学术期刊《自然—免疫学》杂志上。
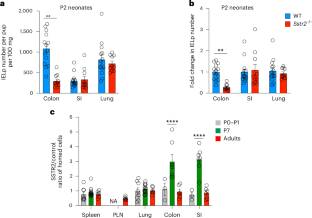
在这里,该课题组研究人员发现胸腺IELps帮助表达生长抑素受体SSTR2,这有助于它们归巢到肠道。IELps归巢依赖于SSTR2,并与新生儿神经内分泌和固有层基质细胞中SST编码生长抑素的诱导相关。Sstr2配体生长抑素和皮质抑素在趋化分析中吸引IELps,生长抑素触发IELps与粘膜血管地址MAdCAM1结合。T细胞与Sstr2的转导使新生儿结肠归巢。人胎儿胸腺IELps样细胞在初始T细胞群时表达SSTR2,肠道基质细胞表达SST,提示发育中的肠道祖细胞播种的保守机制。这些结果揭示了SSTR2-生长抑素轴在早期免疫系统发育中的意想不到的作用,并描述了一个小肽激素G蛋白偶联受体在发育性淋巴细胞运输中的新作用。
研究人员表示,上皮内T细胞(IELps)的祖细胞在出生后从胸腺迁移到肠道,并在隐斑内的胸腺外淋巴形成过程中发育成非常规的TCRγδ和TCRαβ淋巴细胞。外来劳动力迁移的机制尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: An SSTR2–somatostatin chemotactic axis drives T cell progenitor homing to the intestines
Author: Ocn, Borja, Brulois, Kevin F., Hadeiba, Husein, Gaafarelkhalifa, Mohammed, Ayesha, Aiman, Bi, Yuhan, Xiang, Menglan, Gulman, Jacob, Kooshesh, Maryam, Pan, Junliang, Butcher, Eugene C.
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-26
Abstract: Progenitors of intraepithelial T cells (IELps) migrate from the thymus to the intestines after birth where they develop into unconventional TCRγδ and TCRαβ lymphocytes in a process of extrathymic lymphopoiesis within cryptopatches. Mechanisms of IELp migration have remained unclear. Here we show that thymic IELps express the somatostatin receptor SSTR2, which contributes to their homing to the gut. IELp homing is Sstr2 dependent and correlates with neonatal induction of Sst encoding somatostatin in neuroendocrine and lamina propria stromal cells. The SSTR2 ligands somatostatin and cortistatin attract IELps in chemotaxis assays and somatostatin triggers IELp binding to the mucosal vascular addressin MAdCAM1. T cell transduction with Sstr2 confers homing to the neonatal colon. Human fetal thymic IELp-like cells express SSTR2 and intestinal stromal cells express SST at the time of initial T cell population, suggesting conserved mechanisms of progenitor seeding of the developing intestines. These results reveal an unexpected role for the SSTR2–somatostatin axis in early immune system development and describe a new role for a small peptide hormone G-protein-coupled receptor in developmental lymphocyte trafficking.
DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02097-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-025-02097-8
Nature Immunology:《自然—免疫学》,创刊于2000年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:31.25
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ni/
投稿链接:https://mts-ni.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
