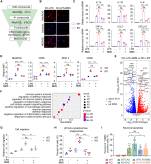
近日,清华大学教授丁胜及其小组揭示了转录因子MEF2C通过抑制激酶CDK2抑制小胶质细胞过度激活。2025年3月25日,国际知名学术期刊《免疫学》发表了这一成果。
课题组研究人员发现MEF2C缺陷(MEF2C/)来源于人多能干细胞(hPSCs)的诱导小胶质样细胞(iMGLs)在脂多糖刺激后表现出过度激活,模仿了在各种神经炎症疾病中观察到的模式。高通量筛选鉴定出周期蛋白依赖性激酶2 (CDK2)抑制剂BMS265246,该抑制剂可抑制MEF2C的过度激活。和正常的炎症反应。从机制上讲,MEF2C通过转录上调p21抑制CDK2激活介导的视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(RB)降解,从而阻止转录因子核因子κB (NFκB)核易位和随之而来的小胶质细胞过度活化。BMS265246治疗显著改善了MEF2C缺陷小鼠的小胶质细胞过度激活和ASD样行为。他们的发现确定了MEF2C-p21-CDK2-RB-NFκB轴是维持小胶质细胞稳态的关键途径,并强调了CDK2作为神经炎症的潜在治疗靶点。
据介绍,小胶质细胞固有免疫检查点是通过防止小胶质细胞过度激活来维持免疫稳态的必要保障,这一过程实质上影响着自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)等神经系统疾病。MEF2C是调节小胶质细胞激活的关键免疫检查点,但其机制尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: The transcription factor MEF2C restrains microglial overactivation by inhibiting kinase CDK2
Author: Xiaodan Hu, Jianchen Wu, Lu Shi, Folin Wang, Kezhang He, Pengcheng Tan, Yanyan Hu, Yuanyuan Yang, Dan Wang, Tianhua Ma, Sheng Ding
Issue&Volume: 2025-03-25
Abstract: Microglial intrinsic immune checkpoints are essential safeguards to maintain immune homeostasis by preventing microglial overactivation, a process that substantially influences neurological disorders such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD). MEF2C is a crucial immune checkpoint that regulates microglial activation, but the mechanism remains unclear. We found that MEF2C-deficient (MEF2C/) induced microglia-like cells (iMGLs) derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) exhibited overactivation following lipopolysaccharide stimulation, mimicking patterns observed in various neuroinflammatory disorders. High-throughput screening identified BMS265246, a cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) inhibitor, which suppressed overactivation of MEF2C/ iMGLs and normalized their inflammatory responses. Mechanistically, MEF2C transcriptionally upregulated p21 to inhibit CDK2 activation-mediated retinoblastoma protein (RB) degradation, thereby preventing transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NFκB) nuclear translocation and consequent microglial overactivation. BMS265246 treatment substantially ameliorated microglial overactivation and ASD-like behaviors in Mef2c-deficient mice. Our findings identify the MEF2C-p21-CDK2-RB-NFκB axis as a critical pathway to maintain microglial homeostasis and highlight CDK2 as a potential therapeutic target for neuroinflammation.
DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2025.02.026
Source: https://www.cell.com/immunity/abstract/S1074-7613(25)00093-7
Immunity:《免疫》,创刊于1994年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:43.474
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/immunity/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/immunity/default.aspx
